 |
IEC820S-INDUSTRIAL ECONOMICS-1ST OPP-NOV 2024 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |
nAm I BI A un IVE RSITY
OF SCIEn CE Ano TECHn OLOGY
FACULTY OF COMMERCE, HUMAN SCIENCESAND EDUCATION
DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS, ACCOUNTING AND FINANCE
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF ECONOMICS HONOURS
QUALIFICATION CODE: 0SBECH
LEVEL: 8
COURSE CODE: IEC820S
COURSE NAME: INDUSTRIAL ECONOMICS
SESSION: NOVEMBER 2024
PAPER: THEORY
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 100
FIRST OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER(S) Ms K. Kavezeri
MODERATOR: Dr E. Tingum
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALL the questions.
2. Write clearly and neatly.
3. Number the answers clearly.
PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS
1. Pens/pencils
2. Calculator
3. Ruler
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF 7 PAGES (including this front page)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 1
[10 Marks]
Select the letter that best represents your answer.
1. A market with few entry barriers and with many firms that sell differentiated
products is:
a) A) purely competitive.
b) A monopoly.
c) Monopolistically competitive.
d) Oligopolistic.
e) None of the answers above is correct.
2.
When average total cost is at a minimum,
a) Marginal cost is also at a minimum.
b) The firm is experiencing constant returns to scale.
c) Marginal cost is constant.
d) Average cost is equal to marginal cost.
e) The firm is maximizing its profit.
3.
Oligopoly differs from other forms of market structure (monopoly and perfect
competition) because
a) Firms frequently engage in collusion.
b) Firms are protected by high barriers to entry.
c) Firms' decisions have direct effects on their rivals' profits.
d) Firms' price decisions are extremely limited.
e) All of the answers above are correct.
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

4.
Which of the following is true for both perfectly competitive and monopolistically
competitive firms in the long run?
a) P = MC.
b) MC= ATC.
c) P > MR.
e) Profit equals zero
e) Sells differentiated products.
5.
The Cournot model concludesthat the equilibrium price in a duopoly will be
a) The same as the monopoly price.
b) Higher than the monopoly price.
c) Lower than the competitive-industry price.
d) Set by collusive agreement between the firms.
e) Between the competitive-industry price and the monopoly price.
6.
In the Cournot model of quantity competition, as the number of firms increases,
total industry output
a) Declines asymptotically.
b) Grows indefinitely.
c) Approaches the equilibrium output of perfect competition.
d) Approaches the profit-maximizing output of a pure monopoly.
e) Approaches the output of a cartel.
7.
The model of the kinked demand curve implies that
a) Strong brand loyalty means there is little incentive for firms to cut price.
b) Free entry will eventually reduce economic profits to zero.
c) A firm's competitors will follow it in a price decrease but not in a price increase.
d) Firms will coordinate prices so as to maximize group profit.
e) Rivals will match any price increases but tend to ignore any price cuts a firm makes.
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

8. The model of the kinked demand curve is used to explain
a) Advertising battles to build brand loyalty.
b) Sales maximization.
c) Price wars.
d) Sticky prices in oligopolies.
e) Collusive price agreements.
9.
Under Bertrand competition,
a) The firm setting the higher price attains a low market share.
b) The firm setting the lower price claims the entire market.
c) The total output supplied by the firms determines the market price.
d) Firms compete on multiple dimensions: quantity, price, and advertising.
e) Firms face kinked demand curves.
10. In the paradigm of the prisoner's dilemma,
a) Participants' interests are strictly opposed.
b) Neither side has a dominant strategy.
c) Pursuit of each person's self-interest leads to a poor group outcome.
d) Cooperation is achieved by the freedom to communicate.
e) None of the answers above is correct.
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 2
[25 Marks]
1. A firm's total cost function is given by the equation:
TC = 4000 + SQ+ 10Q2.
Write an expression for each of the following cost concepts:
(a) Total Variable Cost
(2)
(b) Average Variable Cost
(2)
(c) Average Total Cost
(2)
(d) Marginal Cost
(2)
2. Suppose the airline industry consisted of only two firms: American and Texas Air Corp.
Let the two firms have identical cost functions, C(q) = 40q. Assume the demand curve
for the industry is given by P = 100 - Q and that each firm expects the other to behave as
a Cournot competitor.
(a) Calculate the Cournot-Nash equilibrium for each firm, if each chooses the output
level that maximizes its profits when taking its rival's output as given. First, find
the reaction function for each firm; then solve for price and quantity.
(12)
(b) What are the profits of each firm?
(2)
(c) Define the Cournot model.
(3)
5
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 3
[25 Marks]
1. Amore and Joana Airlines (AJ Airlines) fly only one route: Windhoek-Oranjemund. The
demand for each flight is Q = 500 - P. AJAirlines' cost of running each flight is N$30,000
plus N$100 per passenger.
(a) What is the profit-maximizing price that AJ Airlines will charge? How many
people will be on each flight? What is AJ Airlines' profit for each flight? (10)
(b) AJ Airlines find out that two different types of people fly to Oranjemund from
Windhoek. Type A consists of business people with a demand of QA =260- 0.4P.
Type 8 consists of NUSTGeology and Mining Engineering students who have to
travel regularly for their practical learning. Their total demand is Qa = 240-0.GP.
Because the students are easy to spot, AJ Airlines decide to charge them
different prices.
i. How many people of each type are on each flight? What price should AJ
Airlines charge the students? What price should it charge other
customers?
{10)
ii. What would AJ Airlines' profit be for each flight?
{3)
(c) Do you think that it is a good idea for AJ Airlines to use price discrimination? (2)
QUESTION 4
[40 Marks]
1. Two computer firms, A and 8, are planning to market network systems for office
information management. Each firm can develop either a fast, high-quality system
(High), or a slower, low-quality system {Low). Market research indicates that the
resulting profits to each firm for the alternative strategies are given by the following
payoff matrix:
6
 |
7 Page 7 |
▲back to top |
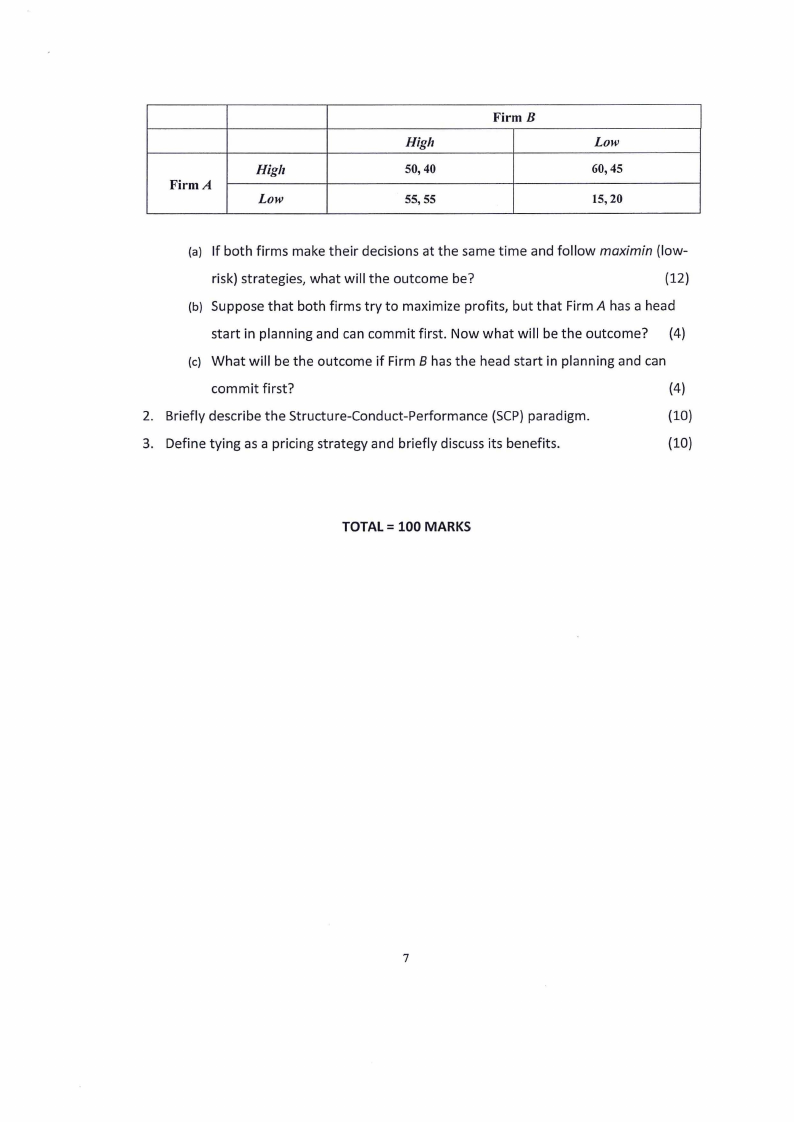
Firm A
High
Low
High
50,40
55,55
Firm B
Low
60,45
15,20
(a) If both firms make their decisions at the same time and follow maximin (low-
risk) strategies, what will the outcome be?
(12)
(b) Suppose that both firms try to maximize profits, but that Firm A has a head
start in planning and can commit first. Now what will be the outcome? (4)
(c) What will be the outcome if Firm 8 has the head start in planning and can
commit first?
(4)
2. Briefly describe the Structure-Conduct-Performance (SCP)paradigm.
(10)
3. Define tying as a pricing strategy and briefly discuss its benefits.
(10)
TOTAL= 100 MARKS
7





