 |
QCM701S - QUANTUM CHEMISTRY SPECTROSCOPY - 2ND OPP - JULY 2022 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

ea,
ee?
NAMIBIA UNIVERSITY
OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
FACULTY OF HEALTH, APPLIED SCIENCES AND NATURAL RESOURCES
DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF SCIENCE
QUALIFICATION CODE: 07BOSC
COURSE NAME: QUANTUM
CHEMISTRY AND SPECTROSCOPY
LEVEL: 7
COURSE CODE: QCM701S
SESSION: JULY 2022
PAPER: THEORY
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 100
SUPPLEMENTARY/SECOND OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER(S) | Prof Habauka M Kwaambwa
MOpeERATOR: | Prof Edet F Archibong
INSTRUCTIONS
Answer ALL the SIX questions
Write clearly and neatly
Number the answers clearly
All written work must be done in bule or black ink
No books, notes and other additional aids are allowed
Mark all answers clearly with their respective question numbers
PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS
Non-programmable Calculators
ATTACHMENT
List of Useful Constants
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF 6 PAGES (Including this front page and list of useful
constants as an attachment)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 1
[18]
(a) Waves can be characterised by amplitude, wavelength and frequency. Define these
three terms.
(3)
(b) The photoelectric effect experiment demonstrates that light has particle-like
properties. What is effect of increasing (i) the frequency of incident light and (ii) the
intensity of the incident light? (iii) Calculate the energy of photon and an electron
when each has a wavelength of 1 A and comment on the relative magnitude of your
answers.
(8)
(c) The work function of potassium (K) is 2.20 eV. (i) Calculate the threshold frequency of
the metal. (ii) Will violet light of wavelength 4000 A cause the photoelectric effect in
K?
(4)
(d) The stopping voltage for the electrons emitted from a metal due to photoelectric
effect is found to be 1 V for light of 2500 A. Calculate the work function of the metal
in eV.
(3)
QUESTION 2
[17]
(a) The normalised wave function, (a), for an electron in the highest occupied
molecular orbital of butadiene based on 1-dimensional particle-in-a-box model is
given by:
1
(x)= (2? sin (=x
forO0 < x < Landn =1, 2,3, etc.
(i) What is the physical meaning of such a normalised wave function?
(1)
(ii) Why is n =O not permissible for the particle-in-a-box model?
(1)
(iii) Sketch the variation of W(x) versus x and ‘Y; (x)? versus x.
(2)
(iv) For what value(s) of x in the range O<x< 30nmis ¥, (x) = 0 for a box of length
30 nm?
(2)
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

(b) On the same diagram show the variation of ¥(n=1), ‘¥(n=2) and the product
Y(n=1):¥(n=2) across the length of the box. Comment on the physical
significance of the product ¥(n=1):'¥(n=2).
(5)
(c) For the five wavefunctions (n = 1 through n = 5) for a particle-in-a-box, state whether
each of the following statements is TRUE or FALSE about the probability of finding the
particle near x = :
(5)
(i) Least forn=1
(ii) The same (and non-zero) for n = 1, 2, 3,4 and 5
(iii) Zero forn=1, 2,3,4and5
(iv) Least forn=5
(v) Least forn=2 andn=4
QUESTION 3
[19]
(a) With reference to a free particle moving in the x-direction whose wave function is
WY =Ae™, derive expressions of the eigenvalue of the momentum operator,
Py = “inex and the expectation value of the momentum of an observable.
(9)
(b) The normalised wave function for a particle-in-a-box is of the form
¥(x)-(2) sin( “x
Show that the particle-in-a-box wavefunctions are not eigenfunctions of the
as7
momentum operator, Py , but they are for Px.
(6)
(c) Show that the position operator, x, and momentum operator, P,, do not commute.
What does this indicate about the measurement of position and momentum?
(4)
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 4
[13]
(a) For the operators A and B, prove the identity [ A’,B | =A[A,B]+[A,B]A.
(4)
(b) Show that ® = Ae’ + Be'”® is a solution to the differential equation
(4)
—®—iddoo? =-m ,
(c) The solution of the Schrédinger equation of a plane rigid rotor is of the form
Y(b)=Acos() forOs <2n.
Determine the normalisation constant, A.
(5)
(Given: cos’ $= (I +cos 26)
QUESTION 5
[13]
(a) A wavefunction of a Quantum Mechanics (QM) particle of an observable is given by
W=Ax
-1sx<1
(i) Determine the normalisation constant A.
(4)
(ii) Evaluate the expectation value of x, <x>.
(4)
(iii) What is the probability of observing the QM particle at x = 0?
(2)
(b) The wavefunctions for a particle confined to move on a circle are
Y(o) -(+1)).e'"® where m = 0, +1, +2, etc. andO< b<2n
What do zero, positive and negative values of the quantum number m mean?
(3)
QUESTION 6
[20]
(a) What are the essential properties required of a molecule in order that it will show:
(i)
A pure rotational (i.e. microwave) spectrum, and;
(ii)
A vibrational (infrared) spectrum?
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

(b) Which of the following molecules will be (i) microwave active, (ii) infrared active, and
(iii) neither microwave active nor infrared active: HCI, OCS, COz2, NH3, CH3Cl, Cle? (5)
(c) Briefly define the terms selection rule, zero point energy and degeneracy as used in
quantum chemistry of atoms and molecules. Use a plane rigid rotator as an example.
(3)
(d) The rotational constant of +H35Cl (hydrogen chloride) is greater than that of 2H*5CI
(deuterium chloride) if bond length is the same. State, with reasons, whether this
statement is true or false.
(3)
(e) The quantum mechanical expression for the vibrational energy (in Joules) of a
diatomic molecule is well approximated as:
Evy = (v+52 }nv-(v+32) xhv
For +H3°Cl, the vibrational frequency is v = 8.97 x 10%? s? and anharmonicity
constant x = 0.018.
(i)
Calculate the energies of the v=0 and v= 1 levels.
(4)
(ii)
What is the relative populations at 300 K of the levels v = 0 and v = 1, i.e.
Nya Comment on the result.
(3)
v=0
END OF EXAM QUESTIONS
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |
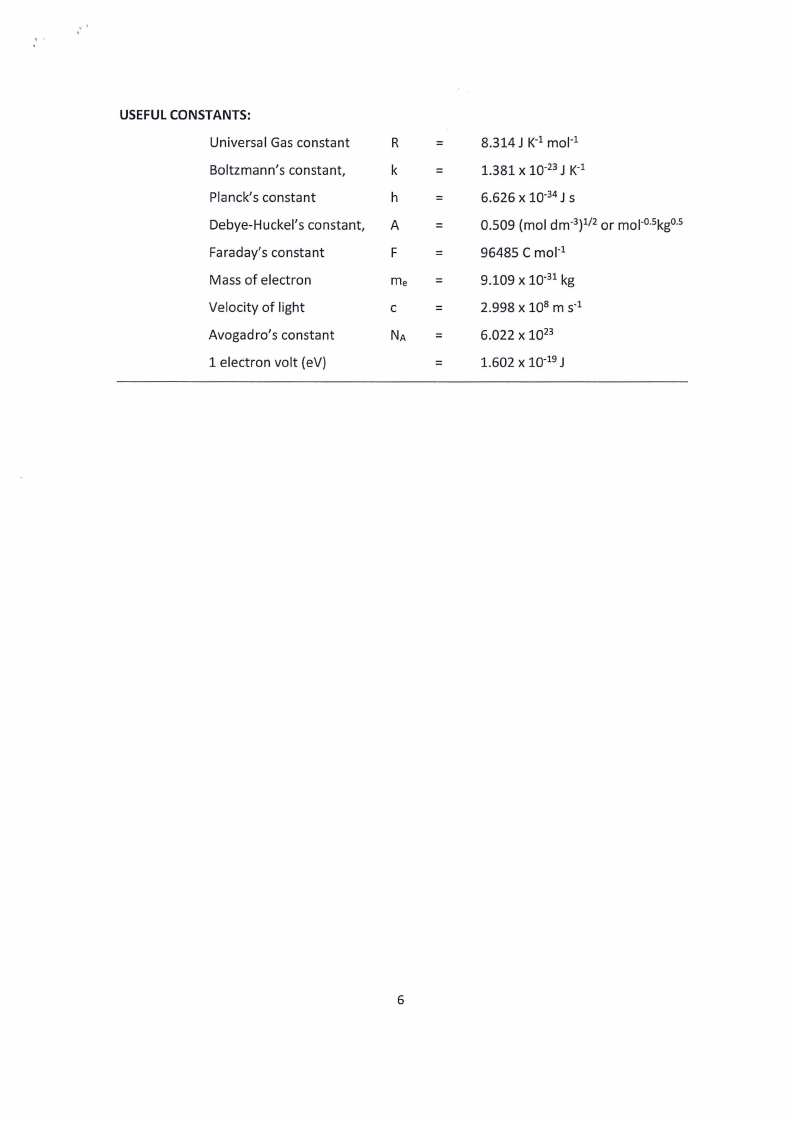
USEFUL CONSTANTS:
Universal Gas constant
Boltzmann’s constant,
Planck’s constant
Debye-Huckel’s constant,
Faraday’s constant
Mass of electron
Velocity of light
Avogadro’s constant
1 electron volt (eV)
8.314J K+ mol
1.381 x 1073J K?
6.626 x 10°4J s
0.509 (mol dm*)*/2 or mol5kg®>
96485 C mol?
9.109 x 10°! kg
2.998 x 108m st
6.022 x 1073
1.602 x 10°79J





