 |
ANP621S - ANATOMICAL PATHOLOGY 2B - 2ND OPP - JAN 2023 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAmlBIA unlVERSITY
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECHnOLOGY
Faculty of Health, Applied Sciences and Natural Resources
Department of Health Sciences
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOROF MEDICAL LABORATORYSCIENCES
QUALIFICATIONCODE: 08BMLS
LEVEL:6
COURSE: ANATOMICAL PATHOLOGY 2B
COURSECODE: ANP621S
DATE: JANUARY 2023
SESSION: THEORY
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 100
SUPPLEMENTARY/ SECONDOPPORTUNITYEXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER(S) Ms Roselin Tsauses
MODERATOR: Ms Ndeshipewa Hamatui - Valombola
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer all questions.
2. Please write neatly and legibly.
3. Do not use the left side margin of the exam paper. This must be allowed for the
examiner.
4. No books, notes and other additional aids are allowed.
5. Mark all answers clearly with their respective question numbers.
Permissable material
Non programmable calculator is allowed.
THIS EXAMINATION PAPERCONSISTSOF 7 PAGES(Excluding this front page)
Page 1 of 8
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

Section A {20 marks)
Question 1
[10]
1.
Evaluate the statements in each numbered section and select the most
appropriate answer. Write "true" or "false" next to the corresponding
number.
1.1 Specimens received in the cytology laboratory are usually unfixed and
are regarded as bio-hazardous.
(1)
a)
True
b)
False
1.2 Most cytology specimens are received as direct smears or cell
suspensions.
(1)
a)
True
b)
False
1.3 In humans, the female reproductive system is already mature at birth. (1)
a)
True
b)
False
1.4 The full range of epithelial cells can be identified by their morphology
and staining properties.
(1)
a)
True
b)
False
1.5 Cytolysis is predominantly observed in an atrophic smear.
(1)
a) True
b)
False
1.6 Dysplasia is a cancerous type of abnormal cell growth characterized
by the loss of normal tissue arrangement and cell structure.
(1)
a)
True
b)
False
1.7 The majority of gynaecological specimens are cervical smears,
followed by smears of the vagina or vulva.
a)
True
b)
False
(1)
Page2 of 8
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |
1.8 Many women with HPV infection develop CIN or cervical cancer.
(1)
a) True
b)
False
1.9 A tumor is a cluster of abnormal cells, forming a mass or lump of tissue
that may resemble swelling that is always cancerous.
(1)
a) True
b)
False
1.10 Alcohol fixation is the first step in the Papanicolaou staining procedure. (1)
a) True
b)
False
Section B (28 marks)
Question 2
[10]
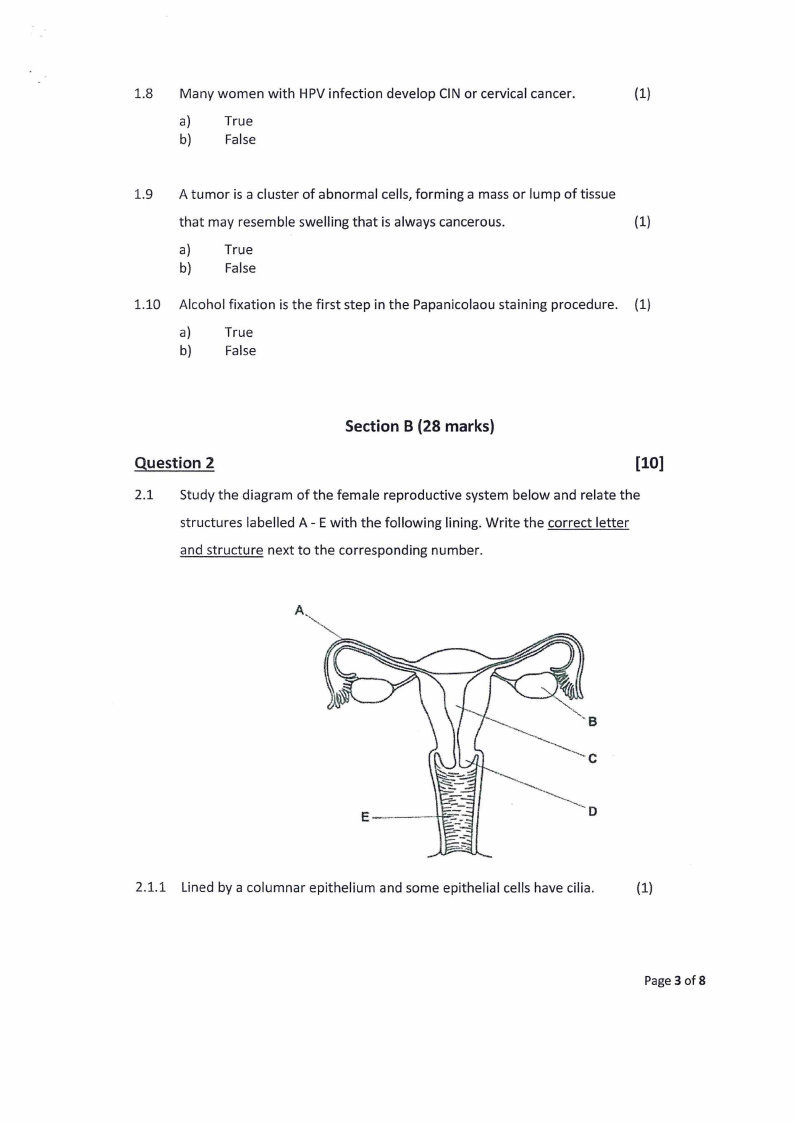
2.1 Study the diagram of the female reproductive system below and relate the
structures labelled A - E with the following lining. Write the correct letter
and structure next to the corresponding number.
2.1.1 Lined by a columnar epithelium and some epithelial cells have cilia.
(1)
Page 3 of 8
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

2.1.2 The actual endometrial epithelial surface of columnar cells, some of
which are ciliated, is not prominent. Endometrium consists of glands
and stroma.
(1)
2.1.3 Lined by a stratified squamous mucosa containing abundant
glycogen. There is no epithelial keratin layer.
(1)
2.1.4 The adult ovary consists of a cortex and a medulla. It also has a
mesothelium, also known as the germinal epithelium.
(1)
2.1.5 Outer cervix lined by a stratified squamous mucosa containing
abundant glycogen. At the os, the squamous epithelium changes to
a tall columnar mucinous epithelium.
(1)
2.2 Describe the criteria used to determine the type of epithelial cells seen
in a cervical smear.
(5)
Question 3
3.1 Apply your knowledge about the criteria used to distinguish between
normal and neoplastic cells and sketch neatly labelled drawings of the
following normal epithelial cells depicting distinct cytological
morphological features.
[18]
3.1.1 Superficial squamous cell
(3)
3.1.2 Intermediate squamous cell
(3)
3.1.3 Parabasal cell
(3)
3.1.4 Endocervical cells
(3)
3.1.5 Endometrial cells
{3)
3.1.6 Metaplastic cells
(3)
Page 4 of 8
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |
Section C (24 marks)
Question 4
4.1 Discuss how different hormones regulate the female reproductive
system.
[18]
(8)
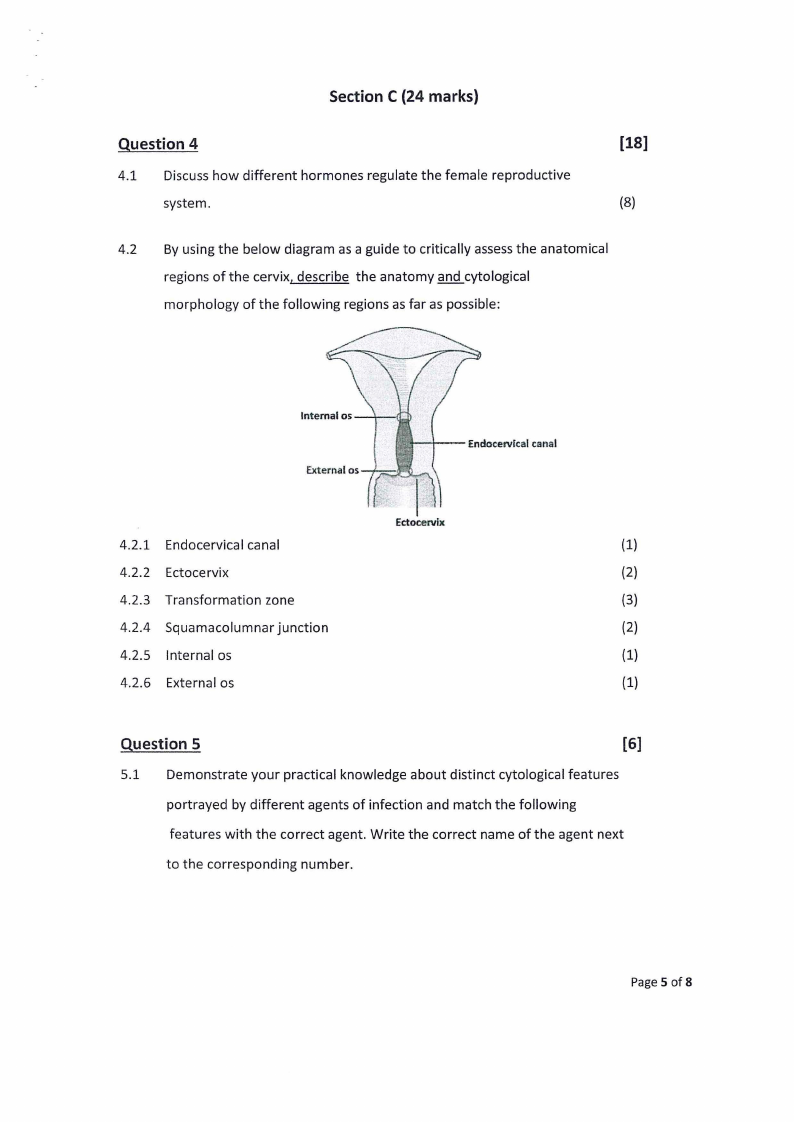
4.2 By using the below diagram as a guide to critically assessthe anatomical
regions of the cervix, describe the anatomy and cytological
morphology of the following regions as far as possible:
4.2.1 Endocervical canal
(1)
4.2.2 Ectocervix
(2)
4.2.3 Transformation zone
(3)
4.2.4 Squamacolumnar junction
(2)
4.2.5 Internal os
(1)
4.2.6 External os
(1)
Question 5
[6]
5.1 Demonstrate your practical knowledge about distinct cytological features
portrayed by different agents of infection and match the following
features with the correct agent. Write the correct name of the agent next
to the corresponding number.
Page 5 of 8
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |
5.1.1 Colonizes intra-uterine devices.
(1)
5.1.2 Hazy blue appearance referred to as clue cells by cytologists.
(1)
5.1.3 Dormant form exists as a population of spores.
(1)
5.1.4 Trichomonas vagina/is and this organism together have been referred
to as "spaghetti and meatballs."
(1)
5.1.5 Cells have a thickened uneven rim of dense cytoplasm giving
them a 'wire loop' appearance.
(1)
5.1.6 Tiny pink granules may also be visible within the cytoplasm of
the organism.
(1)
Section D (38 marks)
Question 6
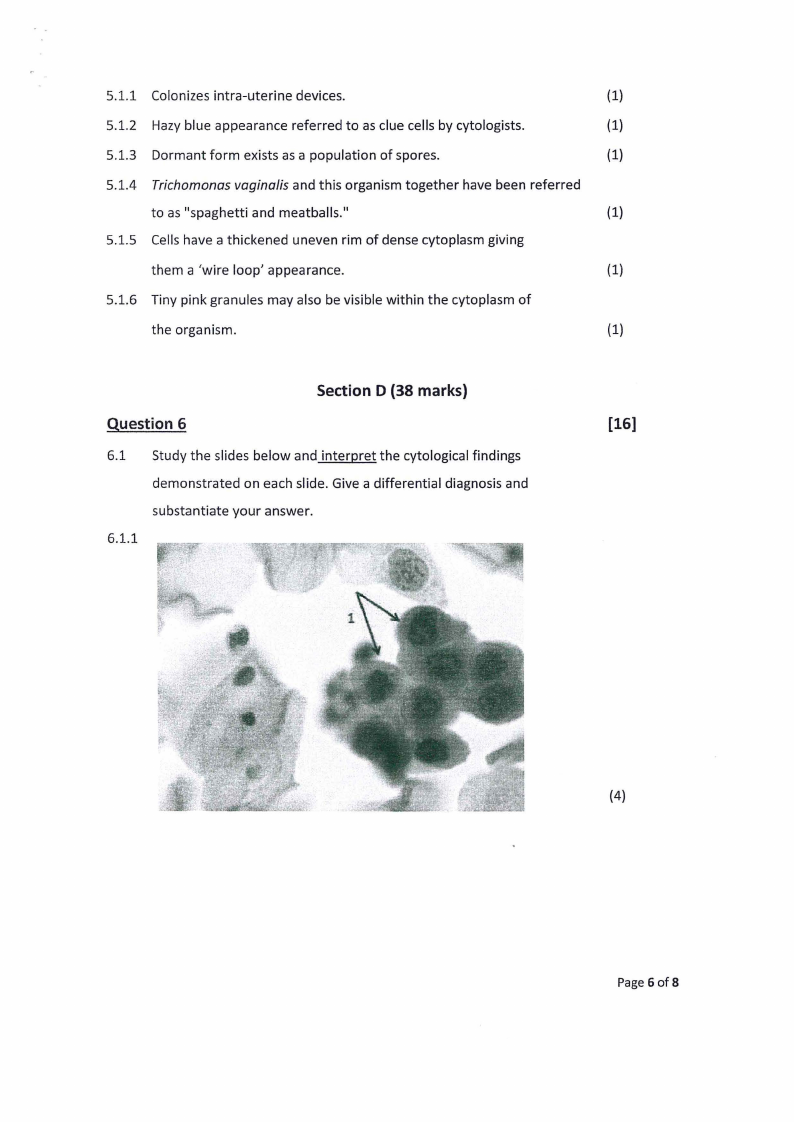
6.1 Study the slides below and interpret the cytological findings
demonstrated on each slide. Give a differential diagnosis and
substantiate your answer.
6.1.1
[16]
(4)
Page 6 of 8
 |
7 Page 7 |
▲back to top |
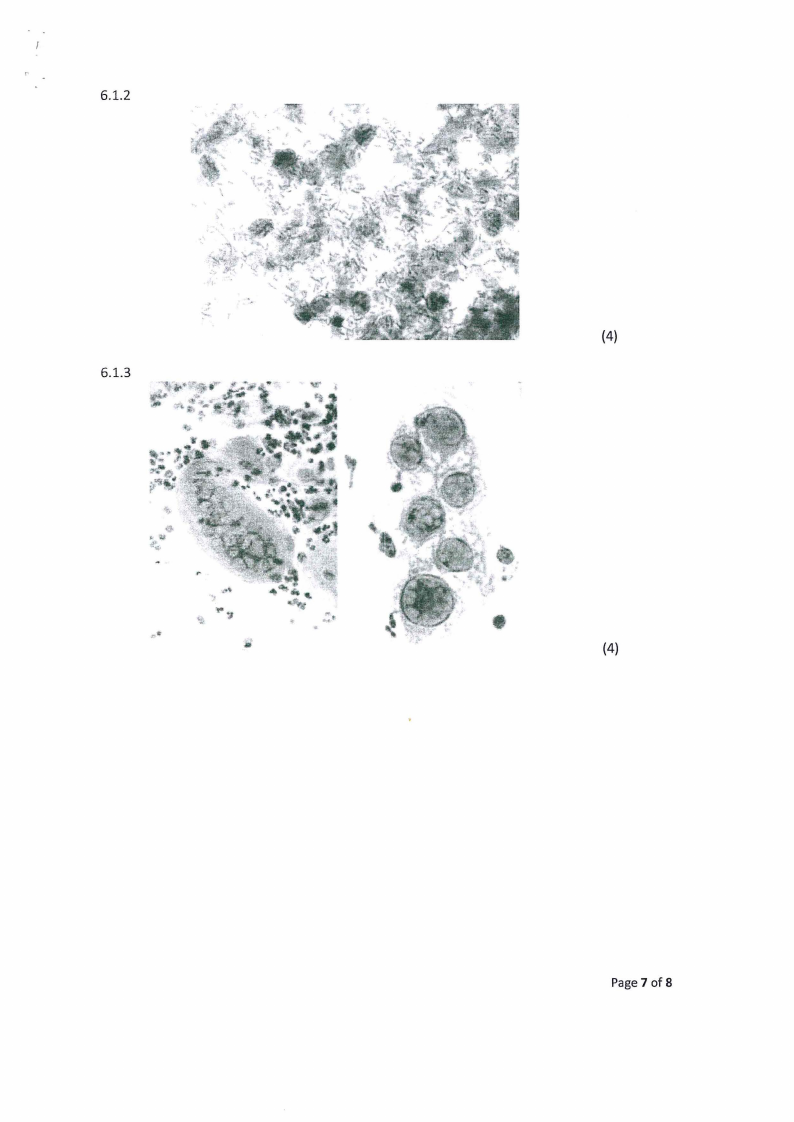
6.1.2
6.1.3
(4)
(4)
Page 7 of 8
 |
8 Page 8 |
▲back to top |

6.1.4
Question 7
7.1 Critique the importance of cell differentiation in cancer studies.
7.2 Report the criteria used to recognize and distinguish between the
three (3) grades of CIN?
7.3 What does CIN stand for?
(4)
[22]
(7)
(14)
(1)
GOOD LUCK!
Page8 of 8





