 |
EPD611S - EPIDEMIOLOGY 2A -2ND OPP - JULY 2022 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |
nAm I BIA UnlVERSITY
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECHnOLOGY
FACULTYOF HEALTH,APPLIEDSCIENCESAND NATURALRESOURCES
DEPARTMENTOF HEALTHSCIENCES
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOROF ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH SCIENCES,HUMAN NUTRITION AND
HEALTH !FORMATION MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
QUALIFICATIONCODE:08BOHS
LEVEL:6
COURSE:EPIDEMIOLOGY 2A
COURSECODE:EPD 611S
DATE:JULY 2022
SESSION:SEMESTERONE, 2022
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 100
SUPPLEMENTARY/SECONDOPPORTUNITYEXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER(S): MR JOSHUA HIDINWA
MODERATOR: DR ROSWITHA MAHALIE
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALL the questions.
2. Write clearly and neatly.
3. Number the answers clearly.
PERMISSIBLEMATERIALS
NONE
THIS QUESTION PAPERCONSISTSOF 7 PAGES(Including this front page)
Page 1 of7
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

SECTION A [30 MARKS]
QUESTION 1
Select most appropriate answer from the options provided.
Example: 1.35 A
1.1 Which of the following is an example of primordial prevention:
A. Malaria spraying
B. Cholera treatment
C. Low salt diet to prevent hypertension
D. Water treatment
E. ARV treatment to prevent HIV
1.2 Which of the following is not an example of secondary prevention:
A. Mass trachoma treatment
B. Mammography
C. Use of calipers
D. Treatment of hypertension
E. Treatment of diabetes
1.3 Which of the following is tertiary prevention:
A. Health promotion
B. Specific protection
C. Early diagnosis and treatment
D. Mechanical vector-borne transmission
E. Disability limitation
1.4 Immunization is:
A. Health promotion
B. Specific protection
C. Early detection and treatment
D. Campaigns for children
E. School Health activity
1.5 Epidemiology involves study of:
A. lmmunazation
B. People in community
C. Viruses activities
D. Distribution of disease
E. Water treatment
Page 2 of7
[10 MARKS]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

'I
1.6 Epidemiology deals with study of:
[1]
A. All health-related events and states in population
B. Epidemic diseases
C. Communicable diseases
D. Communicable and non-communicable disease
E. TB treatment
1.7 The type of epidemiology study which deals with risk factors of disease is:
[1]
A. Descriptive
B. Experimental
C. Analytical
D. Observational
E. Clinical trial
1.8 Protection of infants from infection up to 3 months of age is due to:
[1]
A. Mother and baby relationship
B. Breast feeding corner
C. The care of mother
D. Presence of fetal haemoglobin
E. Formula used for the baby
1.9 Herd immunity depends on:
[1]
A. Subclinical infection
B. Immunization status of herd
C. Herd stracture
D. Herd participation
E. Community leader
1.10 All of the following are non-modifiable risk factors for non-communicable
disease except:
[1]
A. Age
B. Sex
C. Family history
D. Diabetes
E. Heritage
QUESTION 2
[10 MARKS]
Indicate which of the following statements is True or False
2.1 Obesity, sedentary habits, cigarette smoking are all non-modifiable risk factor for non-
communicable disease.
[1]
2.2 Alcohol abuse, smoking and stress factors are major risk factors for
non-communicable disease prevalence.
[1]
Page 3 of7
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

2.3 Obesity and alcohol intake does not associate with the increased risk
of hypertension.
[1]
2.4 Lower salt diet is a method for primary prevention of hypertension.
[1]
2.5 Tobacco is associated with malignancy of urinary bladder.
[1]
2.6 Alcohol intake is associated with malignancy cervix.
[1]
2.7 Low in fat content, low in protein and increased fiber content are essential
aspect of weight reducing diet.
[1]
2.8 Descriptive epidemiology deals with the distribution of disease.
[1]
2.9 Making comparison in epidemiological approach both the study and control
groups should be similar.
[1]
2.10 Air borne transmission of disease occurs by
drinking contaminated water.
[1]
Page 4 of 7
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |
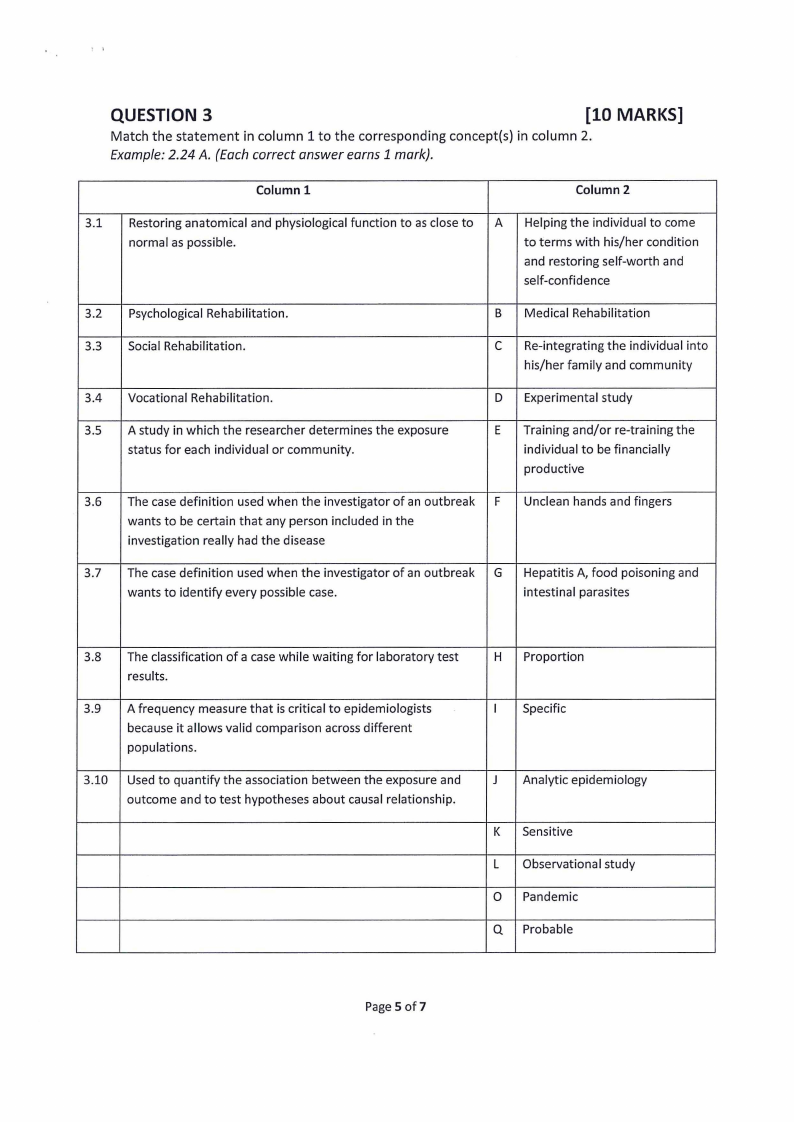
QUESTION 3
[10 MARKS]
Match the statement in column 1 to the corresponding concept(s) in column 2.
Example: 2.24 A. (Each correct answer earns 1 mark).
Column 1
Column 2
3.1 Restoring anatomical and physiological function to as close to A Helping the individual to come
normal as possible.
to terms with his/her condition
and restoring self-worth and
self-confidence
3.2 Psychological Rehabilitation.
B Medical Rehabilitation
3.3 Social Rehabilitation.
C Re-integrating the individual into
his/her family and community
3.4 Vocational Rehabilitation.
D Experimental study
3.5 A study in which the researcher determines the exposure
status for each individual or community.
E Training and/or re-training the
individual to be financially
productive
3.6 The case definition used when the investigator of an outbreak F Unclean hands and fingers
wants to be certain that any person included in the
investigation really had the disease
3.7 The case definition used when the investigator of an outbreak G Hepatitis A, food poisoning and
wants to identify every possible case.
intestinal parasites
3.8 The classification of a case while waiting for laboratory test
results.
3.9 A frequency measure that is critical to epidemiologists
because it allows valid comparison across different
populations.
3.10 Used to quantify the association between the exposure and
outcome and to test hypotheses about causal relationship.
H Proportion
I Specific
J Analytic epidemiology
K Sensitive
L Observational study
0 Pandemic
Q Probable
Page5 of 7
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |

SECTION B [10 MARKS]
QUESTION 4
4.0 Define the following epidemiological terms:
4.1 Epidemiology
4.2 Reservoir
4.3 Environmental factors
4.4 Herd immunity
4.5 Public Health Surveillance
SECTION C [60 MARKS]
[10 MARKS]
[2]
[2]
[2]
[2]
[2]
QUESTION 5
[20 MARKS]
5.0 For an infectious disease to be transmitted, the agent has to leave its reservoir through a
portal of exit and must be conveyed by some mode of transmission in order for it to enter
through an appropriate portal of entry to infect a susceptible host.
Using clear and concise examples, elaborate on these concepts:
5.1 Reservoir
[6]
5.3 Portal of exit.
[4]
5.4 Host.
[10]
QUESTION 6
[20 MARKS]
6.1 Describe factors associated with epidemiological transition of non-communicable
diseases in developing countries.
[6]
6.2 Explain the relationship between Communicable diseases and Con-Communicable
Disease.
[4]
6.3 Discussthe common modifiable risk factors Lifestyle/Personal Habits associated with
Non- communicable diseases.
[10]
Page 6 of 7
 |
7 Page 7 |
▲back to top |

. I'
SECTION D [20 MARKS]
QUESTION 7:
7.1 Describe standard precaution in infection control.
7.2.0 Outline the following terms:
7.2.1 Common source outbreak.
7.2.2 Point source outbreak.
7.2.3 Propagated outbreak.
7.2.4 Differentiate the two types of studies of epidemiology.
Good luck!
[20 MARKS]
[5]
[3]
[3]
[4]
[5]
TOTAL : 100 MARKS
Page 7 of 7





