 |
CSE511S-CONSERVATING ECOLOGY-1ST OPP- JUNE2024 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAm I BIA UnlVERS ITV
OF SCIEnCE
FacultyofHealthN, atural
ResourceasndApplied
Sciences
Schoolof Agricultureand
Natural ResourcesSciences
Department of Natural
ResourceSciences
13JacksonKaujeuaStreet
Private Bag13388
Windhoek
NAMIBIA
T: +26461207214
E: dnrs@nust.na
W: www.nust.na
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF NATURAL RESOURCES MANAGEMENT
QUALIFICATION CODE: 07BNRS
LEVEL: 7
COURSE:CONSERVATION ECOLOGY 1
COURSECODE: CSESllS
DATE: JUNE 2024
DURATION: 3 HOURS
SESSION:1
MARKS: 150
EXAMINER(S}
FIRST OPPORTUNITY: QUESTION PAPER EXAMINATION
Mr Jeremia K.L Amutenya and Prof. Theo Wassenaar
MODERATOR: Mr Helmuth Tjikurunda
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Please write neatly and legibly.
2. Do not use the left-side margin of the exam paper.
3. No books, notes or other additional aids are allowed.
4. Mark all answers clearly with their respective question numbers.
PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS
1. None
ATTACHMENTS
1. None
This paper consists of 6 pages including the front page
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 1
Write short notes to define or explain the following scientific terms:
1.1. Ecology
1.2. Population
1.3. Carrying capacity
1.4. Trophic cascade
1.5. Ecological disturbance
1.6. Nutrient cycling
1.7. Landscape Ecology
1.8. Ecotone
(1)
(1)
(1)
(2)
(1)
(1)
(2)
(1)
[10]
QUESTION 2
Explain the difference between the following pairs of terms.
2.1. Fundamental niche vs. Realised niche
(2)
2.2. Crude density vs. ecological density
(2)
2.3. Autogenic Ecosystem Engineer vs. Allogenic Ecosystem Engineer
(2)
2.4. Habitat resistance vs. Habitat resilience
(2)
2.5. Gross Primary Production (GPP)vs. Net Primary Production (NPP).
(2)
[10]
QUESTION 3
Match definitions or examples with correct words (just write the number and alphabet e.g.
le).
Definitions or examples
Words
1. The environmental factors that support (and
a) Life Histories
influence) the growth, survival and reproduction of
b) Mortality curves
a species.
c) Intermediate
2. Species that create, modify and maintain habitats,
Disturbance Hypothesis
by shaping the habitat to their own needs,
d) Ecosystem engineers
subsequently altering the availability of
e) Ecological succession
microhabitats, food, water, sunlight and shelter for
f) Landscape connectivity
other species, thus making other species' existence
g) Colonization
possible in a community.
h) Keystone species
3. A hypothesis that predicts that local species
i) Natural selection
diversity is maximized when an ecological
j) Ecological niche
disturbance is neither too rare nor too frequent.
k) Keystone species
4. The sequence of events related to survival and
I) Mortality curves
reproduction that occur from birth through death.
m) Endemic species
5. A type of survivorship curve in which individuals
n) Dispersal
tend to live out their physiological life span and
o) Population size
produce few offspring but provide extensive
p) Ubiquitous species
parental care.
q) Evolution
6. A species whose geographic distribution is limited
r) Type Ill
to a specific area or spatial unit (such as a country
s) Population density
I
Conservation Ecology 1 (CSE511S)
pt Opportunity-June 2024
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

or a biome).
7. A process in which individual organisms or
phenotypes that possessfavourable traits are more
likely to survive and reproduce.
8. The process of change in the species structure of an
ecological community over time.
9. The number of individuals per unit area.
10. The degree to which the landscape facilitates or
impedes the movement of organisms among
patches.
t) Type I
QUESTION 4
Multiple choice questions, select only the correct answers.
4.1. Which of the examples below can best be described as interspecific competition? (1)
a) Tilapia in the Zambezi River competing for food.
b) Trees in the woodland savanna compete for light.
c) Male Elephants in Khaudum National Park compete for mates.
d) Lions compete for food in Etosha National Park.
4.2. Lichens are made of fungi and algae and benefit from growing together. Which of (1)
the following words describes this relationship?
a) Commensalism
b) Amensalism
c) Mutualism
d) Neutralism
4.3. An example of a population is________
(1)
a) All shrubs in Waterberg Park
b) All Vachellia erio/oba trees in the Namib Desert
c) All animals in Khaudum National Park
d) A mixture of black and white rhinos in Etosha National Park
4.4. The carrying capacity of an environment for a species at a particular time is (1)
determined by ______
_
a) Number of individuals in the species
b) Reproductive potential of the species
c) Distribution of the population
d) Supply of the most limited resources
4.5. Logistic growth is representative of a population in an environment with (1)
_____
resources.
a) Limited
b) Plenty
c) Constant
d) All the above
4.6. The carrying capacity of an environment for a species at a particular time is (1)
determined by ______
_
a) Number of individuals in the species
b) Reproductive potential of the species
Conservation Ecology 1 (CSESllS)
2
ist Opportunity - June 2024
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

c) Distribution of the population
d) Supply of the most limited resources
4.7. Which of the following characteristics is NOT used to measure community (1)
structure?
a) Species Diversity
b) Multi-dimensional measures
c) Physical Diversity
d) Community composition list
4.8. Which sentence below describes composition?
(1)
a) This is the list of species, including their names, that occur in a particular
community.
b) The proportion (or percentage) of the total number of individuals in the
community that belong to a particular species.
c) The equitability in the distribution of individuals among the species.
d) The set of species present and their relative abundances.
4.9. Food webs are models that shows .............................?.
(1)
a) One sequence of producers and consumers.
b) Stored energy in food chains
c) Complex networks of feeding relationships.
d) Only primary consumers in an ecosystem
4.10. Which statement describes the most likely relationship between Species A and (1)
Species B?
(l)
N
ti)
C
·.0c.-a...
ry-- 1
Species A
/
\\
, Species B
:al . ./ /
0- .
a.
- ~-\\ ,./,
'-
Time
a) Species A is a consumer and Species Bis its producer.
b) Species A competes with Species B.
c) Species A has a mutualistic relationship with Species B.
d) Spedes A is the prey of Species B.
[10]
Conservation Ecology 1 (CSESllS)
3
1st Opportunity -June 2024
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 5
Indicate whether the below questions are True or False.
5.1. Almost all atmospheric vapour is contained in the Troposphere.
(1)
5.2. Temperature differences arise due to radiation from the sun falling unevenly (1)
across the hemispheres of the earth because the earth is tilted on its axis relative
to its orbital plane.
5.3. Pressure differences arise because of temperature differences.
(1)
5.4. The exponential growth model is a prime example of a population model that is (1)
experienced in a Savanna ecosystem.
5.5. Competition is a prime example of a density-independent factor.
(1)
5.6. Greater species richness is reflected by the length of the rank-abundance curve of (1)
a community- the shorter it is, the richer it is in species.
5.7. R.H. Whittaker was the first person to utilize the Rank-abundance plot, hence it is (1)
referred to as the Whittaker Plot.
5.8. Populations of many species do not occur as a single continuously distributed (1)
population but in spatially isolated patches with an exchange of individuals among
the patches.
5.9. An unsuitable matrix can hinder the recolonization of a patch and the population (1)
may fail to locate another suitable habitat patch to settle in.
5.10. The study of meta population dynamics is essentially the study of the conditions (1)
under which these two processes are in balance.
(10]
QUESTION 6
6.1. Explain why we refer to the earth as a "system".
(2)
6.2. Discuss one factor that affects Namibia's climate.
(2)
6.3. List five spheres that make up the Earth system.
(5)
(9]
QUESTION 7
7.1. Discussthe three possible outcomes of interspecific competition by using relevant (6)
ecological terms and examples.
7.2. The term ecological niche has three distinct meanings among scientists, each with (7)
an associated conceptual basis. Name and explain these three distinct meanings
and indicate which of the three is the most common in nature.
(13]
QUESTION 8
8.1. Population dynamics of any species is concerned with the factors that influence (4)
the expansion, decline, and maintenance of populations. Name the four primary
factors that drive population dynamics in nature.
8.2. What are survivorship curves and why are they important?
(5)
8.3. List the two types of population growth curves you have been introduced to in (4)
class and indicate which of the two is more realistic (in nature) and why.
8.4. Study the graph below and describe the two species in terms of:
(6)
Conservation Ecology 1 (CSE511S)
4
1st Opportunity-June 2024
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |
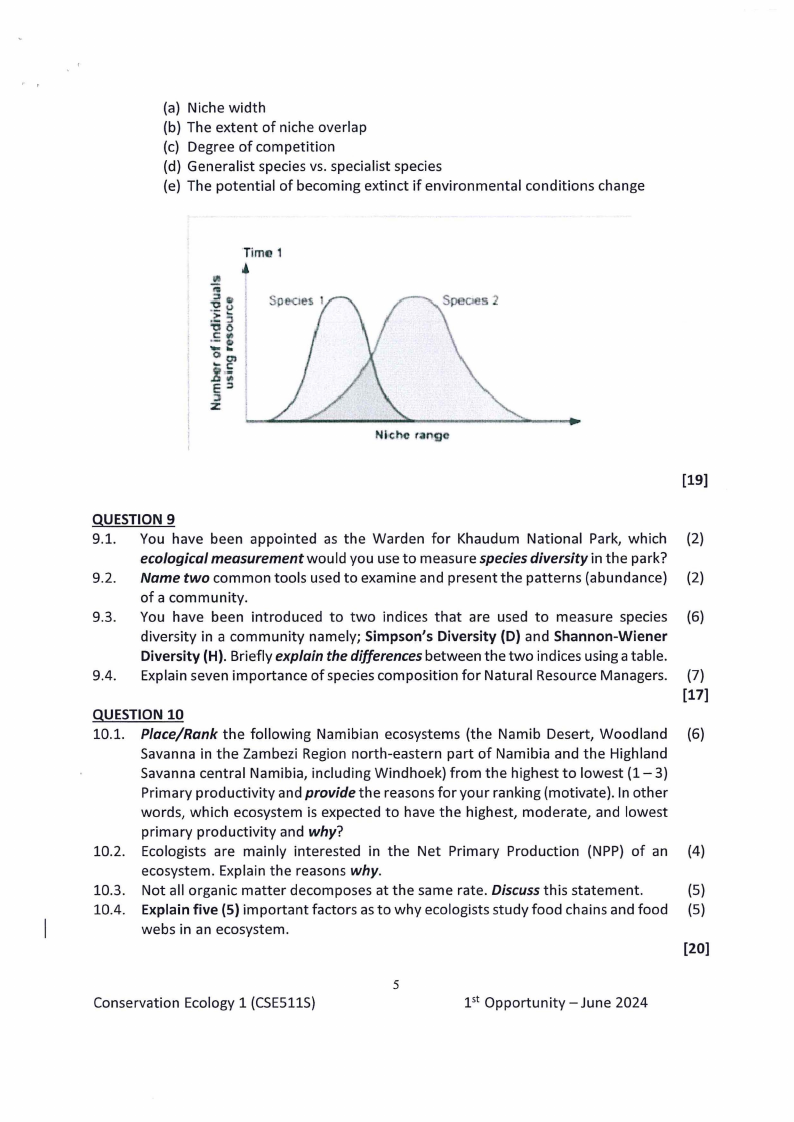
(a) Niche width
(b) The extent of niche overlap
(c) Degree of competition
(d) Generalist species vs. specialist species
(e) The potential of becoming extinct if environmental
conditions change
..·rimo 1
Niche ra gc
[19]
QUESTION 9
9.1. You have been appointed as the Warden for Khaudum National Park, which (2)
ecological measurement would you use to measure species diversity in the park?
9.2. Name two common tools used to examine and present the patterns (abundance) (2)
of a community.
9.3. You have been introduced to two indices that are used to measure species (6)
diversity in a community namely; Simpson's Diversity (D) and Shannon-Wiener
Diversity (H). Briefly explain the differences between the two indices using a table.
9.4. Explain seven importance of species composition for Natural Resource Managers. (7)
[17]
QUESTION 10
10.1. Place/Rank the following Namibian ecosystems (the Namib Desert, Woodland (6)
Savanna in the Zambezi Region north-eastern part of Namibia and the Highland
Savanna central Namibia, including Windhoek) from the highest to lowest (1- 3)
Primary productivity and provide the reasons for your ranking (motivate). In other
words, which ecosystem is expected to have the highest, moderate, and lowest
primary productivity and why?
10.2. Ecologists are mainly interested in the Net Primary Production (NPP) of an (4)
ecosystem. Explain the reasons why.
10.3. Not all organic matter decomposes at the same rate. Discuss this statement.
(5)
10.4. Explain five (5) important factors as to why ecologists study food chains and food (5)
webs in an ecosystem.
[20]
Conservation Ecology 1 (CSE511S)
5
ist Opportunity-June 2024
 |
7 Page 7 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 11
11.1. How is landscape ecology different from other areas of ecological studies that (2)
were discussed in class?
11.2. The structure of a landscape consists of four main elements. Name and explain (8)
these elements.
11.3. How does metapopulation dynamics differ from normal population dynamics? (4)
[14]
QUESTION 12
12.1. Define the theory of island biogeography.
(2)
12.2. Name five ways in which climate change has already affected biodiversity.
(6)
[8]
END OF QUESTION PAPER
Conservation Ecology 1 (CSE511S)
6
1st Opportunity-June 2024





