 |
PCH602S - PHYSICALNCHEMISTRY -2ND OPP - JANUARY 2025 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAm IBIA UnlVERSITY
OF SCIEnCE AnDTECHnOLOGY
FacultyofHealth,Natural
ResourceasndApplied
Sciences
Schoolof NaturalandApplied
Sciences
Departmentof Biology,
ChemistryandPhysics
13JacksonKaujeuaStreet T: +264612072012
PrivateBag13388
F: +264612079012
Windhoek
E: dbcp@nust.na
NAMIBIA
W: www.nust.na
QUALIFICATION: VARIOUS
QUALIFICATION CODE: VARIOUS
COURSE:PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
DATE:JANUARY 2025
DURATION: 3 HOURS
LEVEL:6
COURSECODE: PCH602S
SESSION:1
MARKS: 100
SECOND OPPORTUNITY/ SUPPLEMENTARY: EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER:
MODERATOR:
Prof Habauka Kwaambwa
Dr Euodia Hess
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALL the questions in Sections A and B.
2. Answer all questions on the separate answer sheet.
3. Please write neatly and legibly.
4. Do not use the left side margin of the exam paper. This must be allowed for the
examiner.
5. No books, notes and other additional aids are allowed.
6. Mark all answers clearly with their respective question numbers.
PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS
Non-Programmable Calculator
ATTACHMENTS
List of Useful Constants and Equation
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF 7 PAGES (Including this front page and a list of useful
constants and equation as an attachment)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

SECTIONA: MULTIPLE CHOICEQUESTIONS
[20]
There are 10 questions in this section. Choose the correct answer. Each question carries 2
marks.
1. An ideal gas at 27°C is heated at constant pressure until its volume is double. The
final temperature is:
A. 54°C
B. 327°C
C. 108°C
D. 654°C
E. 600°C
2. Which of the following is not an intensive property?
A. Pressure
B. Temperature
C. Density
D. Heat
E. Molar volume
3. A system does 430 J of work in its surroundings while absorbing 270 J of heat.
Calculate the change in the internal energy of the system.
A. 700 J
B. 160 J
C. -160 J
D. 1600 J
E. Insufficient Information
4. All of the following have a standard heat of formation value of zero at 25°C and 1.0
atm except:
A. N2{g)
B. Fe{s)
C. Ne{g)
D. H{g)
E. Hg{/)
Physical Chemistry (PCH602S}
2nd Opportunity January 2025
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

5. Calculate the standard heat of formation, ~H ~, for FeS2(g), given the following
information:
2FeS2(s) + 5O2(g) 2FeO(s) + 4SO2(g)
~H~n = - 1370 kJ
for SO2(g) = - 297 kJ/mol
for FeO(s) = - 268 kJ/mol
A. -177 kJ
B. -1550 kJ
C. - 774 kJ
D. -686 kJ
E. + 808 kJ
6. If ~G0 < 0, then K is __ . If ~G0 > 0, then K is __ . If ~G0 = 0, then K is __ .
A. > 1, < 1, = 1
B. < 1, > 1, = 1
C. < 0, > 0, = 0
D. > 0, < 0, = 0
E. < 1, > 1, = 0
7. The ~Hsublimation of 12is 60.46 kJ/mol, while its ~Hvaporization is 41.71 kJ/mol. What is the
~Hfusion of 12?
A. 102.17 kJ/mol
B. -102.17 kJ/mol
C. 18. 75 kJ/mol
D. - 18. 75 kJ/mol
E. Insufficient information
8. When a conductance cell was filled with 0.0025 M solution of K2SO4,its resistance
o- was 326 0. If the cell constant is 0.2281 cm-1, the conductivity (in 1cm-1) of K2SO4
solution is
A. 4.997 X 10-4
8. 5.997 X 10-4
C. 7 .997 X 10-4
D. 3.997 X 10-4
E. 6.997 x 10-4
9. Which of the following expressions is correct?
A.
A0
Al SO (
2(
4 )3)
= 3A:(AI3+)+2A~(sot)
B. A0 (AI2 (SO4 ) 3 ) = 11,;(A3+I)+A~(So!-)
C. A0 (NH 4 OH) = A0 (NH 4 Cl)-A 0 (NaCl)+ A0 (NaOH)
D. A0 (FeSO4 ) = 211,;(F2+e)+2A~(So!-)
E. A0 (NH 4 OH) = A0 (NH 4 Cl)-A 0 (NaOH)-A 0 (NaCl)
Physical Chemistry {PCH602S)
2nd Opportunity January 2025
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

10. If the activation for the forward direction of an elementary step is 52 kJ and the
activation energy in the reverse direction is 74 kJ, what is the enthalpy change ad
reaction for this step?
A. 22 kJ
B. - 22 kJ
C. 52 kJ
D. - 52 kJ
E. 126 kJ
SECTION B
[80]
There are FIVE questions in this section. Answer all Questions.
QUESTION 1
[14]
(a) State whether each of the following statements is true or false. If false either correct it or
state briefly the reason for its being false.
(i) w=~dw=O and ~H=~dH=O
(2)
(ii) The compressibility factor, Z > 1 for many gases at high pressures is attributed to finite
size of gas molecules and repulsive forces.
(2)
(iii) For a perfect crystalline substance, S0,,c = 0.
(2)
(aG) (a~G) (iv)
= V and
= -~S
aP T
aT p
(2)
(v) According to Trouton's law, the entropy of vaporisation at normal boiling point of
benzene (C5H6) and water is approximately equal to 88 JK-1moI-1•
(2)
= = (b) Starting with PV 1 Constant, show that Tv 1- 1 Constant, where P, V and Tis pressure,
volume and absolute temperature, respectively, and g is the relationship between Cvand
Cp,
(4)
QUESTION 2
[13]
(a) State whether q, w, flU, flH and flS are positive, negative or zero in adiabatic
compression of an ideal gas.
(5)
(b) A sample consisting of 2.00 mol argon (assume to behave as ideal gas) is expanded
reversibly and isothermally at 0°C from 22.4 dm 3 to 44.8 dm 3. For this process,
calculate q, w flU and flH.
(8)
QUESTION 3
(a) Estimate the enthalpy change of formation for NH3(g) at 100°C given:
2 2 1 N2 (g)+ 3 H2 (g) NH 3 (g), ~H; (25°C) = -46.11 kJmoI-1
Cp(N2,g) = 29.12 JK-1moI-1
Cp(H2,g) = 28.82 JK-1moI-1
Cp(NH3,g) = 35.06 JK-1moI-1
Physical Chemistry {PCH6025)
2nd Opportunity January 2025
[13]
(3)
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |
(b) Calculate b.G0 for 1 mole of N2O4decomposition at 298 K, given Kp= 0.163. If b.S0 for
the reaction is 184.2 JK·1mol·1 at 298 K, calculate b.H0 at 298 K.
(3)
(c) The equilibrium constant of the reaction
COC!i(g) CO)g) + Cl2(g)
was determined as a function of temperature and the data was fitted using the linear
form of the van't Hoff isochore and the result was:
InKP= 14080 + 17.85
T
Use these results to obtain b.H0 , b.S0 and b.G0 •
(4)
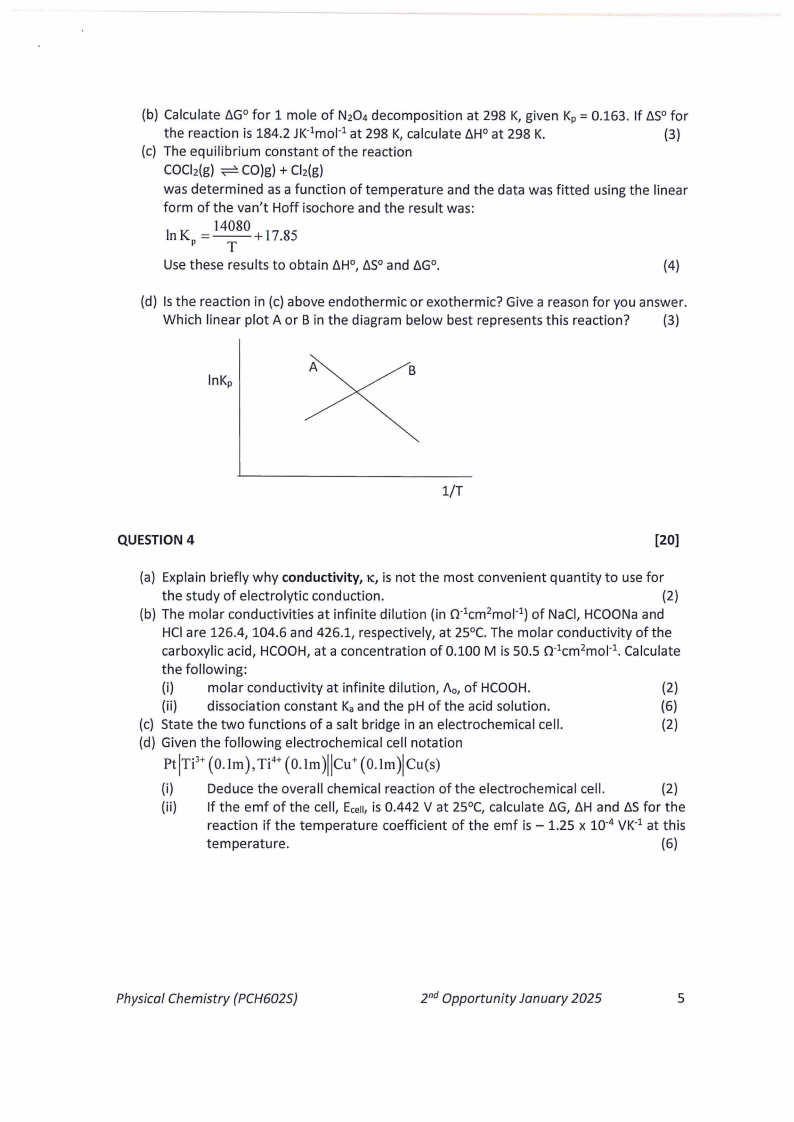
(d) Is the reaction in (c) above endothermic or exothermic? Give a reason for you answer.
Which linear plot A or Bin the diagram below best represents this reaction?
(3)
A
lnKp
B
1/T
QUESTION 4
[20]
(a) Explain briefly why conductivity, K, is not the most convenient quantity to use for
the study of electrolytic conduction.
(2)
(b) The molar conductivities at infinite dilution (in O·1cm2moI-1) of NaCl, HCOONaand
HCIare 126.4, 104.6 and 426.1, respectively, at 25°C. The molar conductivity of the
carboxylic acid, HCOOH,at a concentration of 0.100 M is 50.5 O·1cm2moI·1. Calculate
the following:
(i)
molar conductivity at infinite dilution, Ao,of HCOOH.
(2)
(ii) dissociation constant Kaand the pH of the acid solution.
(6)
(c) State the two functions of a salt bridge in an electrochemical cell.
(2)
(d) Given the following electrochemical cell notation
Pt ITi3+(0. lm), Ti4+(0. lm )lieu+ (0. lm)ICu(s)
(i)
Deduce the overall chemical reaction of the electrochemical cell.
(2)
(ii) If the emf of the cell, Ecelli,s 0.442 V at 25°C, calculate b.G,b.Hand b.Sfor the
reaction if the temperature coefficient of the emf is - 1.25 x 10-4 VK·1 at this
temperature.
(6)
Physical Chemistry {PCH602S}
2nd Opportunity January 2025
5
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 5
[20]
(a) What is the overall order of the reaction described by each of the rate expressions
below? State the units of the rate coefficient of the rate is in moldm- 3s-1.
[A]1.s
(i) Rate= k--
(ii) Rate= k [A][B]°[5c]'5
(4)
[B]'5
(b) The reaction H2 + 12 2HI is first order with respect to [H2] and [12].When [H2] = 1
molL-1 and [12]= 2 molL-1,the following kinetic are observed.
d [HI]
d [HI]
--
= 1.78 x 10-4 molL-1s-1 at 556 Kand --
= 0.2572 molL-1s-1 at 700 K.
dt
dt
Calculate the rate constant at each of the temperatures and evaluate the activation
energy [Assume that the pre-exponential factor is constant]
(6)
(c) The reverse reaction, i.e. 2HI H2+ 12,has an activation energy of 183 kJmoI-1. Does
this make the reaction H2+ 12 2HI exothermic or endothermic? Explain your answer
with a diagram of the energy profile of the reaction.
(6)
(d) Hydrogen peroxide, H2O2,decomposes in water by a first order kinetics process. A
0.156 moldm- 3 solution of H2O2in water has an initial rate of 1.14 x 10-s moldm 3s-1.
Calculate the rate constant, k, for the decomposition reaction and the half-life of the
decomposition.
(4)
END OF EXAM QUESTION PAPER
Physical Chemistry {PCH602S}
2nd Opportunity January 2025
6
 |
7 Page 7 |
▲back to top |

LIST OF USEFUL CONSTANTS AND EQUATION
Van der Waals eqrr. P= nRT
V -nb
n2a
v2
= --R--T
V-b
a
2
V
Universal Gas constant
R
=
8.314 J K-1 mo1-1
Boltzmann's constant,
k
=
1.381 X 10-23 J K-1
Planck's constant
h
=
6.626 X 10-34 J S
Debye-Huckel's constant, A
=
0.509 (mol dm- 3) 112 or mo1-0·5kg05
Faraday's constant
F
=
96485 C mo1-1
Mass of electron
me =
9.109 X 10-31 kg
Velocity of light
C
=
2.998 X 108 m s-l
Avogadro's constant
NA =
6.022 X 1023
1 electron volt (eV)
=
1.602 X 10-19 J
1 atm = 101325 Pa= 760 mm Hg= 760 torr; 1 bar= 105 Pa
Physical Chemistry (PCH602S)
2nd Opportunity January 2025
7





