BIO521S OR IBC521S - BIOCHEMISTRY OR INTRODUCTION TO BIOCHEMISTRY - 2ND OPP - JANUARY 2025
 |
BIO521S OR IBC521S - BIOCHEMISTRY OR INTRODUCTION TO BIOCHEMISTRY - 2ND OPP - JANUARY 2025 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

ii Am i B I H u n i VER s i TV
0 F SCI En CE Ano TECH n DLOGY
p
Faculty of Health, atural
Reso!Jlrceasnd Applied
Sciences
School of Health Sciences
Department of Clinical
Health Sciences
-------------
13 Jackson Kaujeua Stieet
Private Bag 13388
Windhoek
NAMIBIA
T: +264 61 207 2970
F: +264 67 207 9970
E: dchs@nust.na
W: www.nust.na
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOROF MEDICAL LABORATORYSCIENCESOR BACHELOROF
HUMAN NUTRITION
QUALIFICATION CODE: 08BMLS OR 08BOHN
LEVEL: 6
COURSE: BIOCHEMISTRYOR INTRODUCTION TO
BIOCHEMISTRY
COURSECODE: BIO521S OR
IBC521S
DATE: JANAURY2025
SESSION: 1
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 100
SECOND OPPORTUNITY/ SUPPLEMENTARY: QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER:
MODERATOR:
Mr Junias Natangwe Jackson
Ms Vanessa Tjijenda
Mr George Waliomuzibu Mukisa
INSTRUCTIONS:
1. Answer all questions on the separate answer sheet.
2. Please write neatly and legibly.
3. Do not use the left side margin of the exam paper. This must be allowed for the
examiner.
4. No books, notes and other additional aids are allowed.
5. Mark all answers clearly with their respective question numbers.
PERMISSIBLEMATERIALS:
1. Non-Programmable Calculator
ATTACHMENTS:
NONE
This paper consists of 7 pages including this front page
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

[ 20 MARKS]!
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
[10 MARKS]
Evaluate the statements in each numbered section and select the most appropriate answer or phrase
from the given possibilities. Fill in the appropriate letter next to the number of the correct
statement/phrase on your ANSWER SHEET.
[10]
1.1. The function of lipids in the body is:
[1]
a) Provide energy and insulate the body.
b) Store genetic information.
c) Speed up chemical reactions.
d) Give structural support to the body.
1.2. Identify the part an amino acid that varies among different amino acids:
[1]
a) Amino group.
b) Carboxyl group.
c) Hydrogen atom.
d) R group (side chain)
1.3. Determine the function of haemoglobin:
[1]
a) Fight infections.
b) Transport oxygen.
c) Provide energy
d) Build bones
1.4. Identify enzyme responsible for the breaking down lactose:
[1]
a) Amylase.
b) Lipase.
c) Lactase.
d) Protease.
1.5. Determine which of the following is a saturated fatty acid:
a) Oleic acid.
b) Linoleic acid
c) Stearic acid.
d) Arachidonic acid.
Biochemistry/ introduction to biochemistry (BIO521S/IBC521S)
2
[1]
1st opportunity November 2024
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

1.6. Analyse which ofthe following is false about lipids:
[1]
a) They are either strongly hydrophobic or amphipathic.
b) They are more soluble in water.
c) Extraction of lipids from tissues require organic solvents.
d) They are insoluble in water.
1.7. Evaluate which of the following statements is true about affinity chromatography.
[1]
a) During the separation of a mixture of proteins, the protein which does not bind to ligand is
eluted first.
b) During the separation of a mixture of proteins, the protein which does not bind to ligand is
eluted last.
c) During the separation of a mixture of proteins, the protein which binds to ligand is eluted
first.
d) Affinity chromatography separates proteins according to size.
1.8. A tripeptide has ___ _
[1]
a) 3 amino acids and 1 peptide bond.
b) 3 amino acids and 2 peptide bonds.
c) 3 amino acids and 3 peptide bonds.
d) 3 amino acids and 4 peptide bonds.
1.9. ~-pleated sheets are the examples of ___ _
[1)
a) Primary structure
b) Tertiary structure
c) Secondary structure
d) Quaternary structure
1.10. Interpret the following, which is true about Michaelis-Menten kinetics:
[1]
a) Km,the Michaelis constant, is defined as that concentration of substrate at which enzyme is
working at maximum velocity.
b) Km,the Michaelis constant, is defined as that concentration of substrate at which enzyme is
working at half maximum velocity.
c) Km,the Michaelis constant is defined as the dissociation constant of the enzyme-substrate
complex.
d) It assumes covalent binding occurs between enzyme and substrate.
Biochemistry/ introduction to biochemistry (BIO521S/IBC521S)
3
1st Opportunity November 2024
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 2: TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS
[10 MARKS]
Evaluate the statements and select whether the statement is true or false. Write the word 'True'
or 'False' next to the corresponding number on your ANSWER SHEET.
[10]
2.1 There are three chiral centers in open chain structure of fructose.
[1]
2.2 Complete hydrolysis of cellulose yields fructose.
[1]
2.3 Enzymes are derived from polysaccharides.
[1]
2.4 Oleic acid is unsaturated fatty acids.
[1]
2.5 The enzyme which hydrolyses fat into fatty acids and glycerol is called protease.
[1]
2.6 The two forms of D-glucopyranose are commonly described as enantiomers.
[1]
2.7 Irreversible inhibition is a mix between competitive and uncompetitive inhibition.
[1]
2.8 Proenzyme are synthesized as inactive precursors that require proteolysis for activation [1]
2.9 Serine, is a component of protein that can form disulfide bonds.
[1]
2.10 Lactate formed during anaerobic glycolysis is a toxic waste product excreted in the urine.[1]
SECTION B: SHORT/LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
Please answer ALL of the questions in this section.
QUESTION 3
[43 MARKS]
[34]
3.1 Briefly explain an epimers and provide examples of an epimers.
[2]
3.2 List at least two (2) disaccharides and describe their composition, how the monosaccharide
units are joined in their structures?
[4]
3.3 Give the classification of fatty acids. Give examples of each.
[6]
3.4 For each of the mentioned types of interaction in the table below, indicate all the
characteristics (a-h) that apply to that interaction (you can list a given characteristic for several
interaction types). Complete the table below
[6]
3.4.1 Require non polar species
3.4.2
3.4.3
3.4.4
3.4.5
Involve charged species only
Require polar or charged species
Involve either O and H or N and H atoms
Involve nonspecific atoms
3.4.6 Are also called electrostatic
3.4.7 Only exist in water
3.4.8 Are weakened in water
Biochemistry/ introduction to biochemistry (BIO521S/IBC521S)
4
1st Opportunity November 2024
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

Interaction
Hydrophobic interactions
Van der Waal's interactions
Hydrogen bonds
Characteristics
3.5 Why can acetone be detected on breath of diabetic patients?
[3]
3.6 Provide the carbohydrate and fat metabolic events occurring in the liver during fasting?
[3]
3.7 Compare and contrast the following processes:
[2]
3.7.1 Active transport
3. 7.2 Passive transport
3.8 Explain how you will separate a mixture of proteins using affinity chromatography? Indicate
physical or chemical this method takes advantage of in order to separate the proteins. [5]
3.9 Briefly define lipoproteins? List at least 2 types of lipoproteins.
[3]
QUESTION 4: CALCULATIONS
[9]
4.1 Calculate the pKa of lactic acid, given that when the concentration of lactic acid is 0.010 M
and the concentration of lactate is 0.087 M, the pH is 4.80
[3]
4.2 Calculate the [OW] of a solution with a pH of 12.2?
[2]
4.3 An enzyme hydrolyzed a substrate concentration of 0.03 mol/L, the initial velocity was
l.5x10- 3 mol/L.min- 1 and the maximum velocity was 4.5x10- 3 mol/L.min- 1. Calculate the km
value.
[4]
-
SECTION C:
[37 MARKS]
Please answer ALL of the questions in this section.
QUESTION 5: ENZYMES
[8]
"i E + S
E.')' Ii..!. E + P
h_,
5.1 Which of the above species refer to the "enzyme-substrate complex"
[1]
5.2 Write a rate equation for the production of ES
[2]
5.3 What is the rate of product formation from ES
[2]
5.4 If all the enzyme are bound with the substrate, what is the effect on the rate of the forward
reaction when adding more substrate, explain?
[3]
Biochemistry/ introduction to biochemistry (BIO521S/IBC521S)
5
1st Opportunity November 2024
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |
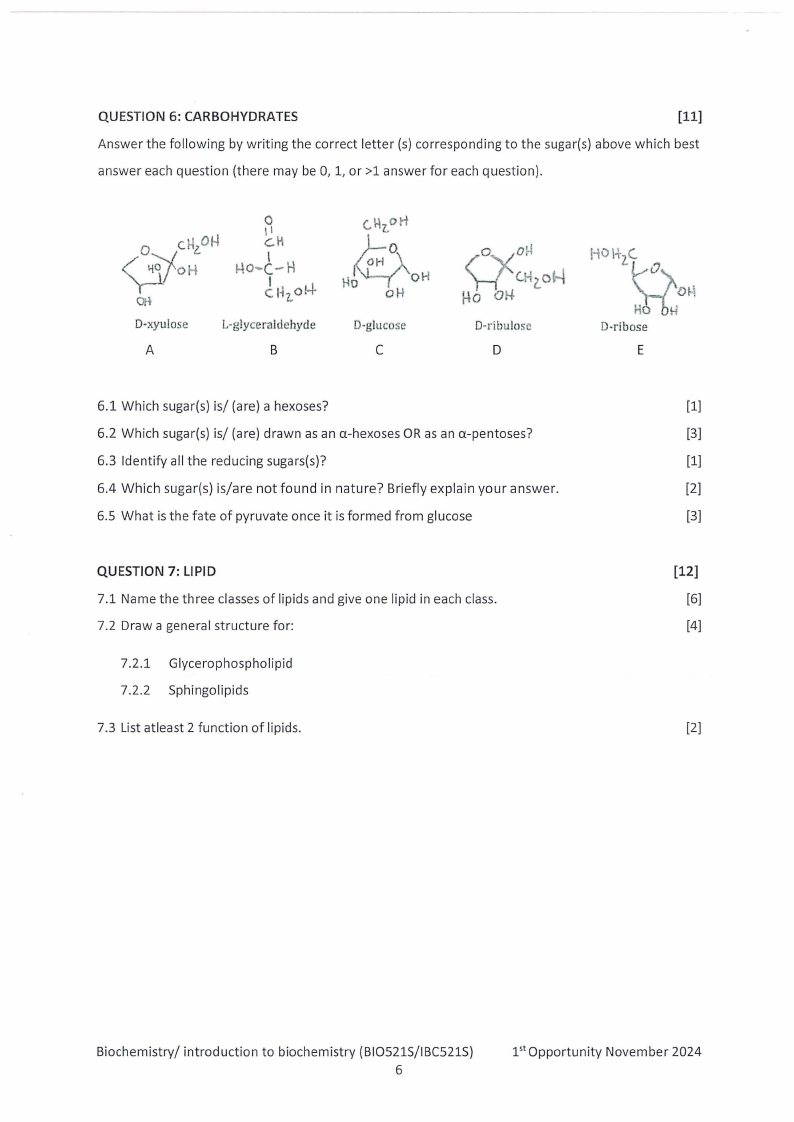
QUESTION 6: CARBOHYDRATES
[11]
Answer the following by writing the correct letter (s) corresponding to the sugar(s) above which best
answer each question (there may be 0, 1, or >1 answer for each question).
0
\\I
(,\\-\\z.OH
0 ,c lOH
cH
)-o
~oH
00
!4o-cl-H '
!QoH CI H-z.OH-
Ho
oH
D-xyulose L-glyceraldehyde
D-glucose
A
B
C
o
0 11
qCHz.oH
~OOH-
0-ribulosc
D
HOl+i~
D-ribose
E
01--\\
1-i
6.1 Which sugar(s) is/ (are) a hexoses?
[1]
6.2 Which sugar(s) is/ (are) drawn as an a-hexoses OR as an a-pentoses?
[3]
6.3 Identify all the reducing sugars(s)?
[1]
6.4 Which sugar(s) is/are not found in nature? Briefly explain your answer.
[2]
6.5 What is the fate of pyruvate once it is formed from glucose
[3]
QUESTION 7: LIPID
7.1 Name the three classes of lipids and give one lipid in each class.
7.2 Draw a general structure for:
7.2.1 Glycerophospholipid
7.2.2 Sphingolipids
7.3 List atleast 2 function of lipids.
[12]
[6]
[4]
[2]
Biochemistry/ introduction to biochemistry (B1O521S/IBC521S)
6
1st Opportunity November 2024
 |
7 Page 7 |
▲back to top |
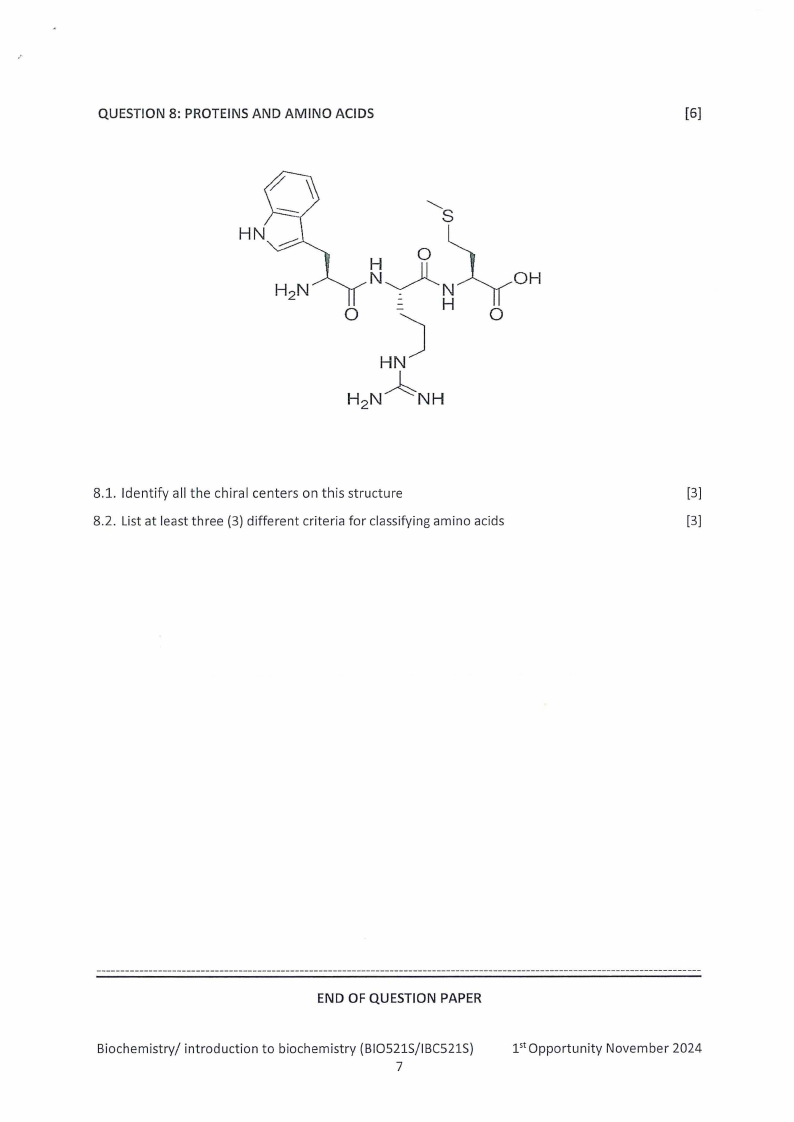
,.
QUESTION 8: PROTEINS AND AMINO ACIDS
[6]
8.1. Identify all the chiral centers on this structure
[3]
8.2. List at least three (3) different criteria for classifying amino acids
[3]
END OF QUESTION PAPER
Biochemistry/ introduction to biochemistry (B1O521S/IBC521S)
7
1st Opportunity November 2024
 |
8 Page 8 |
▲back to top |






