 |
BPP521S - BASIC PATHOPHYSIOLOGY - 1ST OPP - NOVEMBER 20224 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAm I BIA UnlVERSITY
OF SCIEnCE AnDTECHnOLOGY
FacultyofHealthN, atural
ResourceasndApplied
Sciences
Schoolof HealthSciences
Departmentof Preventative
HealthSciences
13JacksonKaujeuaStreet T: +264612072970
Private Bag13388
F: +264612079970
Windhoek
E: dphs@nust.na
NAMIBIA
W: www.nust.na
QUALIFICATION : BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN HEALTH INFORMATION SYSTEMS MANAGEMENT
QUALIFICATION CODE: 07BSHM
COURSE: BASIC PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
LEVEL: 5
COURSECODE: BPP521S
DATE: NOVEMBER 2024
DURATION: 3 HOURS
SESSION: 1
MARKS: 100
EXAMINER:
MODERATOR:
FIRST OPPORTUNITY: EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
DR ROSWITHA MAHALIE
MS ELIZABETHNDAKUKAMO-KASINO
INSTRUCTIONS:
1. Answer all questions on the separate answer sheet.
2. Please write neatly and legibly.
3. Do not use the left side margin of the exam paper. This must be allowed for the examiner.
4. No books, notes and other additional aids are allowed.
5. Mark all answers clearly with their respective question numbers.
PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS:
1. Non-programmable scientific calculator
ATTACHMENTS
1. None
This question paper consists of 6 pages including this front page.
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

.
.
SECTION A: MATCHING, WORD ELEMENTS AND FILL IN THE BLANKS
[ 55 MARKS)
QUESTION 1: FILL IN THE BLANKS
(20 MARKS)
1.1 Fill the missing words in the statements below. Each answer earns one (1) mark.
1.1.1 ______
is a condition caused by abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal
fluid (CSF)in the cerebral ventricular system.
1.1.2 ______
is when the roof of the mouth develops in two separate halves
(before birth).
1.1.3 ______
refers to a disease that resulted from an unintended or unwanted
medical intervention.
1.1.4 ______
refers to the movement and accumulation of leukocytes to the area
of injury.
1.1.5 ______
is defined as bleeding from the nose usually due to rupture of small
blood vessels in the anterior part of the nasal septum.
1.1.6 ______
are painless, cystic masses containing sperm.
1.1.7 ______
refers to a loss of lung volume caused by inadequate expansion of
air spaces.
1.1.8 ______
is a condition in which pigment disappears from a patch of skin and
may be associated with pernicious anaemia, hyperthyroidism, and diabetes mellitus.
1.1.9 ______
refers to decreased bone mass.
1.1.10 ______
are malignant tumours that produce cartilage which commonly
arise in the axial skeleton, the pelvis, shoulder, and ribs.
1.1.11
The ______
begins when light strikes photoreceptors (rod cells and
cone cells) in the retina.
1.1.12
______
are hard granules made of calcium, phosphate, uric acid, and
protein formed within the urinary tract.
1.1.13
______
arises from injury to the abdominal wall, the parietal
peritoneum, the root of the mesentery, or the diaphragm.
1.1.14
______
occurs when oesophageal motility is slowed or disorganized.
1.1.15
______
receive stimuli from inside the body.
1.1.16
______
x-ray pictures taken to determine the blood flow through the
vein.
1.1.17
______
is the formation of a thrombus/clot in the veins when the
flow of blood is reduced.
1.1.18
______
respond to the stretching of muscle fibers, tendons, joints, and
ligaments.
1.1.19
______
is the collection of signs and symptoms that occur together
in
response to a certain condition
1.1.20
______
is a syndrome characterized by progressive deterioration
and continuing decline of memory and other cognitive changes.
Model Answers
Basic Pathophysiology
1st Opportunity November 2024
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 2 CHOOSING APPROPRIATE CONCEPTS
{10 MARKS)
2.0 Evaluate the statements in each numbered section and select the most appropriate answer or
phrase from the given possibilities. Each question carries 1- mark.
2.1 Unusual turbulence in the blood flow due to defective valves that leak or do not open
completely is called:
A. Dyspnoea.
B. Bradycardia.
C. Cardiac murmurs.
D. Stroke.
2.2 The presence of many microorganisms in health facilities is referred to as:
A. Subclinical Infection.
B. Nosocomial infections.
C. In-hospital infections.
D. Clinical Infection.
2.3 Examples of genetic de-arrangement includes the following except:
A. Down Syndrome (trisomy 21).
B. Haemophilia.
C. Paget Disease.
D. Sickle cell Anaemia.
2.4 Small ulcers that occur singly or in groups on the inside of the cheek, lip or underneath the
tongue are called:
A. Mumps.
B. Aphthae.
C. Vincent Disease.
D. Aphthous stomatitis.
2.5 An overactive thyroid gland is referred to as:
A. Graves disease.
B. Cretinism.
C. Myxoedemma.
D. Diabetes lnsipidus.
2.6 A replacement of a mature cell type by a different mature cell type, is called:
A. Dysplasia.
B. Hyperplasia.
C. Hypertrophy.
D. Metaplasia.
2.7 Inflammation of the testis caused by trauma or the reflux of sterile urine up the vas
deferens is called:
A. Cryptorchidism.
B. Epididymitis.
C. Epididymosis.
Basic Pathophysiology
1st Opportunity November 2024
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |
D. Fournier gangrene.
2.8 Increased amount and duration of menstrual flow, is called:
A. Oligomenorrhea.
B. Menorrhagia.
C. Metrorrhagia.
D. Polymenorrhagia.
2.9 Which of the following is known as a short episode of pain:
A. Referred pain.
B. Acute pain.
C. Transient pain.
D. Phantom pain.
2.10 _____
occurs when the placenta is implanted over the cervical os is called:
A. Abruptio placentae.
B. Placenta absentia.
C. Placenta previa.
D. Placentarhagia.
QUESTION 3 MATCHING QUESTIONS /DEFINITION OF CONCEPTS
(25 MARKS)
3.1 Match the appropriate answer from Column A with a meaning in Column B. Write the
appropriate letter next to the corresponding number on your ANSWER SHEET,e.g., 3.1.1 A.
Each question earns 1 mark.
(20)
Nr
3.1.1
Item A
Fomites
3.1.2
3.1.3
3.1.4
Vitamin A
Vitamin K
Vitamin B12
3.1.5 Autophagy
3.1.6 Allostasis
3.1.7
3.1.8
Rheumatic
Heart disease
Prodromal
period
Item B
A. An adaptation to nutrient deprivation in which
cells digest their own organelles and recycle them
to provide energy and substrates.
B. Tear in the tendon/overuse or stretching of a
muscle or tendon.
C. A build-up of fatty deposits on the walls of the
coronary arteries.
D. Signs and symptoms are usually mild and
nonspecific
E. Any inanimate object capable of being an
intermediate in the indirect transmission of an
infectious agent.
F. A
component of visual pigment
G. Scurvy
H. Required for normal folate metabolism and DNA
synthesis.
Basic Pathophysiology
1'1 Opportunity November 2024
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |
3.1.9 Zinc
3.1.10 Vitamin C
3.1.11 Atherosclerosis
3.1.12
3.1.13
3.1.14
Rhabdomyosarc
oma
Strains
Mumps
3.1.15 Cataracts
3.1.16 Nystagmus
3.1.17 Psoriasis
3.1.18 Retention
3.1.19 Nocturia
3.1.20 Atheroma
I. Component of enzymes,
principally oxidases
J. Acute, post-streptococcal, immune mediated,
multisystem inflammatory disease
K. Hardening and narrowing of the arteries (silently
and slowly blocks arteries, putting blood flow at
risk).
L. Is a malignant mesenchymal tumour with skeletal
muscle differentiation.
M. dynamic process that supports and helps the
body achieve a steady state.
N. Complications include pancreatitis, orchitis,
infertility
0. Inability to empty the bladder.
P. Need for urination during sleep period.
Q. Chronic inflammatory skin disorder which
presents with a red raised demarcation of skin
patches with silvery whitish scales.
R. Develop when the lens of the eye becomes
cloudy and light does not pass through easily.
s. Involuntary abnormal movement of one or both
eyes.
T. Bleeding diathesis
u. infection which is localized in the urethra
V. Abnormal sound on auscultation of the heart
3.2 Define the following terms:
(5)
3.2.1 Glasgow Coma Scale
(2)
3.2.2 Otitis Media
(1)
3.2.3 Keloid
(2)
SECTION B SHORT/LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
[45 MARKS]
QUESTION 4 SHORT/LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
(32 MARKS)
4.1 Fractures is a break in the rigid structure and continuity of a bone as a result of direct, indirect
trauma, underlying disease or repeated stress on a bone. Outline the inflammatory and
remodelling phases and the bone activity that takes place during the
Basic Pathophysiology
l51 Opportunity November 2024
5
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |
healing process.
4.2 Enumerate the any three (3) clinical manifestations of the following pathological
conditions.
4.2.1 Type 1 diabetes-Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM
4.2.2 Hypercortisolism
4.2.3 Myocardial Infraction
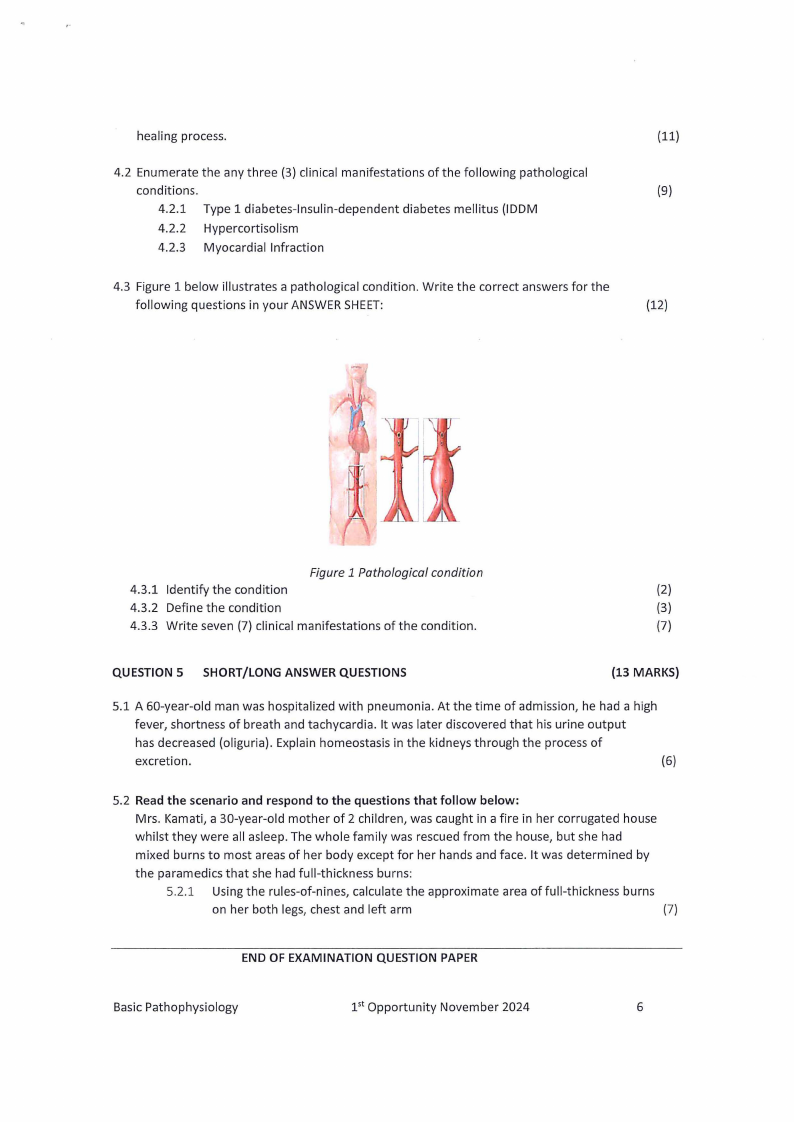
4.3 Figure 1 below illustrates a pathological condition. Write the correct answers for the
following questions in your ANSWERSHEET:
(11)
(9)
(12)
Figure 1 Pathological condition
4.3.1 Identify the condition
(2)
4.3.2 Define the condition
(3)
4.3.3 Write seven (7) clinical manifestations of the condition.
(7)
QUESTION 5 SHORT/LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
{13 MARKS)
5.1 A 60-year-old man was hospitalized with pneumonia. At the time of admission, he had a high
fever, shortness of breath and tachycardia. It was later discovered that his urine output
has decreased (oliguria). Explain homeostasis in the kidneys through the process of
excretion.
(6)
5.2 Read the scenario and respond to the questions that follow below:
Mrs. Kamati, a 30-year-old mother of 2 children, was caught in a fire in her corrugated house
whilst they were all asleep. The whole family was rescued from the house, but she had
mixed burns to most areas of her body except for her hands and face. It was determined by
the paramedics that she had full-thickness burns:
5.2.1 Using the rules-of-nines, calculate the approximate area of full-thickness burns
on her both legs, chest and left arm
(7)
END OF EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
Basic Pathophysiology
1st Opportunity November 2024
6





