 |
TPH601S - THERMAL PHYSICS - 1ST OPP- JUNE 2023 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

n Am I BI A u n IVER s I TY
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECHnOLOGY
FACULTY OF HEALTH, NATURAL RESOURCES AND APPLIED SCIENCES
SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES
DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGY, CHEMISTRY AND PHYSICS
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (MAJOR AND MINOR}
QUALIFICATION CODE: 07BOSC
LEVEL: 6
COURSE CODE: TPH601S
SESSION: JUNE 2023
COURSE NAME: THERMAL PHYSICS
PAPER: THEORY
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 100
EXAMINER(S}
FIRST OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION PAPER
DR VAINO INDONGO
MODERATOR: PROF SYLVANUS ONJEFU
INSTRUCTIONS
1.
Write all your answers in the answer booklet provided.
2.
Read the whole question before answering.
3.
Begin each question on a new page.
4.
The list of constants and useful formulae are on the last page of this paper.
PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS
1. Non-Programmable Scientific Calculator
THIS PAPER CONSISTS OF 5 PAGES
{INCLUDING THIS FRONT PAGE}
llPage
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 1
(20)
1.1 Briefly explain of the following thermodynamic terms:
{i) Environment
(2)
{ii) Universe
{2)
{iii) Isobaric process
(2)
{iv) Temperature
{2)
1.2 State the zeroth law of thermodynamics.
{2)
1.3 A male student in a physics class takes two cups of water at 303 K and mixes them
with one cup of water at 278 K {each mass of water weighs 50 g). Set the equation
Ototal= 0 and calculate the likely temperature of the mixture? Show your work/steps.
{6)
1.4 A brass rod is 0.70 m long at 40°C. Find the increase in length of this rod at 70°C.
{Hint: a= 1.90 x 10-5/ 0 ()
(4)
QUESTION 2
(20)
2.1 A steam in cylindrical glass of height h = 100 mm covered with a piston of mass 3500 g
and has a cross sectional area of 450 cm 2• Determine the:
(i) pressure that is exerted by this piston on the gas in the chamber, as shown in
Figure 1. Assume gravitational acceleration 'g' to be 9.81 m/s 2•
(4)
(ii) work done when the same cylinder is heated afterwards at a constant pressure of
1 atm and its initial volume changes from Voto 5Vo.
(4)
Patm = 100 kpa
Steam
Fig.1
21Page
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |
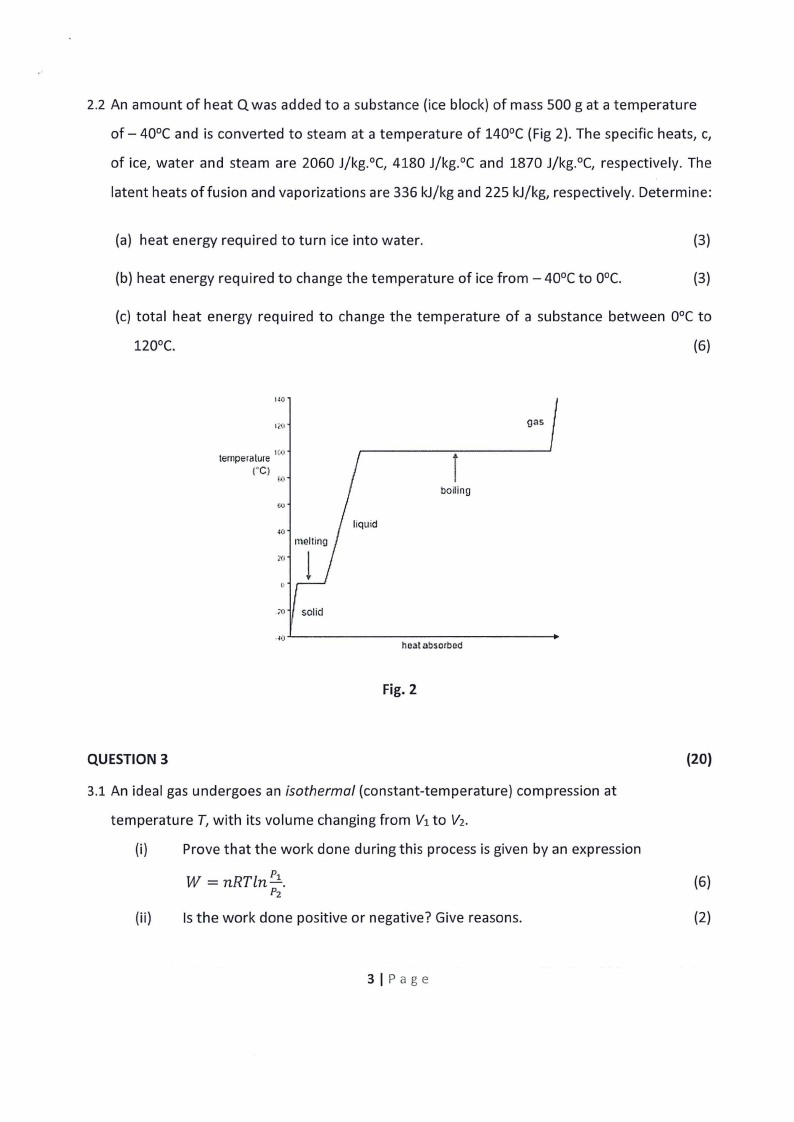
2.2 An amount of heat Q was added to a substance (ice block) of mass 500 g at a temperature
of - 40°C and is converted to steam at a temperature of 140°C {Fig 2). The specific heats, c,
of ice, water and steam are 2060 J/kg.°C, 4180 J/kg.°C and 1870 J/kg.°C, respectively. The
latent heats offusion and vaporizations are 336 kJ/kg and 225 kJ/kg, respectively. Determine:
(a) heat energy required to turn ice into water.
(3)
(b) heat energy required to change the temperature of ice from - 40°C to 0°C.
(3)
(c) total heat energy required to change the temperature of a substance between 0°C to
(6)
temperature 1((1
(°C)
0)
40
1(1
0
gas
l
!>oiling
.w. -'----------------
heat absorbed
Fig. 2
QUESTION 3
(20)
3.1 An ideal gas undergoes an isothermal (constant-temperature) compression at
temperature T, with its volume changing from V1to V2.
(i)
Prove that the work done during this process is given by an expression
=p
W nRT[n-1..
{6)
P2
(ii) Is the work done positive or negative? Give reasons.
{2)
3IPage
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

= 3.2 A temperature of 120 moles of monoatomic ideal gas with a ratio y 1.600 confined
in a cylinder was increased from 273.15 K to 292.15 Kat a uniform atmospheric pressure
{1 atm}. The cylinder was covered with a piston and the volume increases by
4.28 x 10-2 cm3• Calculate the amount of heat transferred.
{5}
3.3 Use the relationships for specific heats, Cv and Cp as well as ideal gas constant R to
prove that TVY- 1 is constant under an adiabatic condition.
(7)
QUESTION 4
(20)
4.1 Define entropy and state the second law of thermodynamics.
(3)
4.2 A gasoline truck engine takes in 35 kJ of heat and delivers 13.5 kJ of mechanical
work per cycle. The heat is obtained by burning gasoline with heat of combustion
= le 5 x 104 J/g. Calculate;
(a} the thermal efficiency of this engine?
{3}
(b} heat discarded per cycle
(3)
(c} If the engine goes through 8 cycles per second, what is its power output in kW
and hp? Hint: 1 hp= 746W
(4)
(d} How much gasoline is burned in each cycle in kg?
(4)
4.3 Suppose an engine absorbs 1000 J of heat at 383.15 Kand expels 713 J at 273.15 K
per cycle. Determine the total entropy of the system in one cycle.
(3}
QUESTION 5
(20)
5.1 Show that internal energy (U} is a thermodynamic potential which is a function of
entropy and volume.
(4)
5.2 Derive the differential form of Gibb's free energy/function from G = U + pV - TS.
(6)
41Page
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

5.3 (i) The speeds of five molecules of a gas are 24k, 25k, 26k, 23k, 30k all in ms-1, where k
is equal to the number of molecules. Evaluate therms speed.
(7)
(ii) Detemine average kinetic energy of a gas at a temperature 27°C.
(3)
END
Useful equations and constants:
The ideal gas law PV = NkaT
Boltzman's constant: ks= 1.38x10-23 JK-1,
Avogadro's number: NA= 6.022 x 1023 mo1-1
= Mean free path: 11. ,Jkz8ctTzp
1 atm = 1.01 x 105 Pa
= ]f Maxwell-Boltzmann Distribution: f(V)
4n
m
[-2kT-T sT
v
2
e _mv
2
;
2ksT
SI Page





