 |
ZLY621S - ZOOLOGY 2 - 2ND OPP -NOV 2022 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |
nAmlBIA UnlVERSITY
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECHnOLOGY
FACULTYOF HEALTH,NATURALRESOURCESAND APPLIEDSCIENCES
DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTUREAND NATURAL RESOURCESSCIENCES
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF NATURAL RESOURCESMANAGEMENT (NATURE
CONSERVATION)
QUALIFICATION CODE: 07BNTC
LEVEL: 7
COURSE CODE: ZLY621S
DATE: January 2023
COURSE NAME: Zoology 2
DURATION: 3 hours
MARKS: 150
SECOND OPPORTUNITY/ SUPPLEMENTARY EXAMINATION PAPER
EXAMINER(S) Mr R. Kavari
MODERATOR: Ms L. Theron
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALL the questions.
2. Write clearly and neatly.
3. Number the answers clearly.
PERMISSIBLEMATERIALS
1. Question paper
2. Answering book
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF 5 PAGES (Excluding this front page)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

SECTION A: Terminology
QUESTION 1
Give the correct zoological term for each of the following descriptions:
1.1 A configuration of blood vessels (arteries and veins) in a sinus at the base of the
brain. The structure that helps to keep the brain cooler than the body in desert
adapted antelopes such as Oryx gazelle and Antidorcas marsupialis.
(1)
1.2 A chemical given off by one animal that acts as a signal to another of the same
species.
(1)
1.3 Social grooming between members of the same species.
(1)
1.4 A periodic condition in bull (male) elephants; characterized by highly aggressive
behaviour and accompanied by a large rise in reproductive hormones.
(1)
1.5 A form of learning in which reflex behaviour is extinguished when the animal finds
that it has no adaptive value.
(1)
1.6 The occurrence in one habitat of more than two forms of a species.
(1)
1.7 The behaviour of male birds and other animals aimed at attracting a mate.
(1)
1.8 Modifications in structure and function shared by the members of a group that aid
survival. (An evolutionary process of becoming adjusted to a mode of life in a
certain environment!)
(1)
1.9 An association (symbiotic relationship) between two organisms in which one
benefits and the other derives neither benefit nor harm.
(1)
1.10 Historical reconstruction of the origin, dispersal, and extinction of taxa. (2 words)
(1)
[10)
QUESTION 2
Give the scientific name of each of the following mammals (spelling counts):
2.1 Klipspringer
(1)
2.2 wild dogs
(1)
2.3 Southern Africa hedgehog
(1)
Give the supercohort and order to which each of the following mammals belongs (spelling
counts):
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

2.4 Loxodonta africana
2.5 Papioursinusursinus
2.6 Melivoracapensis
Question 3
Make use of appropriate examples to explain each of the following ethological terms.
3.1 Hierarchy
3.2 Camouflage
3.3 Blubber
3.4 Harem
3.5 Synchronised calving
(1)
(1)
(1)
[6]
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
[10]
SECTION B: Classification, Morphology, Adaptation, Endemism
QUESTION 4
4.1 Explain how reptiles show evolutionary advancement over amphibians.
(6)
4.2 Name the four types of flight in birds.
(4)
4.3 Give the scientific name of the nocturnal Namib Dune gecko, and say why they glow (2)
under ultra-violet light.
4.4 Give the scientific name of the Damara Tern and explain why it is considered to be a
breeding endemic.
(2)
[14]
SECTION C: Ethology
QUESTION 5
5.1 Most animals live in organised social units/groups where they share mutual
advantages. Elaborate this statement.
(5)
5.2 You have to give a talk to environmental club at NUST. Your topic is "The
importance of Tactile communication in Mammals". You have to include examples
of how and why ruminants, non-ruminants, carnivores and primates make use of
tactile communication. Provide a script of your full report.
(5)
[10]
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |
QUESTION 6
6.1 Papio ursinus ursinus is one of the most insightful species. Use realistic examples to
explain how the aforementioned species demonstrate intelligence.
(4)
6.2 When is the Aardvark, Orycteropusafer, usually active and how is it adapted to its
diet?
(5)
6.3 Explain the anti-predator behaviour of Suricatasuricata.
(5)
6.4 Give 5 behavioural characteristics of the family Hippotamidae.
(5)
[19)
QUESTION 7
7.1 Explain the behaviour associated exclusively with ruminants.
(6)
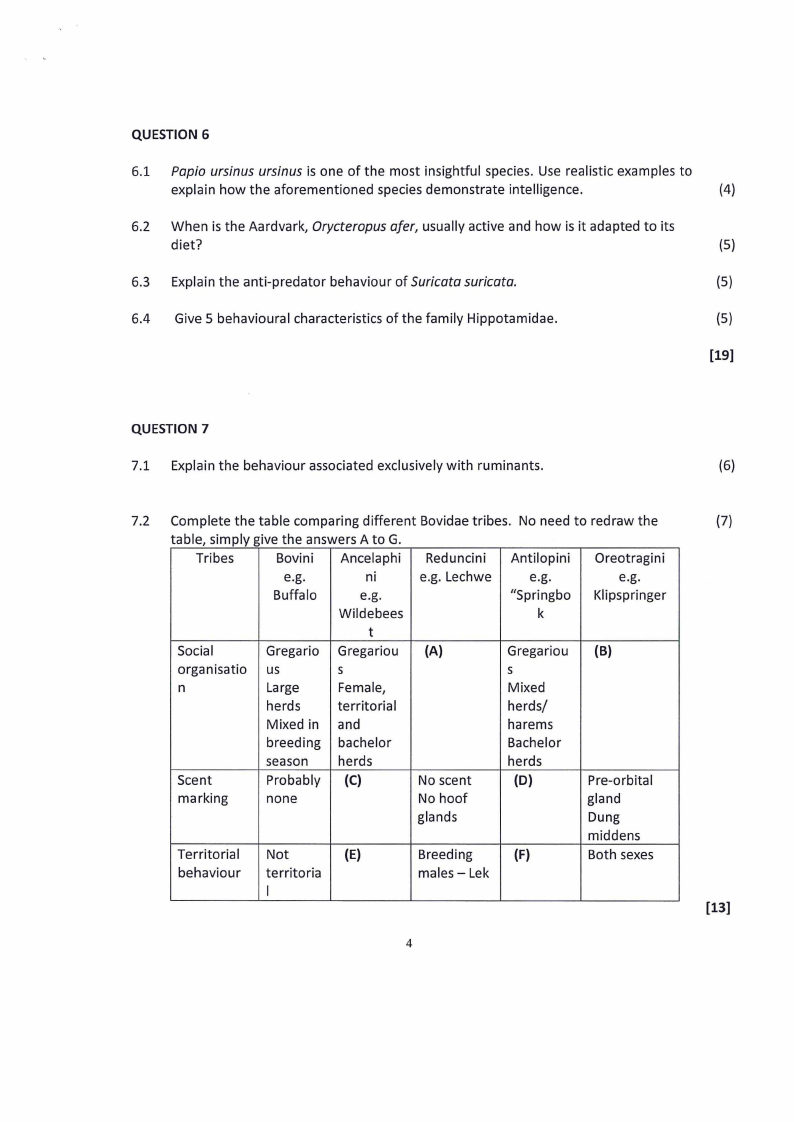
7.2 Complete the table comparing different Bovidae tribes. No need to redraw the
table, simply give the answers A to G.
Tribes
Bovini Ancelaphi Reduncini Antilopini Oreotragini
e.g.
ni
e.g. Lechwe
e.g.
e.g.
Buffalo
e.g.
"Springbo Klipspringer
Wildebees
k
t
Social
Gregario Gregariou (A)
Gregariou (B)
organisatio us
s
s
n
Large
Female,
Mixed
herds
territorial
herds/
Mixed in and
harems
breeding bachelor
Bachelor
season herds
herds
Scent
Probably (C)
No scent
(D)
Pre-orbital
marking
none
No hoof
gland
glands
Dung
middens
Territorial Not
(E)
Breeding
(F)
Both sexes
behaviour territoria
males - Lek
I
(7)
[13)
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |
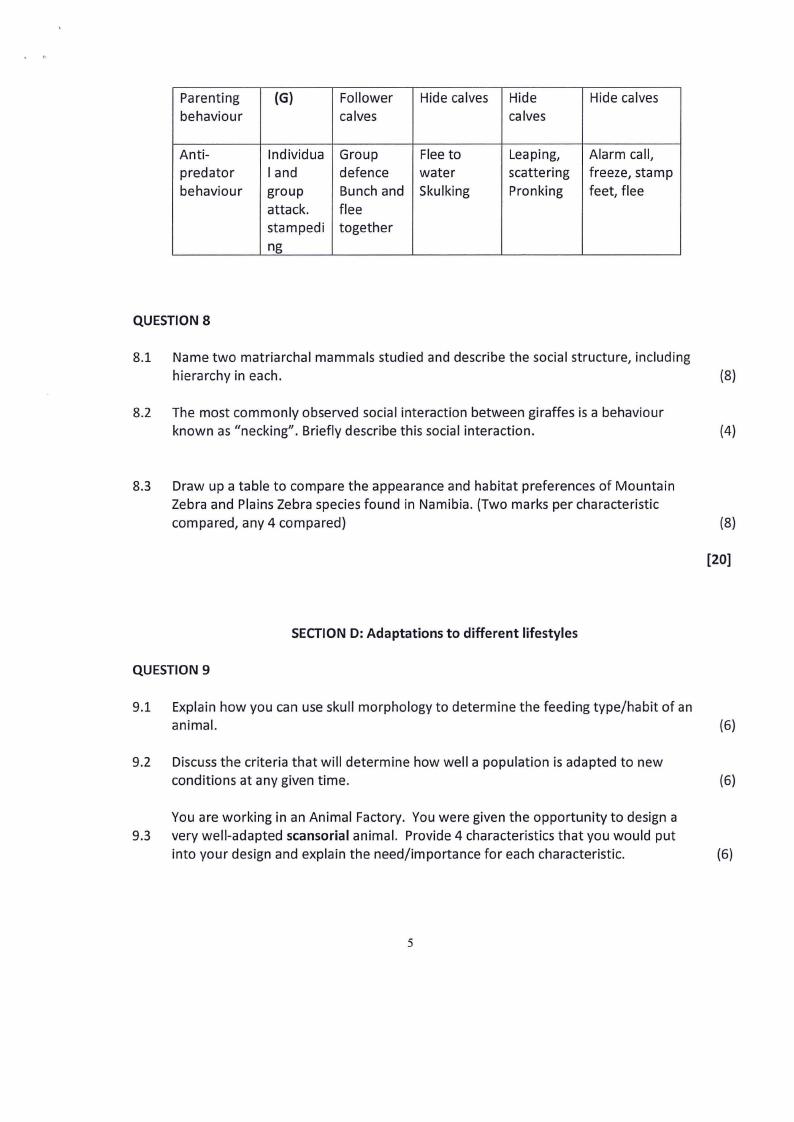
Parenting
(G}
behaviour
Follower
calves
Hide calves Hide
calves
Hide calves
Anti-
predator
behaviour
lndividua
land
group
attack.
stampedi
ng
Group
defence
Bunch and
flee
together
Flee to
water
Skulking
Leaping,
scattering
Pranking
Alarm call,
freeze, stamp
feet, flee
QUESTION 8
8.1 Name two matriarchal mammals studied and describe the social structure, including
hierarchy in each.
(8)
8.2 The most commonly observed social interaction between giraffes is a behaviour
known as "necking". Briefly describe this social interaction.
(4)
8.3 Draw up a table to compare the appearance and habitat preferences of Mountain
Zebra and Plains Zebra species found in Namibia. (Two marks per characteristic
compared, any 4 compared)
{8)
[20)
SECTION D: Adaptations to different lifestyles
QUESTION 9
9.1 Explain how you can use skull morphology to determine the feeding type/habit of an
animal.
(6)
9.2 Discussthe criteria that will determine how well a population is adapted to new
conditions at any given time.
(6)
You are working in an Animal Factory. You were given the opportunity to design a
9.3 very well-adapted scansorial animal. Provide 4 characteristics that you would put
into your design and explain the need/importance for each characteristic.
(6)
5
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |

9.4 Use the theory of Darwin's finches to explain the concept of isolation and
(3)
speciation.
9.5 Natural selection is one of the basic mechanisms of evolution, along with mutation,
migration, and genetic drift. Explain how Charles Darwin used the example of
peppered moth to substantiate the theory of Natural selection (during industrial
(3)
revolution).
9.6 Provide 5 examples of Namibian animals that handle active prey and explain how
they do it.
(5)
[29]
SECTION E: Zoogeography
QUESTION 10
10.1 Name all the zoogeographic regions.
(5)
10.2 In plate tectonics, the lithospheric plates ride on the asthenosphere. These plates
move in 3 ways. Discussthese 3 types of boundaries and what each creates/causes.
Make use of drawings to further clarify your answers.
(9)
10.3 According to scientists South America, Africa, India, Australia and Antarctica were
formerly connected to each other, forming a large land mass known as
Gondwanaland. On what evidences do they base these allegations?
(5)
[19]
TOTAL [150]
End
6





