 |
MAP512S - MICROBIOLOGY AND PARASITOLOGY - 1ST OPP - NOV 2022 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAmlBIA UnlVERSITY
OF SCIEn CE Ano TECHn OLOGY
FACULTYOF HEALTH,APPLIEDSCIENCES& NATURALRESOURCES
DEPARTMENTOF HEALTHSCIENCES
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOROF ENVIRONMENTALHEALTHSCIENCES
QUALIFICATIONCODE: 08BOHS
LEVEL: 5
COURSECODE: MAP512S
COURSENAME: MICROBIOLOGY AND PARASITOLOGY
SESSION:NOVEMBER 2022
DURATION: 3 HOURS
PAPER:THEORY
MARKS: 120
FIRSTOPPORTUNITYEXAMINATION PAPER
EXAMINER(S) Mr DAVID CARELSE
MODERATOR: Dr LARAI AKU AKAi
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALL the questions in the answer book provided.
2. Write clearly and neatly.
3. Number the answers clearly.
4. All written work MUST be done in blue or black ink.
PERMISSIBLEMATERIALS
1. Scientific Calculator
THIS QUESTION PAPERCONSISTSOF 8 PAGES(including this cover page)
····-~--
llPage
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

SECTION A: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS [20]
• There are 15 multiple choice questions in this section.
• Answer ALLquestions by selecting the letter of the correct answer.
(Each question carries 1 mark)
QUESTION 1 (20)
1.1 Most eukaryotic cells produce by:
A. Budding
B. Spore formation
C. Binary fusion
D. None of the above
E. All the above
1.2 Clostridium botulinum is known to be:
A. A gram-negative diplococcus
B. A gram-positive coccus
C. A gram-positive bacillus
D. A gram-negative spiral bacillus
E. All the above
1.3 A slippery outer covering in some bacteria that protects them from phagocytosis by
host cells is:
A. Peptidoglycan
B. Capsule
C. Cell wall
D. Flagellum
E. Peptidoglycan
1.4 Sporozoite is the infective stage of which parasite:
A. Schistosoma haematobium
B. Hook worm
C. Strangeaides stercorais
D. Taenia sulium
E. None of the above
21Page
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

1.5 Concerning malaria parasites the infective form of the parasite to man is:
A. Schizont
B. Trophozoite
C. Ring form
D. Sporozoite
E. All the above
1.6 A bactericide is a substance that:
A. Slows down bacterial growth
B. Kills some bacteria while allowing some to grow
C. Have no effect on bacteria
D. Kills bacteria
E. None of the above
1.7 Which of the following chemical-based preservatives do not act on fungi:
A. Propionic acid
B. Sorbic acid
C. Benzoic acid
D. Dihydroacetic acid
E. None of the above
1.8 Which alga can be used as food for the human being?
A. Chlorella
B. Polysiphonia
C. Ulothrix
D. Spirogyra
E. None of the above
1.9 Tuberculosis is a:
A. Water borne disease
B. Air borne disease
C. Food borne disease
D. Arthropod borne disease
E. None of the above
3IPage
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

1.10 HACCPis the acronym for:
A. Health Analysis and Critical Cause Prevention
B. Hazard Analysis and Critical Cause Prevention
C. Health Analysis and Critical Control Point
D. Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point
E. None of the above
1.11 Which of the following chemical-based preservatives act on C/ostridia:
A. Sodium diacetate
B. Dihydroacetic acid
C. Sorbic acid
D. Sodium Nitrite
E. None of the above
1.12 The application of UV radiation in food preservation is for:
A. Killing microbes in moist food
B. Creating peroxides that oxidize cellular constituents
C. Removing or displacing electrons
D. Sterilizing surfaces of food-handling equipment
E. None of the above
1.13 Which of the following are not effects of probiotics?
A. Control diarrhea
B. lmmunomodulation
C. Anti-cancer effects
D. Improve blood circulation
E. None of the above
1.14 Clostridium perfringens is found in high-risk foods such as:
A. Water
B. Cooked, dished meat and poultry
C. Unpasteurized fruits and vegetables
D. Raw eggs
E. All of the above
41Page
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

1.15 Most human pathogens prefer temperatures near that of the human body. They are
called:
A. Psychrophiles
B. Thermophiles
C. Mesophiles
D. Halophiles
E. None of the above
1.16 Who was the first to observe "animalcules" under the microscope?
A. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek
B. Otzi the Iceman
C. Marcus Terentius Varro
D. Robert Koch
E. None of the above
1.17 Which of the following is a prokaryotic microorganism?
A. Helminth
B. Protozoan
C. Cyanobacterium
D. Mold
E. All of the above
1.18 Which of the following is acellular?
A. Virus
B. Bacterium
C. Fungus
D. Protozoan
1.19 If a culture starts with 50 cells, how many cells will be present after five generations
with no cell death?
A. 200
B. 400
C. 1600
D. 3200
E. Not enough information given to determine
SI Page
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |

1.20 Streptococcus mutans is a major cause of cavities. It resides in the gum pockets, does
not have catalase activity, and can be grown outside of an anaerobic chamber. The
bacterium is probably which of the following?
A. A facultative anaerobe
B. An obligate aerobe
C. An obligate anaerobe
D. An aerotolerant anaerobe
E. Not enough information given to determine
SECTIONB [100]
QUESTION 2 (20)
Define the following terms (Each correct answer earns 2 marks):
2.1 Bacteriocin
2.2 Antiseptic technique
2.3 Thermal death point
2.4 Autoclaving
2.5 Phytoremediation
2.6 Symbiosis
2.7 Resolving power
2.8 Genetic engineering
2.9 Pilus (plural= Pilli)
2.10 Microaerophile
QUESTION 3 (21)
3.1 Define endomycorrhiza and ectomycorrhiza and list three (3) major characteristics
of both.
(8)
3.2 Differentiate between selective and differential media and provide three (3) forms
that solid media are prepared as.
(5)
GI Page
 |
7 Page 7 |
▲back to top |
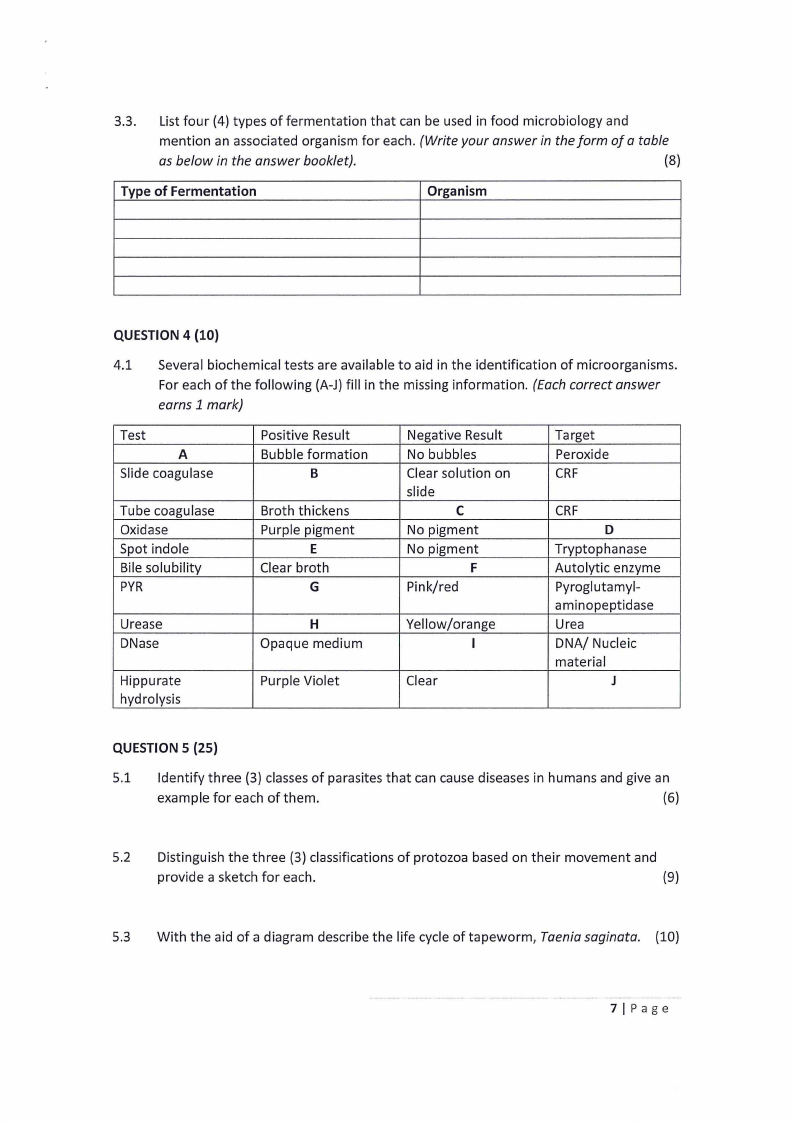
3.3. List four (4) types of fermentation that can be used in food microbiology and
mention an associated organism for each. (Write your answer in the form of a table
as below in the answer booklet).
(8)
Type of Fermentation
Organism
QUESTION 4 (10)
4.1 Several biochemical tests are available to aid in the identification of microorganisms.
For each of the following (A-J) fill in the missing information. (Each correct answer
earns 1 mark)
Test
A
Slide coagulase
Tube coagulase
Oxidase
Spot indole
Bile solubility
PYR
Urease
DNase
Hippurate
hydrolysis
Positive Result
Bubble formation
B
Broth thickens
Purple pigment
E
Clear broth
G
H
Opaque medium
Purple Violet
Negative Result
No bubbles
Clear solution on
slide
C
No pigment
No pigment
F
Pink/red
Yellow/orange
I
Clear
Target
Peroxide
CRF
CRF
D
Tryptophanase
Autolytic enzyme
Pyroglutamyl-
aminopeptidase
Urea
DNA/ Nucleic
material
J
QUESTION 5 (25)
5.1 Identify three (3) classes of parasites that can cause diseases in humans and give an
example for each of them.
(6)
5.2 Distinguish the three (3) classifications of protozoa based on their movement and
provide a sketch for each.
(9)
5.3 With the aid of a diagram describe the life cycle of tapeworm, Taenia saginata. (10)
71Page
 |
8 Page 8 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 6 (24)
6.1 With the aid of a diagram explain the life cycle of the Intestinal hookworm
(10)
6.2 Mention four (4) critical points where foodborne illnesses may occur.
(4)
6.3 Plants can be genetically engineered with useful genes placed on the Ti plasmid of
Agrobacterium tumefaciens. With the aid of diagrams, briefly outline the 7 steps to
produce a drought resistant plant with the hypothetical (dR-gene) using
Agrobacterium tumefaciens
(10)
THE END
Bl Page





