 |
HAM611S - HAEMATOLOGY 2A - 2ND OPP - JULY 2022 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |
nAmlBIA UnlVERSITY
FACULTYOF HEALTH, APPLIED SCIENCESAND NATURAL RESOURCES
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES
QUALIFICATION: MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCES
QUALIFICATION CODE: 08BMLS
LEVEL: 6
COURSE CODE: HAM611S
COURSE NAME: HAEMATOLOGY 2A
SESSION:
JULY 2022
PAPER:
THEORY
DURATION:
3 HOURS
MARKS:
100
EXAMINER(S)
SUPPLEMENTARY/SECOND OPPORTUNITY PAPER
Ms EDWIG HAUWANGA
MODERATOR:
Dr MAURICE NYAMBUYA
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALL the questions.
2. Write clearly and neatly.
3. Number the answers clearly.
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF 7 PAGES {Including this front page)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

SECTION A {20 MARKS)
QUESTION1
[10]
Evaluate the statements in each numbered section and select the most appropriate
answer or phrase from the given possibilities. Write the appropriate letter next to the
number of the statement/phrase.
1.1 The following cells all stem from the myeloid progenitor except:
(1)
A) Neutrophils
B) Lymphocytes
C) Platelets
D) Megakaryocytes
1.2 Identify the term in which bone marrow becomes sole site for haemopoiesis? (1)
A) First few weeks of gestation
B) First few weeks post-natal
C) 2-3 moths pre-natal
D) 6-7 months post-natal
1.3 Describe a pro-normoblast:
(1)
A) 14-25um big, with 1:8 N:C ratio, 1-2 nucleoli, deep blue cytoplasm
B) 12-17um, 75% nucleus, 1-2 nucleoli, blue cytoplasm with reddish tint
C) 10-15um, 25-50% nucleus, no nucleoli, nucleus eccentric location, blue-
grey cytoplasm
D) 10-15um, 25% nucleus, pyknotic nucleus, blue-grey nucleus
1.4 Which of the following cells are not part of the bone marrow stroma:
(1)
A)
Adipocytes
B)
Fibroblasts
C)
Erythroblast
D) Macrophage
1.5 Bending twisted chain into a 3 dimensional "pretzel" shape describes the:
(1)
A)
Primary HB structure
B) Secondary HB structure
C) Tertiary HB structure
D) Quaternary HB structure
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |
1.6 The red cell inclusion that is consistent with a defect in the hexose (1)
monophosphate shunt is:
A) Heinz body
B) Cabot ring
C) Pappenheimer body
D) Howell Jolly body
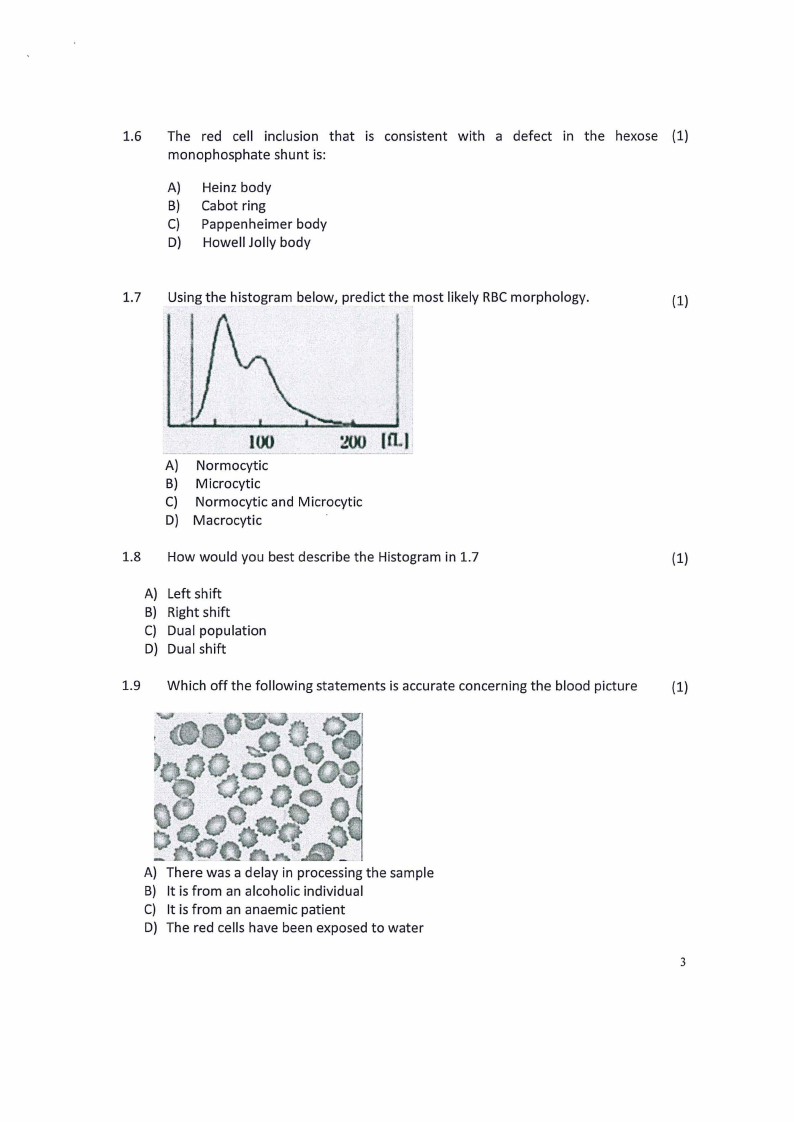
1.7 Using the histogram below, predict the most likely RBCmorphology.
(1)
A) Normocytic
B) Microcytic
C) Normocytic and Microcytic
D) Macrocytic
1.8 How would you best describe the Histogram in 1.7
(1)
A) Left shift
B) Right shift
C) Dual population
D) Dual shift
1.9 Which off the following statements is accurate concerning the blood picture
(1)
A) There was a delay in processing the sample
B) It is from an alcoholic individual
C) It is from an anaemic patient
D) The red cells have been exposed to water
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

1.10 Identify the anaemia that is classified under decreased production
(1)
A) Megaloblastic
B) Aplastic
C) Iron deficiency
D) All of the above
QUESTION 2
[10]
For each of the following phrases, give the appropriate technical/scientific term:
2.1 Increased rate of red cell destruction
(1)
2.2. When red cells stain diffusely basophilic/ blue grey with routine haematological (1)
stains
2.3 Another term for haemopoietic growth factors
(1)
2.4 Non-functional haemoglobin molecule with ferrous iron molecules
(1)
2.5 The site in which the first stem cells are observed during foetal life
(1)
2.6 The shape of a red cell
(1)
2.7 Haemoglobin with all four alpha chains missing/deleted
(1)
2.8 Bone marrow with loss of haemopoietic tissues and mainly fatty tissues only (1)
present
2.9 Receptor of Vitamin B12 on the gastric parietal cells whose deficiency leads to (1)
pernicious anaemia
2.10 Disorder whereby there is a lack of haemoglobin beta chains resulting in excess (1)
alpha chains
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

SECTION B (38 MARKS)
QUESTION 3
3.1 Use the values provided from an adult male to calculate all red cell indices,
mean cell volume, mean cell haemoglobin and Mean Cell Haemoglobin
concentration. Show your workings:
Haemoglobin
Hct
Rbc
MCV
MCH
MCHC
11.1
g/dl
31.9
%
3.79
x 1012 /I
A
B
C
[20]
(12)
(2)
3.2 List all parameters that are out of range.
(6)
3.3 State reasons for falsely decreased and falsely increased platelet values:
QUESTION 4
Micronutrients such as iron and vitamin B12 are a very import part of our daily diets
and can lead to unpleasant consequences such as anaemia when deficient. Clearly
outline importance of these two micronutrients under the following headings:
4.1 Haemopoietic function.
4.2 Morphologically classify the types of anaemia they cause.
4.3 Outline the most common haematological findings in these anaemias.
4.4 Mention other non-haematological tests one can use to investigate anaemias
resulting from deficiency of these micronutrients.
[18]
(4)
(2)
(6)
(6)
5
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |

SECTION C (42 MARKS)
QUESTION 5
[22]
2-year-old girl from the Maldives in the Mediterranean Islands, presents with cough,
dyspnoea, and fatigue. She had an enlarged liver, and her x-rays reveal maxillary
expansions. Her FBCrevealed an HB of 3.6g/dl and her peripheral blood smear was as
... follows.
• ,. ... l\\o('•
r'ii:,
)..
)'
..
.
• X.
~:,,J""J
<i:/A
f
0
• .-.,·
5.1 Attempt diagnosis and support your answer.
(5)
5.2 Comment on the red cell morphology
(6)
5.3 The doctor requests an HB electrophoresis, draw the expected results of the HB (6)
electrophoresis with clear labels.
5.4 What is the principle of the HB electrophoresis and what is its main purpose? (3)
5.5 These patients are usually treated with blood transfusion; however, this is without (2)
consequence. What are the consequences of repeated blood transfusions and
how can they be countered?
6
 |
7 Page 7 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 6
[20]
6.1 Identify and explain the two mechanisms in which red cells can be broken down? {10)
6.2 What is the major differentiating findings between the two mechanisms
{2)
6.3 List the common laboratory findings in haemolytic anaemia.
(6)
6.4 What test can be used to differentiate immune from non-Immune haemolytic {2)
anaemia?
END OF PAPER (TOTAL MARKS 100)
7





