 |
AEM520S - AGRICULTURAL ECONOMICS - 1ST OPP - NOV 2024 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |
" nAmlBIA unlVERSITY
OF SCIEn CE Ano TECHn OLOGY
FACULTYOF HEALTH1 NATURALRESOURCESAND APPLIEDSCIENCES
SCHOOLOF AGRICULTUREAND NATURALRESOURCESSCIENCES
DEPARTMENTOF AGRICULTURALSCIENCESAND AGRIBUSINESS
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOROF SCIENCEIN AGRICULTURE/ HORTICULTUREand REGIONAL
AND RURALDEVELOPMENT
QUALIFICATION CODE:
07BAGA/07BHOR/07BRAR
LEVEL: 7
COURSECODE:AEM520S
COURSENAME: AGRICULTURALECONOMICS
DATE: NOVEMBER 2024
DURATION: 3 HOURS
PAPER:1
MARKS: 100
FIRSTOPPORTUNITYQUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER(S) MR ANDREAS ERASTUS
MS ESTHERKWAAMBWA
MODERATOR: MR MWALA LUBINDA
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALL the questions.
2. Write clearly and neatly.
3. Number your answers clearly.
PERMISSIBLEMATERIALS
1. Examination Question paper
2. Examination Answer booklet
3. Calculator
THIS QUESTION PAPERCONSISTSOF 6 PAGES(Including this front page)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

[22 MARKS]
1.1 Agriculture is the backbone of many national economies, particularly in Africa. Discuss the
importance of the agricultural sector in the Namibian economy, providing at least four key points.
[8]
1.2 When markets fail to achieve efficiency, government intervention can improve societal welfare by
promoting fairness (equity). Discuss two policies currently implemented by the Namibian
government to ensure a fair distribution of economic resources to all citizens, regardless of their
background or status.
[4]
1.3 "Production Possibilities Frontier is an economic model used to explain the principle of
opportunity cost". Explain the meaning of the following terms within the context of the PPF
model.
[6]
(i) Production Efficiency
(ii) Allocative efficiency
(iii) Infeasible production regions
1.4 Explain what happens to the PPFwhen the economy experiences economic growth.
[2]
1.5 Explain why consumers are faced with opportunity costs when buying their goods.
[2]
Total
[22]
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

2.1 Consider the following functions that describe the market for oranges in Namibia:
P = 15 + 0.3Qs
P= 70- ZQd
Where Pis the price (N$ per kg), Qs is the quantity of oranges supplied (in thousand kilograms), and
Qd is the quantity of Oranges demanded (in thousand kilograms).
2.1.1 Calculate the choke price and minimum selling price.
[2]
2.1.2 Calculate the quantity supplied when the selling price is N$18 per kg.
[2]
2.1.3 Determine the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity.
[4]
2.1.4 Draw the market for oranges, illustrating the demand curve, supply curve, minimum
selling price, choke price, equilibrium quantity, and equilibrium price
[S]
2.1.5
Suppose the government introduces a price floor for oranges of N$30 per kg.
(i) Determine if there will be a surplus or shortage in the market at this price.[2]
(ii) Calculate the size of the surplus or shortage in thousand kilograms.
[2]
(iii) Illustrate the price floor on the graph from Question 2.1.4.
[2]
Total
[19]
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

[ 20MARKS]
3.1 Calculate the cross-price elasticity of demand for Irish potatoes given the following information:
The price of sweet potatoes increased from N$9.00 to N$10.00 per kg.
When the price of sweet potatoes was N$9.00 per kg, the quantity demanded of Irish potatoes
was 150 kg per week.
When the price of sweet potatoes increased to N$10.00 per kg, the quantity demanded of Irish
potatoes increased to 190 kg per week.
(i) Calculate the cross elasticity of demand for Irish potatoes.
[3]
(ii) Interpret the cross elasticity of demand for Irish potatoes.
[2]
(iii) Given the answer of cross elasticity, are Irish potatoes and sweet potatoes substitute or
complementary goods? Motivate your answer.
[2]
3.2 A farmer who specializes in two cash crops, groundnuts and cowpeas, is looking to hire a suitable
candidate from NUST.To evaluate the candidates, she presented the following scenario:
Groundnuts:
Initial price: N$90 per ton
Proposed price: N$100 per ton
Projected demand decrease: from 1,500 tons to 1,100 tons
Cowpeas:
Initial price: N$120 per ton
New price: N$125 per ton
Demand change: from 1,240 tons to 1,226 tons
Using this information,
(i) Calculate the price elasticity for both groundnuts and cowpeas?
[S]
(ii) What type of elasticity of demand is groundnut and cowpeas?
[2]
(iii) If the farmer want to select one of the crop for increasing her revenue which crop are you
recommending her to choose for her to make more profit?
[2]
(iv) By calculation, prove why you have chosen that cash crop in (iii)?
[4)
Total
[20)
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |
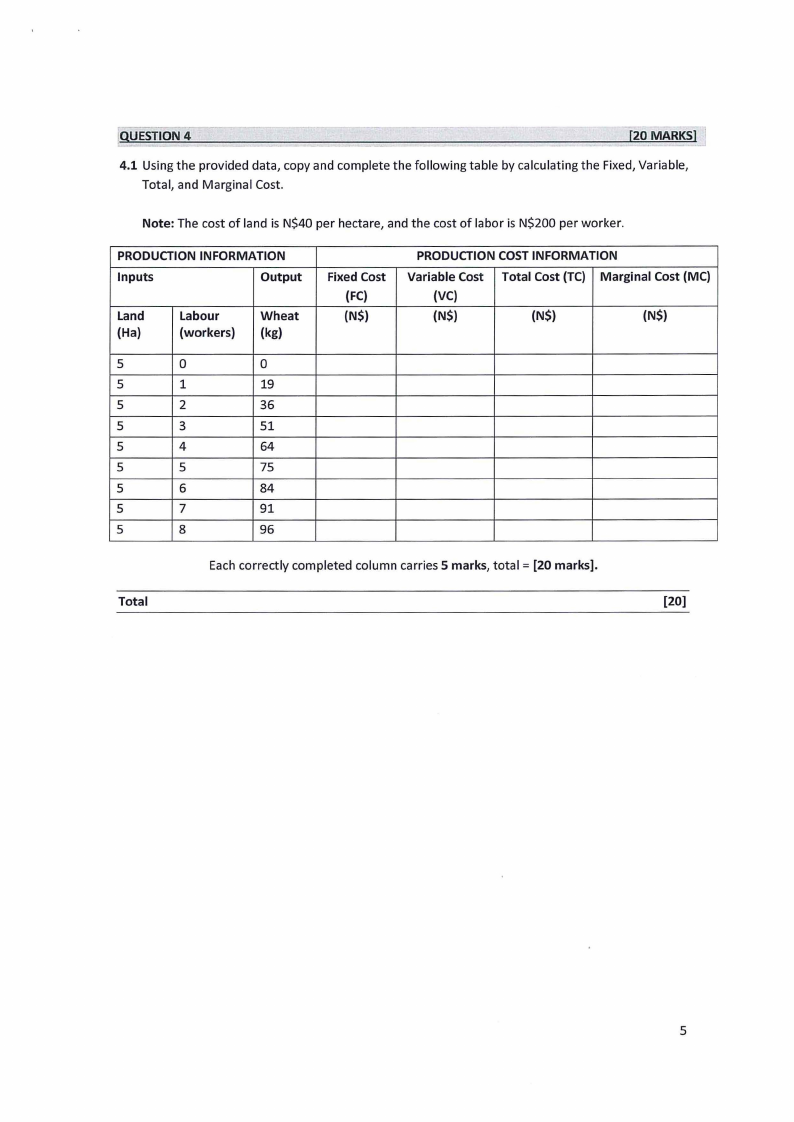
QUESTION4
4.1 Using the provided data, copy and complete the following table by calculating the Fixed, Variable,
Total, and Marginal Cost.
Note: The cost of land is N$40 per hectare, and the cost of labor is N$200 per worker.
PRODUCTION INFORMATION
Inputs
Output
Land
(Ha}
Labour
(workers)
Wheat
(kg)
Fixed Cost
(FC)
(N$)
PRODUCTION COST INFORMATION
Variable Cost Total Cost (TC) Marginal Cost (MC)
(VC)
(N$)
(N$}
(N$)
5
0
0
5
1
19
5
2
36
5
3
51
5
4
64
5
5
75
5
6
84
5
7
91
5
8
96
Each correctly completed column carries 5 marks, total= [20 marks].
Total
[20]
5
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |

!QUESTION5
[
[ 19 MARKS)
5.1 "Money is any good widely accepted as payment for goods and services, whether in paper or
coins." Explain the functions of money in the Namibian economy.
[41
5.2 State three key advantages of conducting National Income Accounting for any national economy.
[3]
5.3 Discussthree approaches used in measuring Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
[6]
5.4 Identify and explain the key determinants of loan interest rates.
[6]
Total
[19]
END OF QUESTION PAPER
6





