 |
EPD612S - EPIDEMIOLOGY 2B - 2ND OPP - JAN 2023 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |
nAm I BIA unlVERSITY
OF SCIEnCE AnD TECHnOL0GY
FACULTYOF HEALTH,APPLIEDSCIENCESAND NATURALRESOURCES
DEPARTMENTOF HEALTHSCIENCES
QUALIFICATION:BACHELOROF ENVIRONMENTALHEALTHSCIENCESH, UMAN NUTRITIONAND
HEALTHINFORMATIONMANAGEMENT SYSTEM
QUALIFICATIONCODE:
08BOHS,08BOHN, 07BHIS
LEVEL:6
COURSE:EPIDEMIOLOGY 2B
COURSECODE:EPD 612S
SESSIONJ:ANUARY 2023
PAPER:THEORY
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 100
SUPPLEMENTAR/YSECOND OPPORTUNITYEXAMINATION PAPER
EXAMINER(S):
MR JOSHUA HIDINWA
MODERATOR:
DR ROSWITHAMAHALIE
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALLthe questions.
2. Write clearly and neatly.
3. Number the answers clearly.
PERMISSIBLEMATERIALS
NONE
THIS QUESTION PAPERCONSISTSOF 7 PAGES{Including this front page)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

SECTION A [30 MARKS]
QUESTION 1
[10 MARKS]
Select most appropriate answer from the options provided.
Example: 1.35 A
1.1 Which of the following is secreted in the saliva of the infected animals:
[1]
A. Malaria
B. Cholera
C. Anaemia
D. Congo fever
E. Rabies
1.2 Which of the following is the reservoirs of the rabies infections:
[1]
A. Faecal hands
B. Sewerage
C. Humans
D. Dogs
E. Contaminated water
1.3 Which of the following disease causes abortion, premature delivery of the foetus
And death in animal:
[1]
A. P. Mansonei
B. P. Respiratory infection
C. Brucellosis
D. Mechanical vector-borne transmission
E. P. falciparum
1.4 Mode of transmission of Brucellosis is:
[1]
A. Wastewater
B. Ingestion of untreated water
C. Overcrowded
D. Contact with infected blood
E. Unvaccinated animals
1
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

1.5 What is the incubation period of Rift Valley Fever?
[1]
A. 2 to 5 days
B. 1 day
C. 4 to 6 hours
D. 1 to 6 days
E. 12 hours
1.6 Which of the following is an acute disease of domestic ruminants caused by a
mosquito-borne virus:
[1]
A. Brucella
B. Malaria
C. Tuberculosis
D. Rift Valley Fever
E. Rabies
1.7 Which of the following is a highly contagious acute respiratory illness which
affects humans and animals:
[1]
A. HIV
B. Tuberculosis
C. Plasmodium
D. Malaria
E. Influenza
1.8 Protection of infants from infection up to 3 months of age is due to:
[1]
A. Mother and baby relationship
B. Breast feeding corner
C. The care of mother
D. Presence of fetal haemoglobin
E. Formula used for the baby
2
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

1.9 Herd immunity depends on:
[1]
A. Subclinical infection
B. Immunization status of herd
C. Herd stracture
D. Herd participation
E. Community leader
1.10 All of the following are symptoms of Hepatitis B except:
[1]
A. Nausea,
B. Jaundice
C. Fatigue,
D. Vomiting,
E. Runny nose
QUESTION 2
Indicate which of the following statements is True or False
2.1 Most Influenza A viruses are classified as low pathogenic strains.
2.2 Anthrax is not common in agricultural regions.
[10 MARKS]
[1]
[1]
2.3 Ebola is transmitted by direct contact with the blood, body fluids and tissues of
infected persons.
[1]
2.4 Animals are infected with Anthrax during milking.
[1]
2.5 Plague is an acute disease of animals and humans caused by a bacteria
Transmitted from small animals to humans by the bite of infected fleas.
[1]
2.6 Streptococcus pneumoniae it does not Infect bronchi, and alveoli.
[1]
2.7 Trypanosomiasis is a disease that only affects humans.
[1]
2.8 Ebola is not highly virulent viral haemorrhagic fever that is often fatal in man
and other primates.
[1]
2.9 Plague can be a very severe disease with a case-fatality ratio of 30%-60% if
untreated.
[1]
2.10 Influenza A viruses does not cause any type of pandemics.
[1]
3
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |
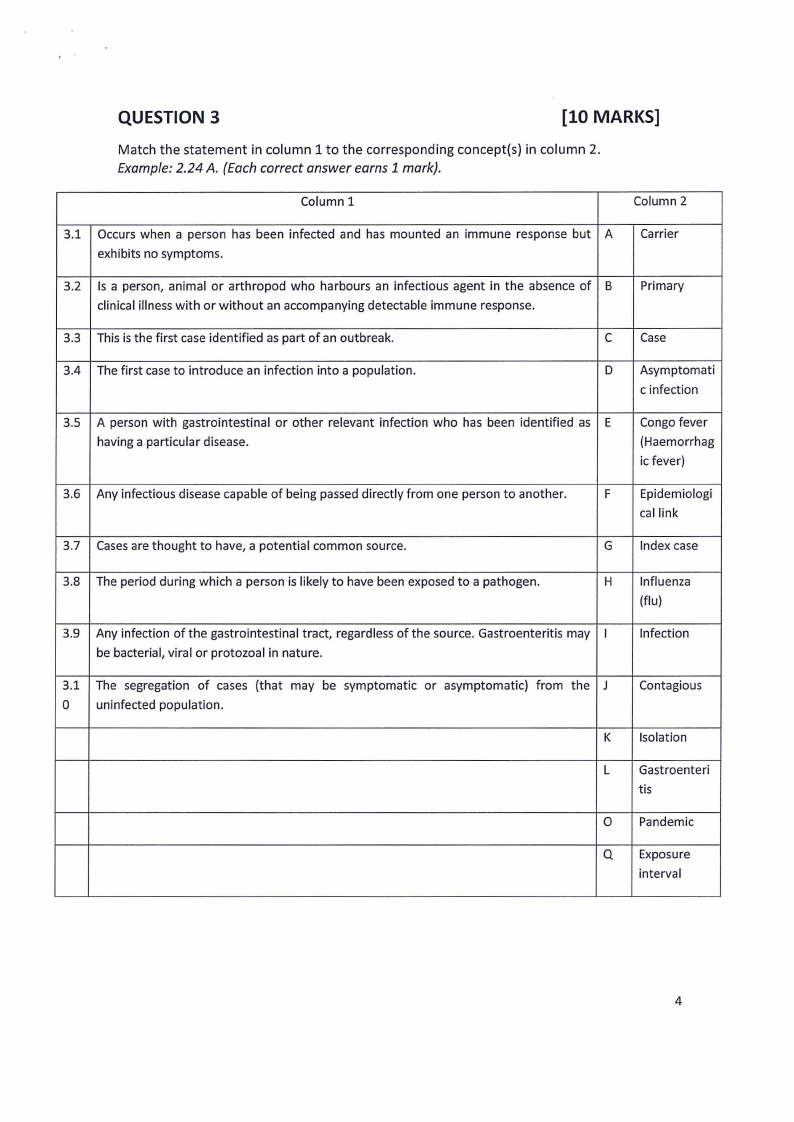
QUESTION 3
[10 MARKS]
Match the statement in column 1 to the corresponding concept(s) in column 2.
Example: 2.24 A. (Each correct answer earns 1 mark).
Column 1
Column 2
3.1 Occurs when a person has been infected and has mounted an immune response but A
exhibits no symptoms.
Carrier
3.2 Is a person, animal or arthropod who harbours an infectious agent in the absence of B
clinical illness with or without an accompanying detectable immune response.
Primary
3.3 This is the first case identified as part of an outbreak.
C Case
3.4 The first case to introduce an infection into a population.
D Asymptomati
c infection
3.5 A person with gastrointestinal or other relevant infection who has been identified as E
having a particular disease.
Congo fever
(Haemorrhag
ic fever)
3.6 Any infectious disease capable of being passed directly from one person to another.
F Epidemiologi
cal link
3.7 Casesare thought to have, a potential common source.
G Index case
3.8 The period during which a person is likely to have been exposed to a pathogen.
H
3.9 Any infection of the gastrointestinal tract, regardless of the source. Gastroenteritis may I
be bacterial, viral or protozoa! in nature.
3.1 The segregation of cases (that may be symptomatic or asymptomatic) from the J
0 uninfected population.
K
L
0
Q
Influenza
(flu)
Infection
Contagious
Isolation
Gastroenteri
tis
Pandemic
Exposure
interval
4
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |

ON B f20 MARKS]
QUESTION 4
Define the following epidemiological terms:
4.1 Microbiological clearance:
4.2 Poliomyelitis:
4.3 Salmonella food poisoning:
4.4 Larvicide:
4.5 Repellent:
4.6 Asymptomatic infection:
4.7 Carrier:
4.8 Contact:
4.9 Epidemiological link:
4.10 Exposure-prone groups:
[20 MARKS]
[2]
[2]
[2]
[2]
[2]
[2]
[2]
[2]
[2]
[2]
SEC110N C [30 MARKS]
QUESTION 5:
[20 MARKS]
5.1 Vectors are classified according to their method of transmitting disease into
mechanical and biological vectors elaborate on those methods.
[10]
5.2 Discussthe challenges for IHR 2005 implementation of member states.
[10]
5
 |
7 Page 7 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 6:
[10 MARKS]
6.1 Surveillance is an essential feature of epidemiologic practice discuss the uses
of surveillance.
[10]
SECTION O [20 MARKS]
QUESTION 7:
7.1 Outline Surveillance under the following activities:
A. Passivesurveillance.
B. Active surveillance.
C. Sentinel reporting.
7.2. Discussthe Criteria for Selecting Vector Control Measures.
Good luck!!
[20 MARKS]
[10]
[3]
[3]
[4]
[10]
TOTAL: 100 MARKS
6





