 |
PPM712S PRODUCT PRICING MANAGEMENT - 2ND OPP SUPL - JAN 2023 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAmtBIA untVERSITY.
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECHnOLOGY
FACULTY OF COMMERCE, HUMAN SCIENCE AND EDUCATION
DEPARTMENT OF MARKETING, LOGISTICS AND SPORT MANAGEMENT
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF MARKETING
QUALIFICATION CODE: 07MARB
LEVEL: 7
COURSE CODE: PPM712S
COURSE NAME: PRODUCT PRICING MANAGEMENT
SESSION: NOVEMBER 2022
PAPER:THEORY
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 100
EXAMINER(S)
SECOND OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
MR. C. KAZONDOVI
MR. D. KANDJIMI
MODERATOR: DR. E. SIMATAA
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALL the questions.
2. Write clearly and neatly.
3. Number the answers clearly.
4. Use the tables provided on page [6] to answer Questions 6 & 7:
Detach and insert into your answer booklet.
5. Write as legible as possible, and as precise as possible.
6. Read each question carefully.
7. Use a non-programmable calculator (STRICTLY NO USE OF
CELLPHONE/MOBILE CALCULATOR).
8. Round your answers to two (2) Decimal places.
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF 6 PAGES (Including this front page)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |
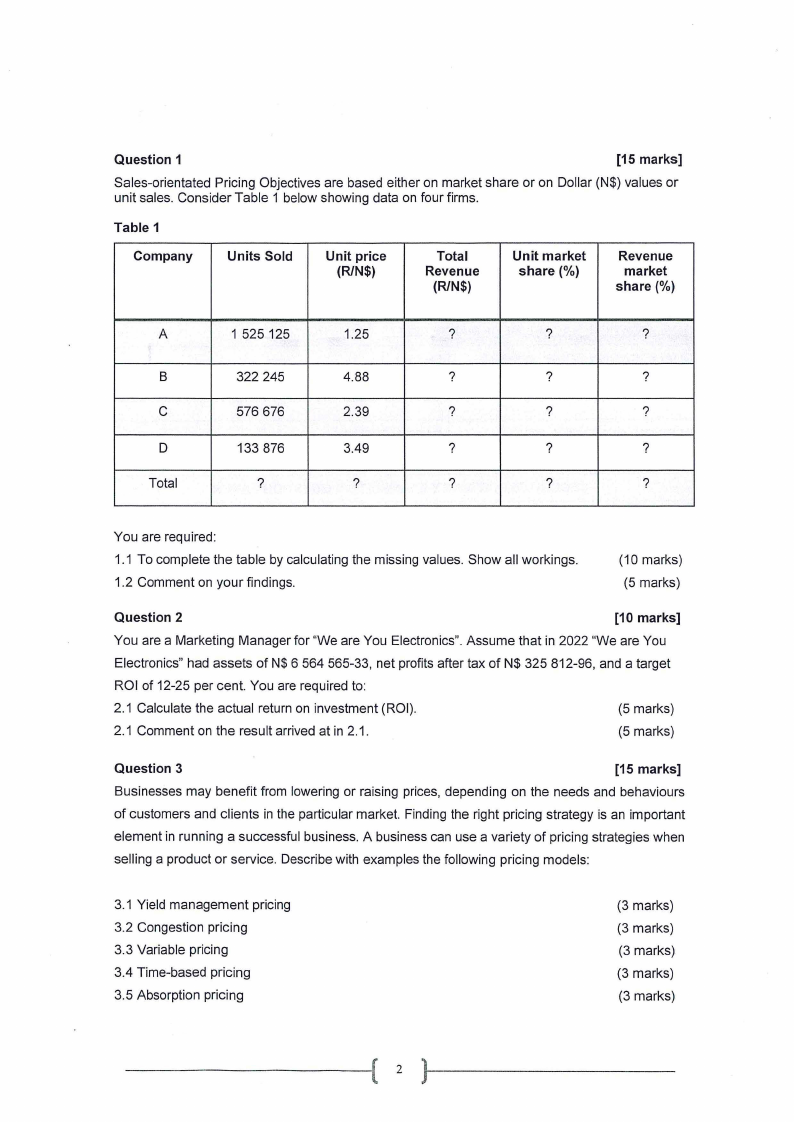
Question 1
[15 marks]
Sales-orientated Pricing Objectives are based either on market share or on Dollar (N$) values or
unit sales. Consider Table 1 below showing data on four firms.
Table 1
Company
Units Sold
Unit price
(R/N$)
Total
Revenue
(R/N$)
Unit market
share(%)
Revenue
market
share(%)
A
1 525 125
1.25
?
?
?
B
322 245
4.88
?
?
?
C
576 676
2.39
?
?
?
D
133 876
3.49
?
?
?
Total
?
?
?
?
?
You are required:
1.1 To complete the table by calculating the missing values. Show all workings.
1.2 Comment on your findings.
(10 marks)
(5 marks)
Question 2
[10 marks]
You are a Marketing Manager for "We are You Electronics". Assume that in 2022 "We are You
Electronics" had assets of N$ 6 564 565-33, net profits after tax of N$ 325 812-96, and a target
ROI of 12-25 per cent. You are required to:
2.1 Calculate the actual return on investment (ROI).
(5 marks)
2.1 Comment on the result arrived at in 2.1.
(5 marks)
Question 3
[15 marks]
Businesses may benefit from lowering or raising prices, depending on the needs and behaviours
of customers and clients in the particular market. Finding the right pricing strategy is an important
element in running a successful business. A business can use a variety of pricing strategies when
selling a product or service. Describe with examples the following pricing models:
3.1 Yield management pricing
3.2 Congestion pricing
3.3 Variable pricing
3.4 Time-based pricing
3.5 Absorption pricing
(3 marks)
(3 marks)
(3 marks)
(3 marks)
(3 marks)
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

Question 4
[10 marks]
Clearly distinguish between Oligopoly and Monopolistic competition with specific examples.
Question 5
[20 marks]
5.1 The selling price of a ballpoint pen is N$ 75-23 and the shopkeeper used a markup of 25-50.
What is the cost of the ballpoint pen?
(2 marks)
5.2 A calculator is sold for N$42-00, which is 140% of cost. How much is the store's cost?
(2 marks)
5.3 A car part dealer pays N$9.28 per 15 litres of windshield washer fluid and the markup is 33%
on selling price. Find the selling price.
(2 marks)
5.4 It's the end of the model year, and the new cars are about to arrive. The dealer decides to
reduce the price of the car you want from N$200 000-00 to N$185 000-00 to try to sell it before
the new cars arrive. What's the markdown percent?
(2 marks)
5.5 Penembo's starting price for her T-Shirts is N$ 130-95. If she wants to decrease her prices to
N$ 99.95, how much of a markdown in percentage does she need?
(2 marks)
5.6 Based on Question 5.5 above, what if Penembo wanted to calculate the T-shirt price based
on a percentage markdown? What if she wanted to only mark down her prices by 20%? How
much would her T-shirts cost then?
(2 marks)
5.7 The 30% discount on a tennis racket amounts to N$89-70. Compute the list/original selling
price and the net price after discounts.
(2 marks)
5.8 Jet stores can cover its cost and make a reasonable profit if it sells a shirt for N$ 125-55. At
what price should the article be listed so that a discount of 25% can be allowed?
(2 marks)
5.9 An item listed at N$150-00 is subject to the discount series 20%, 10%, and 5%.
Determine the net price.
(2 marks)
5.10 A retail kiosk has listed a pair of sunglasses for N$136-00 less 30%. A department store in
the shopping mall lists the same model for N$126-00 less 20%, less an additional 15%. What
additional rate of discount must the kiosk give to meet the department store price? (2 marks)
Question 6
[15 marks]
True or False Questions
Use the table provided on [page 6] to answer these questions. Detach and insert it into your
answer booklet. 1.5 mark will be awarded for each correct answer.
6.1 Converting percent markup on cost to percent markup on selling price:
% Ms = % markup on cost
-------X
100%
100% - % markup on cost
6.2 Converting percent markup on selling price to percent markup on cost:
% Mc = % markup on selling price
-------------·-----
X 100%
100% - Markup on cost
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

6.3 There are a not really a lot of examples of perfect competition and pure monopoly.
6.4 Conditions necessary for a monopoly includes being a single seller of product, having no
close substitutes and having significant barriers to entry.
6.5 Price discrimination is the practice of setting a different price for the same product in the
same segments of the market.
6.6 Limit pricing set prices low as signal to possible entrants or other competitors of your
willingness ·and ability to defend your market share.
6.7 The Oligopolist recognise interdependence in pricing and output decisions.
6.8 The inverse relationship between the quantity of a good desired by people in a market and
the factors that affect that the quantity desired is referred to as the demand for the product.
6.9 Premium pricing is the practice of keeping the price of a product or service artificially high in
order to encourage favourable perceptions among buyers, but not necessarily based on the
price.
6.10 Many firms would prefer to engage in non-price competition by building brand equity and
relationships with customers.
Question 7
[15 marks]
Multiple Choice Questions
Use the table provided on [page 6] to answer these questions, detach and insert it into your
answer booklet. 1.5 mark will be awarded for each correct answer.
7.1 The relationship between the quantity supplied of a good and the price of that good is
referred to as the ___
curve
A) supply
B) demand
C) sales
D) costs
E) None of the above
7. 2 Throughout most of history, prices were set by ____
_
A) fixed-price policies constructed by sellers
B) negotiation between buyers and sellers
C) governments and regulatory agencies
D) ruling monarchs
E) None of the above
7.3 Before setting price, the company must decide on its strategy most likely for:
A) distribution
B) promotion
C) the environment
D) the product
E) all of these
7.4 Companies set ______
as their major objective if they are troubled by too
much capacity, heavy competition, or changing consumer wants.
A) current profit maximization
B) survival
C) market share leadership
D) product quality leadership
E) all of these
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

7.5 _____
is the practice of charging different prices depending on individual
customers and situations.
A) Fixed-pricing
B) Standard-pricing
C) Barter-pricing
D) Dynamic pricing
E) none of these
7.6 When a company sets a price for a new product on the basis of what it thinks the
product should cost, then develops estimates on what each component should cost to
meet the proposed price with an acceptable profit margin, the company is practicing:
A) predatory pricing
B) target costing
C) strategic pricing
D) low cost leadership
E) none of these
7.7 Pricing to cover variable costs and some fixed costs, as in the case of some
automobile distributorships that sell below total costs, is typical of which of the
following pricing objectives?
A) current profit maximization
B) product quality leadership
C) market share leadership
D) going-rate pricing
E) survival
7.8 Choosing a price based upon its short-term effect on current profit, cash flow, or
return on investment reflects which of the following pricing objectives?
A) current profit maximization
B) product quality leadership
C) market share leadership
D) survival
E) going-rate pricing
7.9 When a company sets a price for a new product on the basis of what it thinks the
product should cost, then develops estimates on what each component should cost to
meet the proposed price with an acceptable profit margin, the company is practicing:
A) predatory pricing.
B) target costing.
C) strategic pricing.
D) low cost leadership.
E) none of these
7.10. ______
product.
A) Supply
B) Demand
C) Costs
D) Nonprofit factors
E) none of these
set(s) the floor for the price that the company can charge for its
GRAND TOT AL = 100
THE END
5 )-----
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |
Question 6
ANSWER SHEET
· True
s.1r·-·,
6.21 '
6.3
6.4
6.5 -
6.6
6.7__ ..
6.8
6.9
6.1L0
Question 7
False
A
B
C
7.11
7.2
7.3
7.4
7.5
7.6
7.7
7.8
7.9
7.10
[Total: 10 X 1.5 = 15 Marks]
[Total: 10 X 1.5 = 15 Marks]
D
E
STUDENT NAME & STUDENT NO: ----------------
6





