 |
ENC702S-ENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY-NOV 2020 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |
eo
NAMIBIA UNIVERSITY
OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES
DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF SCIENCE
QUALIFICATION CODE: 07BOSC
LEVEL: 7
COURSE NAME: ENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY | COURSE CODE: ENC702S
SESSION: NOVEMBER 2019
DURATION: 3 HOURS
PAPER: THEORY
MARKS: 100
FIRST OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER(S) | Dr JULIEN LUSILAO
MODERATOR: Dr JAMES ABAH
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALL the questions in the answer book provided.
2. Write and number your answers clearly.
3. All written work MUST be done in blue or black ink.
PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS
Non-programmable Calculators
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF 5 PAGES (Including this front page)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |
Question 1
[15]
1.1 How would you define environmental chemistry if you must consider the different
spheres of the Earth system?
(4)
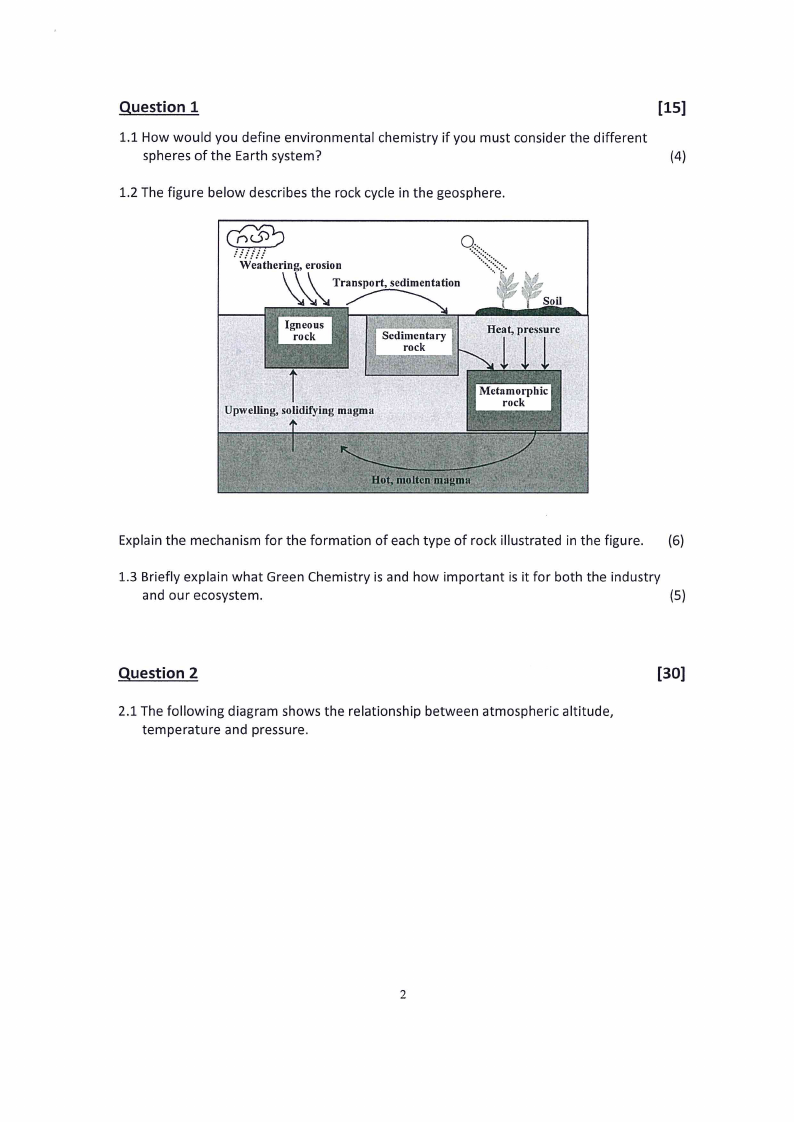
1.2 The figure below describes the rock cycle in the geosphere.
wre ese
Weathering, erosion
Transport, sedimentation
we
Explain the mechanism for the formation of each type of rock illustrated in the figure. (6)
1.3 Briefly explain what Green Chemistry is and how important is it for both the industry
and our ecosystem.
(5)
Question 2
[30]
2.1 The following diagram shows the relationship between atmospheric altitude,
temperature and pressure.
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

Temperature, °C
-100 -80 -60 -40 -20
0
100 SS
log py
What observations can be made from this diagram and what are the known
implications of these observations?
(5)
2.2 Briefly describe the main categories of atmospheric chemical reactions.
(6)
2.3 (a) How would you define air pollution? Avoid the word “pollutant” in your
definition.
(2)
(b) Complete the following reactions related to the formation of inorganic particles:
(i) 3FeS2 +802 > _ + _
(1)
(ii) Clo + 2NaOH >
+
+ H20
(1)
(iii) SO + 22 NaOH + —— >
+ H20
(1)
2.4 In 2006, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency proposed lowering the allowable
PM2.5 level to 35 g/m?. How many particles would this be in a cubic meter of air
if all the particles were spheres of a diameter of 2.5 um and had a density of exactly
1 g/cm?? Note: The volume of 1 sphere, V = 4/3 nr?
(5)
2.5 The plot below shows the level OF some species in the atmosphere during a smoggy
day
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

0.4
Non-methane hydrocarbons
0.3
0.2
0.1
0.0
M
4 A.M
8 A.M.
N
4P.M. 8P.M.
M
Time of day
Explain why NOx (i.e. NO, NOz) and non-methane hydrocarbons reach their
maximum concentrations in the early hours of the morning (i.e. between about 6
and 8 am) whereas the aldehydes and oxidants exhibit maximum peaks around
mid-day.
(4)
2.6 (a) What are the two main reactions associated with the formation of acid rain?
(2)
(b) Give three harmful effects of acid precipitation.
(3)
Question 3
[30]
3.1 The study of water is known as
whereas
is
the branch of the science dealing with the characteristics of fresh water, and
the science that deals with about 97% of all Earth’s water.
(3)
3.2 (a) Differentiate between acidity and alkalinity.
(2)
(b) Water with an alkalinity of 2.00 x 10 equivalents/litre has a pH of 7.00. Calculate
[CO2], [HCOs], [CO3*], and [OH].
Kai (H2CO3) = 4.45 x 1077; Kaz (HCO3*) = 4.45 x 107
(5)
3.3 (a) What is the mathematical expression of pE?
(1)
(b) What determines the upper and lower limits, respectively, for the
thermodynamic stability of water (Show the reactions involved)?
(4)
3.4 (a) Define phycology.
(1)
(b) Differentiate between chemoautotrophs and chemoheterotrophs. Provide an
example in each case.
(4)
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

3.5 (a) Match the pollutants from the list (A) to (D) with effects or other significant aspects
on the bottom list, below:
(A) Salinity (B) Alkalinity (C) Acidity (D) Nitrate
(1) Excessive productivity (2) Can enter water from pyrite or from the atmosphere
(3) Osmotic effects on organisms (4) From soil and mineral strata
(4)
(b) Discuss the chemical, physical and biological characteristics of Acid Mine Drainage
(AMD).
(6)
Question 4
[25]
4.1 Give four examples showing the interaction between the geosphere and the
Hydrosphere.
(4)
4.2 Define the following terms:
(a) Evaporites
(1)
(b) Weathering
(1)
(c) Clays
(1)
(d) Sediments
(1)
4.3 Briefly discuss the soil breakdown (or composition).
(8)
4.4 Match the soil or soil-solution constituent in (1) to (4) with the soil condition
described in (A) to (D) below:
(1) High Mn?* content in soil; (2) Excess H*; (3) High H* and SO4* concentrations;
(4) High organic content.
(A) “Cat clays” containing initially high levels of pyrite, FeS2; (B) Soil in which
biodegradation has not occurred to a great extent; (C) Waterlogged soil; (D) Soil, the
fertility of which can be improved by adding limestone.
(4)
4.5 (a) Explain the meaning of “internal processes” of natural hazards.
(1)
(b) What are the destructive effects of earthquakes?
(4)
END





