 |
IPP521S - INTRODUCTION TO PHONETICS AND PHONOLGY - 2ND OPP - JAN 2025 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAmlBIA UnlVERSITY
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECHnOLOGY
FACULTY OF COMMERCE, HUMAN SCIENCESAND EDUCATION
DEPARTMENT OF COMMUNICATION AND LANGUAGES
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF ENGLISH AND LINGUISTICS
QUALIFICATION CODE: (07BENL)
LEVEL: 5
COURSE CODE: IPP5215
COURSE NAME: Introduction to Phonetics and Phonology
SESSION: JANUARY 2025
TIME:
3 HOURS
PAPER: THEORY
MARKS: 100
EXAMINER(S)
MODERATOR:
SECOND OPPORTUNITY/SUPPLEMENTARY EXAMINATION PAPER
Dr Sylvia N lthindi
Ms N Haimbodi
Ms Anneli Nghikembua
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALLthe questions.
2. Read all the questions carefully before answering.
3. Number the answers clearly
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF 4 PAGES INCLUDING THE COVER PAGE
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |
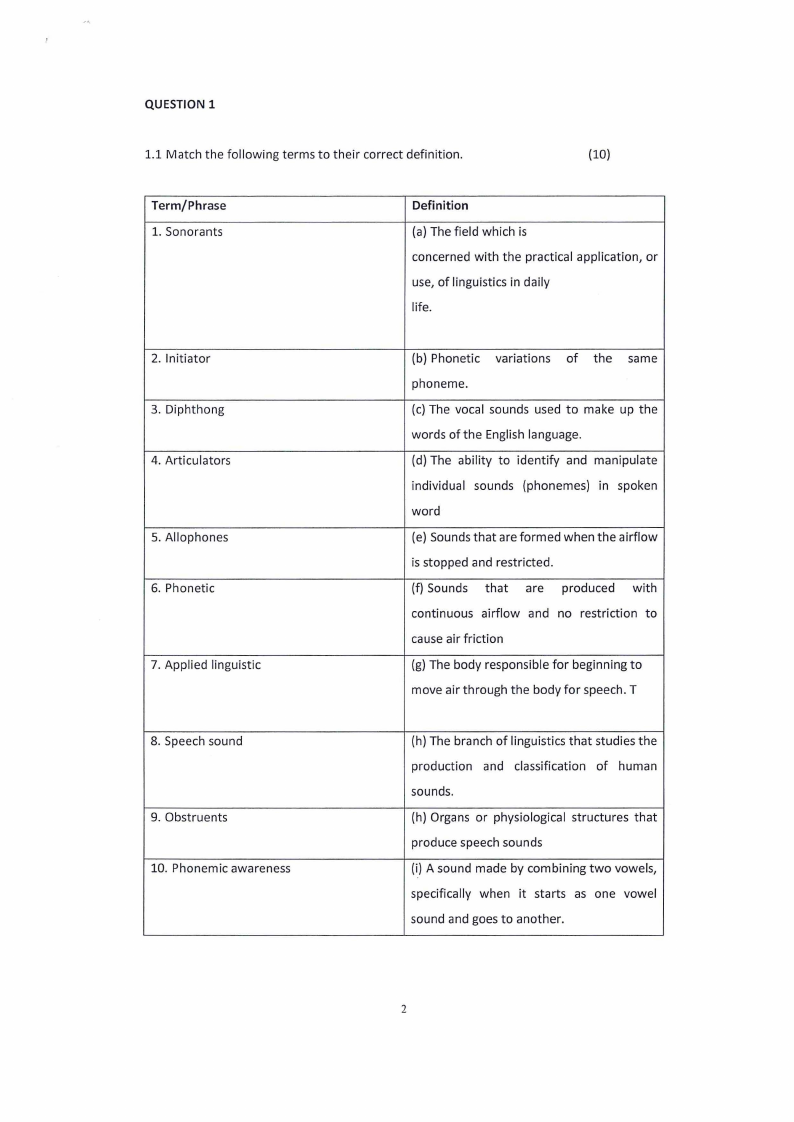
QUESTION 1
1.1 Match the following terms to their correct definition.
(10)
Term/Phrase
1. Sonorants
Definition
(a) The field which is
concerned with the practical application, or
use, of linguistics in daily
life.
2. Initiator
3. Diphthong
4. Articulators
5. Allophones
6. Phonetic
7. Applied linguistic
(b) Phonetic variations of the same
phoneme.
(c) The vocal sounds used to make up the
words of the English language.
(d) The ability to identify and manipulate
individual sounds (phonemes) in spoken
word
(e) Sounds that are formed when the airflow
is stopped and restricted.
(f) Sounds that are produced with
continuous airflow and no restriction to
cause air friction
(g) The body responsible for beginning to
move air through the body for speech. T
8. Speech sound
9. Obstruents
10. Phonemic awareness
(h) The branch of linguistics that studies the
production and classification of human
sounds.
(h) Organs or physiological structures that
produce speech sounds
(i) A sound made by combining two vowels,
specifically when it starts as one vowel
sound and goes to another.
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

1.2 The figure below illustrates the anatomy of speech production. Name the parts labelled
D, E, F, G, and H.
(10)
E
D
'
:;):~~~-" '
\\ C (~
F
.. ···G
QUESTION 2
2.1 Name and explain the parameters to describe consonants. Support your explanation with
examples.
(10)
2.2 Copy and complete the table below by placing the given vowels into their correct
categories.
(6)
Vowels: /-<E/,aua/, /3/, /ua/, /ara/, /er/
Monophthong
Diphthong
Triphthong
2.3 Explain the meaning of the following characteristics of phonemes.
(4)
(a) Phonemes are indivisible, minimal units.
(b) Phonemes are contrastive.
QUESTION 3
3.1 Describe the following phonological processes discussed in this course. Illustrate your
answers with relevant practical examples.
(15)
(a) Deletion
(b) Substitution
(c) Cluster reduction
3.2 Phonetics plays a big role in the identification of homophones in English. By using two
different examples, discuss what homophones are.
(5)
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 4
4.1 By using examples, differentiate between obstruents and sonorants.
(6)
4.2 Give the difference between phonemes and allophones.
(4)
4.3 Provide the alphabet version for the following phonetic transcription.
(10)
(a) /kJ:Jan/
(b) /srlab!/
(c) /md3ad/
(d)/mtJaz/
(e) /toprkal/
QUESTION 5
Four processes of speech were discussed in this course. Name these four processes and
explain what happens during each process. Each process should be explained separately.
(20)
END OF EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
4





