 |
LTS520S - LAND TENURE SYSTEMS - 2ND OPP - JAN 2024 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |
nAmlBIA unlVERSITY
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECHnOLOGY
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND THE BUILT ENVIRONMENT
DEPARTMENT OF LAND AND SPATIALSCIENCES
QUALIFICATION(S): BACHELOR/DIPLOMA- PROPERTYSTUDIES, LAND ADMINISTRATION,
GEOMATICS, AND TOWN AND REGIONAL PLANNING
QUALIFICATION(S) CODE: 08BPRS, 06DPRS,
07BLAM, 06DGEO, 06DGEM, NQF LEVEL: 5
07BGEO,07BGEM,07BTAR
COURSECODE: LTS520S
COURSENAME: LAND TENURE SYSTEMS
EXAMS SESSION:JANUARY 2024
PAPER:
THEORY
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS:
100
SECONDOPPORTUNITY/SUPPLEMENTARYEXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER(S) PROF UCHENDU E. CHIGBU
MODERATOR: MR AMIN ISSA
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Read the entire question paper before answering the Questions.
2. Please write clearly and legibly!
3. The question paper contains a total of 4 questions.
4. You must answer ALLQUESTIONS.
5. Make sure your Student Number is on the EXAMINATION BOOK(S).
PERMISSIBLEMATERIALS
a) None
THIS QUESTION PAPERCONSISTSOF 5 PAGES(Including this front page)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

Land Tenure Systems
LTS520S
Question 1
For each of the following statements indicate whether it is 'TRUE'or 'FALSE'.Each correct answer
carries 2 marks.
(30)
a) Complimentary interests in land exist when different parties share conflicting interests in the
same parcel of land, e.g., common rights to grazing.
b) Land tenure exists within a regime of legal, institutional and procedural systems.
c) Overriding interests in land is when a sovereign power (state or community) has powers to
allocate, cancel and reallocate.
d) The exercise of land rights and ownership has implications in the way in which we develop
urban and rural areas.
e) The environmental concept of land considers land as a place requiring management to
preserve its capacity to sustain life, carrying restrictions and responsibilities.
· f) Competing interests occur when different parties contest the same interests in the same
parcel of land - source of land disputes.
g) Overlapping interests in land is when several parties are allocated different rights to the
same parcel of land, e.g., conservancies in communal areas, family members.
h) The right to exclude others from a parcel of land constitutes a land right.
i) Land tenure is the relationship people share with land and its associated natural resources.
j) In a customary regime of land tenure, ownership is vested in chiefs or headsmen/women
and foreign governments.
SecondOpportunity/SupplementaryQuestion Paper Page2 of 5
January 2024
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

Land Tenure Systems
k) In a leasehold, ownership of land is not in perpetuity.
LTS520S
I) Usufruct rights are the rights to use land for cultivation, grazing and residential purposes.
m) Control rights are the right to make decisions on how the land should be used, and what
crops to plant etc.
n) Transferable rights entail right to sell, mortgage or convey land to others through inter-
community allocations, inheritance and reallocation of control rights.
o) Different people may hold one or several land rights simultaneously.
[30]
Question 2
Identify (and list) five challenges related to land in Namibia. Briefly explain measures that can be
used to solve each of the challenges you identified. Each challenge listed and explained carries 4
marks. Spread of marks: challenge (1); measure (1); and understanding of the subject presented
through explanation (2)
(20)
[20]
Question 3
In one or two sentences, answer the following questions. Each correct question carries 2 marks.
(30)
a) List 2 characteristics of informal settlements?
b) What is the main objective of the ongoing land reform in Namibia?
c) Why do we register land rights?
Second Opportunity/Supplementary Question Paper Page 3 of 5
January 2024
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |
Land Tenure Systems
d} Differentiate between "land access" and "land availability."
LTS520S
e) Why was the flexible land tenure system introduced in Namibia?
f) What makes land a major factor in the development of any country?
g) What do you understand by "enumeration of tenure?"
h) List the two tenure types that the Flexible Land Tenure Act (2012) provide?
i) What do you understand by "continuum of land rights?"
j) In the context of Namibia's colonial history, what do you understand by the "red line?"
k) What do you understand by a bundle of land rights?
I) What do you understand by informal settlement upgrading?
m) What is land dispossession?
n) Why were native reserves established in colonial Namibia?
o) How can you distinguish/differentiate between rural and urban areas in Namibia?
[30]
Question 4
Second Opportunity/Supplementary Question Paper Page 4 of 5
January 2024
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

Land Tenure Systems
LTS520S
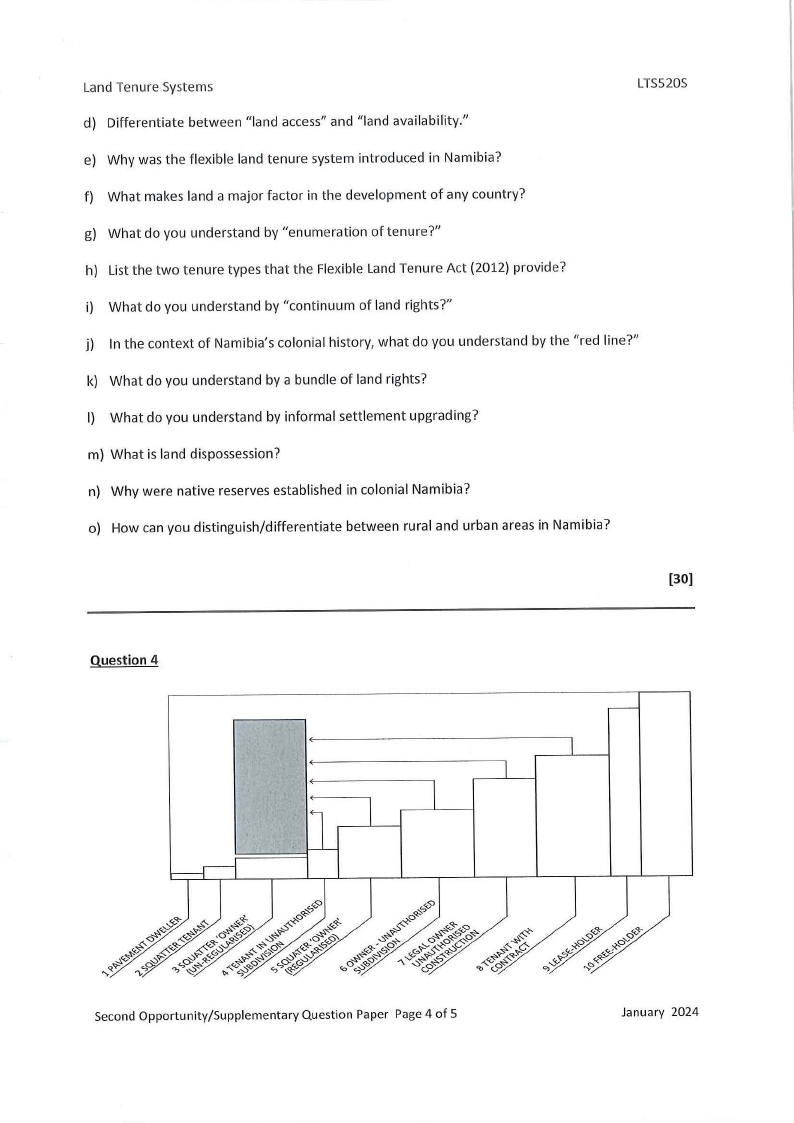
Study the diagram shown above carefully. Answer all questions below based on the information
depicted in the diagram. Each challenge listed and explained carries 2 marks.
{20)
a) What does the diagram represent?
b) Considering the positions of the "lease-holder" and "tenant with contract" in the diagram,
who is more secure?
c) Who is the most insecure in the diagram?
d) Who is a freeholder?
e) Why is the freeholder identified as no. 10 in the diagram?
f) What can a pavement dweller do to become a squatter tenant?
g) What is the difference between a lease-holder and a free-holder?
h) Considering the positions of the "tenant with contract" and "tenant in unauthorized
subdivision" in the diagram, who is more insecure?
i) Who is the most secure in the diagram?
j) What do the bars in the diagram represent in the context of land tenure?
(20]
Second Opportunity/Supplementary Question Paper Page 5 of 5
January 2024





