 |
PDF711S - Phase Diagram and Formatting Processes 314 - 1st Opp - June 2022 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

n Am I BI A u n IVER s ITY
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECHnOLOGY
FACULTYOF ENGINEERINGAND SPATIALSCIENCES
DEPARTMENT OF MINING AND PROCESSENGINEERING
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF ENGINEERING IN METALLURGY
QUALIFICATION CODE: 08BMET
LEVEL: 7
COURSE CODE: PDF711S
COURSE NAME: PHASE DIAGRAMS AND FORMING
PROCESSES314
SESSION: JUNE 2022
DURATION: 2 HOURS
PAPER: THEORY
MARKS: 65
EXAMINER(S)
FIRSTOPPORTUNITYQUESTION PAPER
Mrs. Jaquiline Tatenda Kurasha
MODERATOR:
Professor Sofya Mitropolskaya
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer all questions.
2. Read all the questions carefully before answering.
3. Marks for each question are indicated at the end of each question.
4. Please ensure that your writing is legible, neat and presentable.
PERMISSIBLEMATERIALS
1. Examinationpaper.
2. Non-programmablecalculator.
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF 4 PAGES (Including this front page)
1
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

Question 1 {15 Marks)
(a) What is the significance of the atomic packing factor?
[1]
(b) Linear density in a given crystallographic direction represents a fraction of the line length that
is occupied by atoms. At room temperature, the crystal structures of iron and aluminium are
BCCand FCCrespectively.
(i)
Calculate the linear density for [110] and (111] directions in iron and aluminium
respectively.
[4]
(ii)
Comment on your answers in (i), and explain why aluminium is softer and more ductile
than iron based on your answers in (i).
[2]
(c) Both XRD analysis and elemental analysis in the SEM generate peaks and troughs in the
spectrum. What is the fundamental difference between the EDS spectrum and the x-ray
diffraction spectrum?
[1]
(d) The {100} planes of a body-centred cubic crystal have a separation of 0.1181 nm. If these
planes are irradiated with x-rays from a copper target, the strongest line has a wavelength of
0.1541 nm.
(i)
At what angle will first order reflection occur?
[2]
(ii)
At what angle will second order reflection occur? What conclusion can you make?
[3]
(iii) Calculate the lattice parameter of the crystal.
[2]
Question 2 (20 marks)
(a) Distinguish between an intrinsic and extrinsic staking fault.
[2]
(b) The activation enthalpy for the formation of vacancies in gold is 91 500 J/mol. Calculate the
equilibrium concentration of vacancies in gold at 727 °C.
[2]
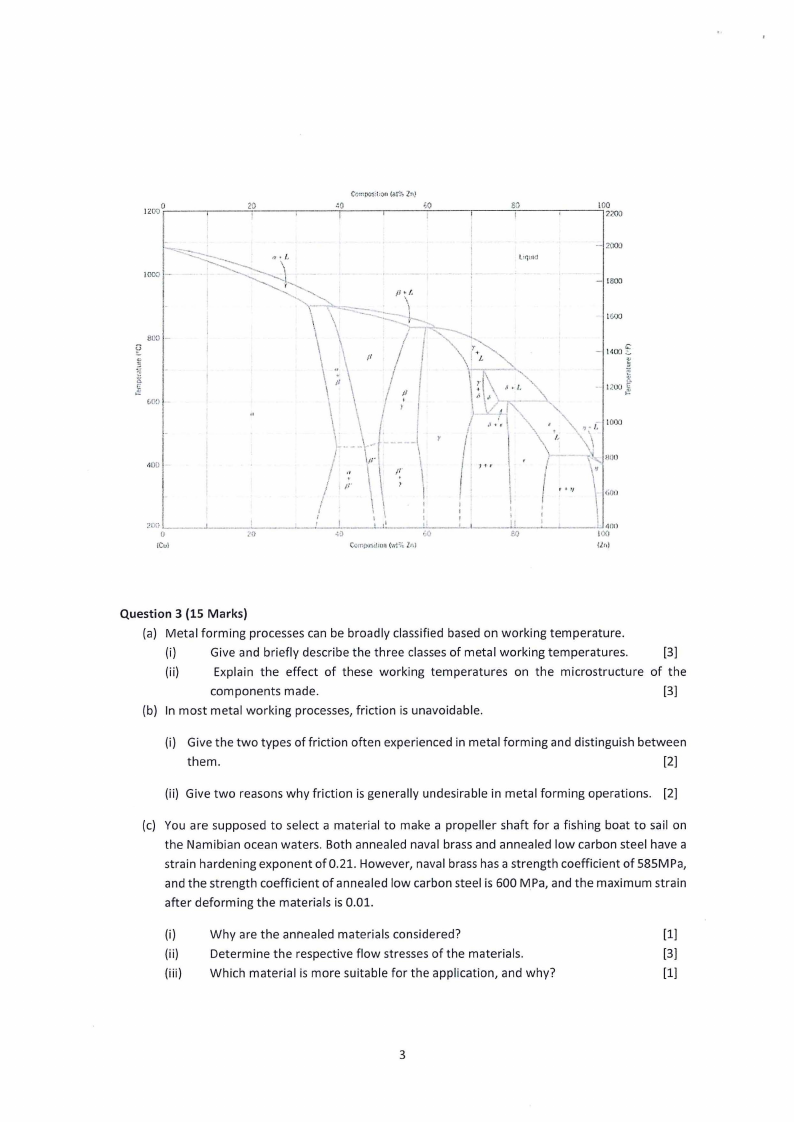
(c) The diagram below shows the Cu-Zn phase diagram. A copper-20%-zinc alloy is made from
cooling molten metal in a sand mold.
(i)
Calculate the phase fractions in this alloy at 1000°C.
[2]
(ii)
If the pouring temperature for the alloy is 1200°C, sketch the cooling curve for this
alloy.
[3]
(iii) With the aid of a clearly labelled diagram, explain the typical microstructure expected
from this casting (show all the zones).
(5]
(iv) What type of nucleation would you expect on solidification, and why?
[2]
(v)
If solidification proceeds slowly, there is a possibility of composition variation across
the casting. What is the common term used for this variation and explain how it
happens.
[2]
(vi) Suggest two ways to eliminate the composition variation indicated in (iv).
[2]
2
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |
!ODO -
01)0
- 2000
- l800
!GOO
"=
-- LUU!
Question 3 (15 Marks)
(a) Metal forming processes can be broadly classified based on working temperature.
(i)
Give and briefly describe the three classes of metal working temperatures.
(ii)
Explain the effect of these working temperatures on the microstructure
components made.
(b) In most metal working processes, friction is unavoidable.
[3]
of the
[3]
(i) Give the two types of friction often experienced in metal forming and distinguish between
them.
[2]
(ii) Give two reasons why friction is generally undesirable in metal forming operations. [2]
(c) You are supposed to select a material to make a propeller shaft for a fishing boat to sail on
the Namibian ocean waters. Both annealed naval brass and annealed low carbon steel have a
strain hardening exponent of 0.21. However, naval brass has a strength coefficient of 585MPa,
and the strength coefficient of annealed low carbon steel is 600 MPa, and the maximum strain
after deforming the materials is 0.01.
(i)
Why are the annealed materials considered?
[1]
(ii)
Determine the respective flow stresses of the materials.
(3]
(iii) Which material is more suitable for the application, and why?
[1]
3
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

Question 4 (15 marks)
(a) In metallurgical joining operations, there is generally the need to shield/protect
area from the atmosphere during joining.
(i)
Give the three main types of metallurgical joining operations.
(ii)
Explain why shielding is required.
(iii) Give the two basic methods of shielding often used.
the joint
[3]
[1]
[2]
(b) The diagram below shows the relationship between the joint clearance and joint strength in
brazing.
(i)
Explain the meaning of joint clearance.
[1]
(ii)
Comment on the effect of the joint clearance on the shear strength and the tensile
strength of the joint respectively.
[2]
,>.
"'~-
v~
'½
~0
&.
I
Joint clear,,nce-
(c) Soldering is suitable for joining thin metal sheets, and not suitable for joining load bearing
components. Explain.
[2]
(d) (i) Give three advantages of non-destructive over destructive testing?
[3]
(ii) Suggest two scenarios where non-destructive testing is the cost-effective option.
[2]
End of Question Paper.
4
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |






