 |
BPP702S - BIOCHEMISTRY BIOCHEMICAL PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE - 2ND OPP - JAN 2023 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |
nAm I BI A u n IVE RS ITY
OF SCIEn CE TECHn OLOGY
FACULTY OF HEALTH, NATURAL RESOURCES AND APPLIED SCIENCES
DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF SCIENCE(MAJOR/MINOR)
QUALIFICATION CODE:07BOSH
LEVEL: 7
COURSENAME: BIOCHEMISTRY: BIOCHEMICAL
PRINCIPLESAND PRACTICE
COURSECODE: BPP702S
SESSION:JANUARY 2023
DURATION: 3 HOURS
PAPER:THEORY
MARKS: 100
SUPPLEMENTARY/SECOND OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER
DR LAMECH MWAPAGHA
MODERATOR ASSOC PROF PETRINA KAPEWANGOLO
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALL the questions.
2. Write clearly and neatly.
3. Number the answers clearly.
4. All written work MUST be done in BLUEor BLACKink.
PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS
None
THIS QUESTION PAPERCONSISTSOF FOUR (4) PAGES
(Including this front page)
1
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 1
[14)
a) Briefly, discuss FOUR (4) factors that affect enzyme action
(8)
b) Consider the Lineweaver Burk plot shown below:
1/[S]
I. The enzyme carboxypeptidase-A catalyzes the hydrolysis of the peptide AGEs (Advanced
glycation end products) in l0mM phosphate buffer at pH 7.0. This enzyme obeys
Michaelis-Menten kinetics when Km= 3mM, Vo= 150mmol/min and [S] = 0.5 mM.
Calculate the Vmaxof this enzyme.
(4)
II. What effect (increase, decrease, no Change) does the inhibitor carboxypeptidase-A
have on Vmax-
(1)
Ill. What effect (increase, decrease, no Change) does the inhibitor carboxypeptidase-A
have on Km.
(1)
QUESTION 2
[11)
a) Draw the dominant structural form of glycine in a highly acidic solution, pH= 1.5.
(2)
b) Sketch the pH titration curve of glycine in 2.1 and show clearly the following:
(3)
I. lsoelectric point
II. pK1 (-COOH) and pK2 (-NH; )
Ill. Point only zwitterions exist
c) State SIX (6) main functions of the amino acid tryptophan
(6)
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |
QUESTION 3
[14]
a) Outline the FOUR (4) enzyme sites that regulate gluconeogenesis
(4)
b) Using structural formulas, write the balanced chemical equation for the reactions where
GTP is produced in the Kreb cycle.
(4)
c) Briefly describe the anabolic role of the TCA cycle in fatty acid synthesis
(6)
QUESTION 4
[17]
a) Schematically describe the following patterns of metabolic regulation
(8)
b) State FOUR (4) functions performed by metabolism in living cells
(4)
c) Give the possible symptoms of deficiency of the following vitamins
(5)
I. Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin);
II. Vitamin B12;
Ill. Vitamin A (Retinal);
IV. Vitamin K (Phylloquinone);
V. Vitamin D;
QUESTION 5
[15]
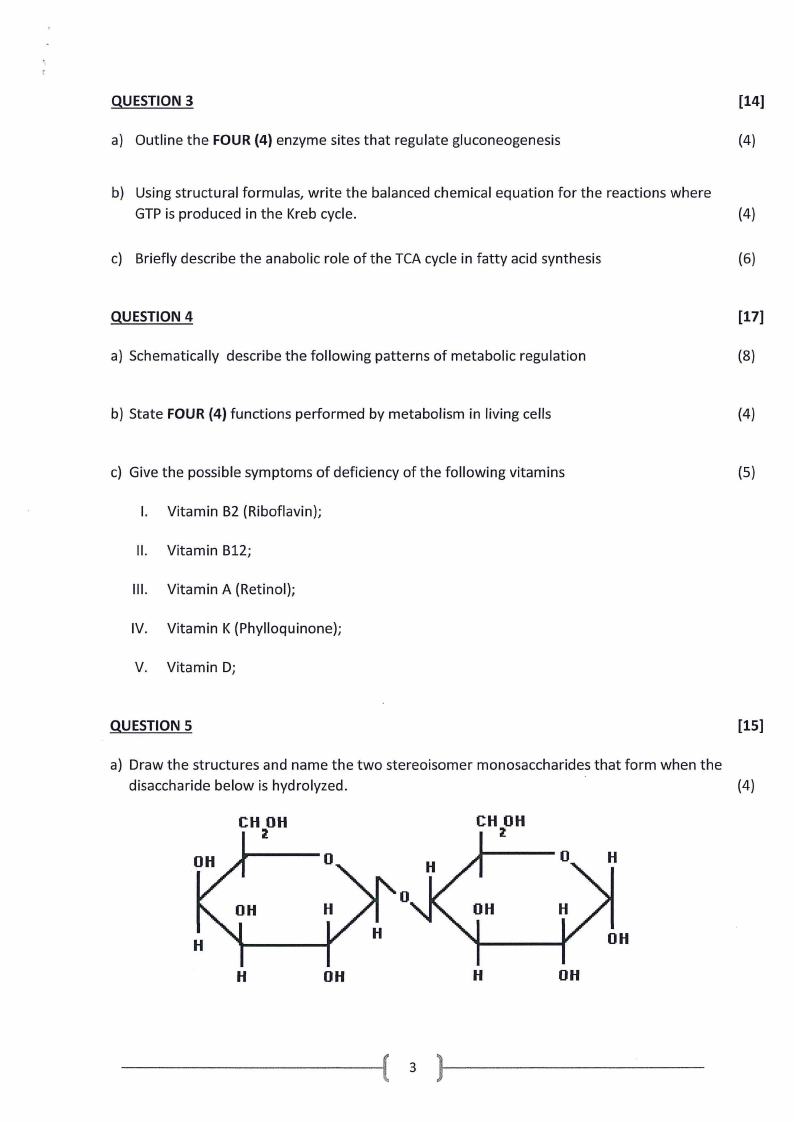
a) Draw the structures and name the two stereoisomer monosaccharides that form when the
disaccharide below is hydrolyzed.
(4)
CH OH
2
CH OH
2
0
H
OH
H
OH
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

b) Give a detailed description of how a DNA molecule is translated into a protein
(5)
c) Describe the following techniques used for the separation and purification of amino acids
and proteins
(6)
I. Affinity Chromatography;
II. Size Exclusion Chromatography;
Ill. Gel Electrophoresis;
QUESTION 6
[17]
a) Inositol triphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG) are all small molecules that can be found
inside most cells, yet they are known to be important second messengers that can increase or
decrease in response to a wide variety of signals. However, each signal often produces completely
different responses. Describe how such responses are regulated following GPCRsignalling. (5)
b) Lipids are known to be insoluble in water, briefly elucidate on how dietary lipid are digested,
absorbed and transported in the body.
(4)
c) With the aid of the fatty acyl CoA structure below, discuss the production of energy
(ATP) through the process of r-oxidation (breakdown) of fatty acids.
(8)
0u
CH3- (CH2>.r-CH2- Ct½-C-S-CoA
Fatty acyt CoA
QUESTION 7
[12]
a) Based on ADME properties, why is drug development a challenging task?
(4)
b) Describe the two pathways utilized by the body for the excretion of compounds once they have
entered the bloodstream
(4)
c) Discuss how cholera toxin disrupts the regulation of intestinal secretion following GPCR
signalling.
(4)
THE END
4





