 |
TEC711S - TRANSPORT ECONOMICS - 2ND OPP - JAN 2020 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |
NAMIBIA UNIVERSITY
OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
FACULTY OF MANAGEMENT SCIENCES
DEPARTMENT OF ACCOUNTING, ECONOMICS AND FINANCE
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF ECONOMICS
QUALIFICATION CODE: 12BECO
LEVEL: 7
COURSE CODE: TEC711S/TEC411S
COURSE NAME: TRANSPORT ECONOMICS
SESSION: JANUARY 2020
DURATION: 3 HOURS
PAPER: THEORY
MARKS: 100
SUPPLEMENTARY/ SECOND OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER(S)
EDEN TATE SHIPANGA
MODERATOR:
ANTHONY ADEYANJU
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALL the questions.
2. Write clearly and neatly.
3. Number the answers clearly.
PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS
1. PEN,
PENCIL
3. CALCULATOR
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF 2 PAGES (Including this front page)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |
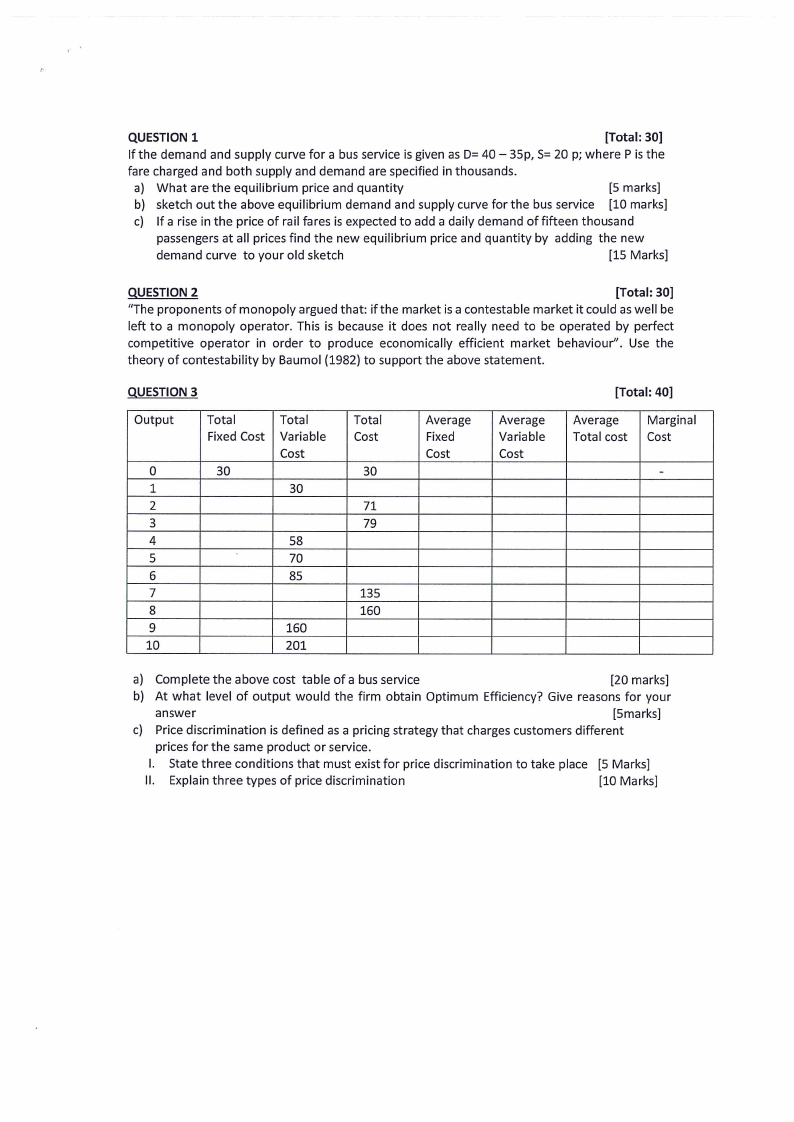
QUESTION 1
[Total: 30]
If the demand and supply curve for a bus service is given as D= 40 — 35p, S= 20 p; where P is the
fare charged and both supply and demand are specified in thousands.
a) What are the equilibrium price and quantity
[5 marks]
b) sketch out the above equilibrium demand and supply curve for the bus service [10 marks]
c) Ifarise in the price of rail fares is expected to add a daily demand of fifteen thousand
passengers at all prices find the new equilibrium price and quantity by adding the new
demand curve to your old sketch
[15 Marks]
QUESTION 2
[Total: 30]
“The proponents of monopoly argued that: if the market is a contestable market it could as well be
left to a monopoly operator. This is because it does not really need to be operated by perfect
competitive operator in order to produce economically efficient market behaviour”. Use the
theory of contestability by Baumol (1982) to support the above statement.
QUESTION 3
Output
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Total
Total
Fixed Cost | Variable
Cost
30
30
58
70
85
160
201
Total
Cost
30
71
79
135
160
Average
Fixed
Cost
Average
Variable
Cost
[Total: 40]
Average
Marginal
Total cost | Cost
=
a) Complete the above cost table of a bus service
[20 marks]
b) At what level of output would the firm obtain Optimum Efficiency? Give reasons for your
answer
[Smarks]
c) Price discrimination is defined as a pricing strategy that charges customers different
prices for the same product or service.
I. State three conditions that must exist for price discrimination to take place [5 Marks]
ll. Explain three types of price discrimination
[10 Marks]





