 |
BPP521S - BASIC PATHOPHYSIOLOGY - 2ND OPP - JANUARY 20225 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAm I BIA UnlVERSITY
OF SCIEnCE AnDTECHnOLOGY
FacultyofHealthN, atural
ResourceasndApplied
Sciences
Schoolof HealthSciences
Departmentof Preventative
HealthSciences
13JacksonKaujeuaStreet
Private Bag13388
Windhoek
NAMIBIA
T: +264612072970
F: +264612079970
E: dphs@nust.na
W: www.nust.na
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN HEALTH INFORMATION SYSTEMS MANAGEMENT
QUALIFICATIONCODE: 07BSHM
COURSE: BASIC PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
LEVEL: 5
COURSECODE:BPP521S
DATE: JANUARY 2025
SESSION: 1
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 100
SECOND OPPORTUNITY/SUPPLEMENTARY: EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER:
MODERATOR:
DR ROSWITHAMAHALIE
MS ELIZABETHNDAKUKAMO-KASINO
INSTRUCTIONS:
1. Answer all questions on the separate answer sheet.
2. Please write neatly and legibly.
3. Do not use the left side margin ofthe exam paper. This must be allowed for the examiner.
4. No books, notes and other additional aids are allowed.
5. Mark all answers clearly with their respective question numbers.
PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS:
1. Non-programmable scientific calculator
ATTACHMENTS
1. None
This question paper consists of 5 pages including this front page.
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

SECTION A: TRUE AND FALSE, FILL IN THE BLANKS AND MATCHING
[ 50 MARKS]
QUESTION 1: TRUE AND FALSE
{20 MARKS)
1.1 Assess the following statements and indicate whether they are True or False. Write your
answer next to each number in your ANSWERSHEETe.g. 1.1.1: True. Each question carries
one (1) mark.
1.1.1 The type of necrosis seen in a myocardial infraction is caseous necrosis.
1.1.2 Autophagy is a process in which a cell eats its own contents.
1.1.3 Monoplegia is a type of paralysis that affects only one limb or one part of the body.
1.1.4 Encephalitis: an acute inflammation of the brain parenchyma, caused by viruses
and bacteria only.
1.1.5 Diastolic blood pressure, refers to the higher number is the pressure exerted by blood
when ejected from the left ventricle.
1.1.6 Cyanosis is referred to as the bluish coloration ofthe skin and mucosa caused by
increased haemoglobin in arterial blood.
1.1.7 Development of whitish reddish appearance in pupil of the eye are part of
Cancer's Warning Signs in Children.
1.1.8 The Universal precautions for control of infections is stipulated in the Blood borne
Pathogens Standard 39 CFR1910.1030(b) definitions.
1.1.9 Guillain-Barre syndrome Alzheimer disease refers to an excessive neuronal
degeneration in adulthood.
1.1.10 Increased movement of antibody proteins out of the blood stream is called
tra nscytos is.
1.1.11 Bipolar disorder is characterized mood alternates between phases of intense
excitement and depression.
1.1.12 Increased lntracranial Pressure (ICP) is the pressure exerted by the contents
of the cranium, and it normally ranges from Oto 50 mm Hg.
1.1.13 The clinical manifestation of Congestive heart failure is neck vein distention
and restlessness.
1.1.14 An example of a bacilli or rod-shaped bacteria is Trepnonema pallidum.
1.1.15 The pineal gland produces calcitonin.
1.1.16 Vasopressin causes milk ejection and contraction of the uterus in labour.
1.1.17 Osteopetrosis, also known as marble bone disease, refers to a group of rare
genetic diseases that are characterized by reduced bone resorption and diffuse
symmetric skeletal sclerosis resulting from impaired formation or function
of osteomyelitis.
1.1.18 Ectrodactyly is a rare condition in which the middle three toes are absent and the
two outer ones are turned in (split hand/foot malformation (SHFM) type 1).
1.1.19 Hearing depends on the ear, the cochlear nerve, and the auditory areas of the
cerebral cortex.
1.1.20 Hertz usually measures loudness of sound.
Basic Pathophysiology
2nd Opportunity January 2025
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 2: FILL IN THE BLANKS
(15 MARKS)
2.0 Fill the missing words in the statements below. Each answer earns one (1) mark.
(15)
2.1 ______
is an infection affecting the renal tubules, pelvis, and calices.
2.2 ______
is when the roof of the mouth develops in two separate halves
(before birth).
2.3 ______
are disorders are found in children, especially when there is an
interference with the deposition of bone in the growth plates.
2.4 ______
is farsightedness that develops if the eyeball and the image is
focussed behind the retina.
2.5 -----~
is an infection of the larynx with accompanying hoarseness, leading
to the inability to talk in an audible voice.
2.6 ______
syndrome is caused by inflammatory lesions of glomeruli.
2.7 ______
are reddish-brown insect 3 to 6 mm long that turn purple after
feeding.
2.8 ______
fractures are when the bone is damaged with little or no soft tissue
damage.
2.9 ______
is a sudden, violent, involuntary muscle contraction of a large group
of muscles.
2.10 ______
refers to diseased endocrine gland secretes an abnormally high
amount of its hormone resulting in excessive negative feedback.
2.11 ______
presents when the urethra opens on the dorsal aspect of the
penis at a point proximal to the glans.
2.12 ______
means ultrasound of the heart.
2.13 ______
is an increased in the frequency and fluidity of bowel
movements.
2.14 ______
refers to the swelling and infection of the peritoneum which is
the lining that covers the abdominal viscera.
2.15 ______
are interoceptors that monitor the pH of the blood.
QUESTION 3 MATCHING QUESTIONS
(15 MARKS)
3.1 Match the appropriate answer from Column A with a meaning in Column B. Write the
appropriate letter next to the corresponding number on your ANSWER SHEET,
e.g., 3.1.1 A. Each question earns 1 mark.
Nr
3.1.1
3.1.2
3.1.3
Item A
Fomites
Inspiration
Chondromas
Vitamin K
Item B
A.
Bleeding diathesis
B.
Is a malignant mesenchymal tumour
with skeletal muscle differentiation.
C.
Inability to empty the bladder.
D.
Any inanimate object capable of being
an intermediate in the indirect
transmission of an infectious agent.
Basic Pathophysiology
2nd Opportunity January 2025
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |
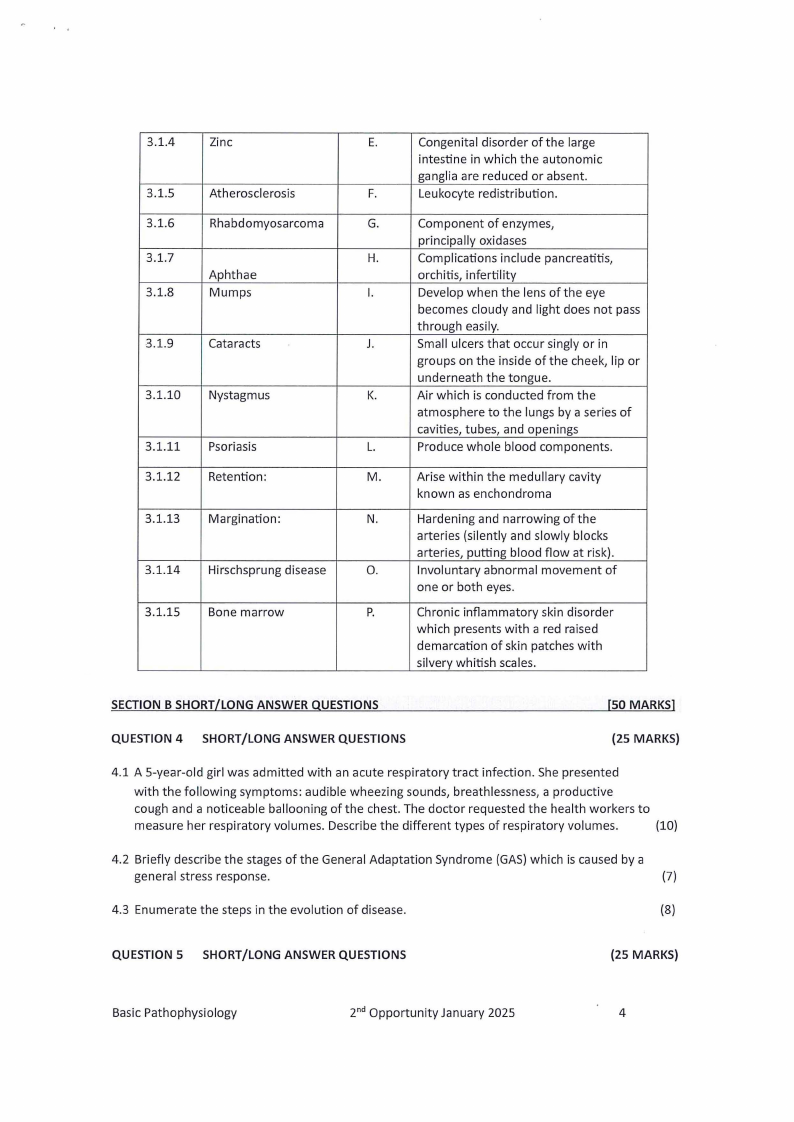
3.1.4
Zinc
3.1.5
3.1.6
3.1.7
3.1.8
Atherosclerosis
Rhabdomyosarcoma
Aphthae
Mumps
3.1.9
Cataracts
3.1.10
Nystagmus
3.1.11
3.1.12
Psoriasis
Retention:
3.1.13
Margination:
3.1.14
Hirschsprung disease
3.1.15
Bone marrow
E.
Congenital disorder of the large
intestine in which the autonomic
ganglia are reduced or absent.
F.
Leukocyte redistribution.
G.
Component of enzymes,
principally oxidases
H.
Complications include pancreatitis,
orchitis, infertility
I.
Develop when the lens of the eye
becomes cloudy and light does not pass
through easily.
J.
Small ulcers that occur singly or in
groups on the inside of the cheek, lip or
underneath the tongue.
K.
Air which is conducted from the
atmosphere to the lungs by a series of
cavities, tubes, and openings
L.
Produce whole blood components.
M.
Arise within the medullary cavity
known as enchondroma
N.
Hardening and narrowing of the
arteries (silently and slowly blocks
arteries, putting blood flow at risk).
0.
Involuntary abnormal movement of
one or both eyes.
P.
Chronic inflammatory skin disorder
which presents with a red raised
demarcation of skin patches with
silvery whitish scales.
SECTION B SHORT/LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
[50 MARKS]
QUESTION 4 SHORT/LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
{25 MARKS)
4.1 A 5-year-old girl was admitted with an acute respiratory tract infection. She presented
with the following symptoms: audible wheezing sounds, breathlessness, a productive
cough and a noticeable ballooning of the chest. The doctor requested the health workers to
measure her respiratory volumes. Describe the different types of respiratory volumes.
(10)
4.2 Briefly describe the stages of the General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS) which is caused by a
general stress response.
(7)
4.3 Enumerate the steps in the evolution of disease.
(8)
QUESTION 5 SHORT/LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
(25 MARKS)
Basic Pathophysiology
2nd Opportunity January 2025
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

5.1 Disease develops when cell structure and function change. Describe any four (4) types
of cellular adaptation.
(8)
5.2 Read the scenario below and respond to the questions that follow:
Mrs. Kamati, a 30-year-old mother of 2 children, was caught in a fire in her corrugated
house whilst they were all asleep. The whole family was rescued from the house but
she had mixed burns to most areas of her body except for her face. It was determined
by the paramedics that she had full-thickness burns. Mrs Kamati's five-year old girl also
sustained several burn wounds:
5.2.1 Explain to a group of grade 12 learners what measurement you will use to
determine the percentage of burn wounds sustained by Mrs Kamati's five-year
old girl.
(2)
5.2.2 Describe the term full-thickness burns
(7)
5.2.3 Using the rules-of-nines, calculate the approximate area offull-thickness
burns on her both legs, chest and left arm.
(8)
END OF EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
Basic Pathophysiology
2nd Opportunity January 2025
5





