 |
MMB621S - MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY 2B - 1ST OPP -NOVEMBER 2024 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAml Bl A un1VERS ITY
OF SCIEnCE AnDTECHnOLOGY
Faculty of Health, Natural
Resources and Applied
Sciences
School of Health Sciences
Department of Clinical
Health Sciences
13 Jackson Kaujeua Street
Private Bag 13388
Windhoek
NAMIBIA
T: +264 61 207 2970
F: +264 61 207 9970
E: dchs@nust.na
W: www.nust.na
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR of MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCES
QUALIFICATION CODE: 08BMLS
LEVEL: 6
COURSE:MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY 28
COURSECODE: MMB621S
DATE: NOVEMBER 2024
SESSION: 1
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 105
FIRST OPPORTUNITY: EXAMINATION PAPER
EXAMINER:
MODERATOR:
MRS FREDRIKAENGELBRECHT
MS VANESSATl/JENDA
INSTRUCTIONS:
1. Answer all questions on the separate answer sheet.
2. Please write neatly and legibly.
3. Do not use the left side margin of the exam paper. This must be allowed for the
examiner.
4. No books, notes and other additional aids are allowed.
5. Mark all answers clearly with their respective question numbers.
PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS:
1. Non-Programmable Calculator
ATTACHEMENTS
1. NONE
This paper consists of 7 pages including this front page
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

1SECTIONA: MULTIPLECHOICEAN·oTRUE/ FALSE
[28 MARKS]
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE CHOICEQUESTIONS
[20 MARKS]
1.1 Corynebacterium diphtheria is known as:
A) a motile, spore forming gram positive bacilli.
B) a non-motile, non-spore forming gram positive bacilli.
C) a motile, spore forming gram negative bacilli.
D) a non-motile, non-spore forming gram positive cocci.
(1)
1.2 For primary syphillus to occur you need:
A) > 10 Treponema pallidum spirochaetes to be introduced in the body.
B) < 10 Treponema pallidum spirochaetes to be introduced in the body.
C) 50 - 100 Treponema pallidum spirochaetes to be introduced in the
body.
D) > 100 Treponema pallidum spirochaetes to be introduced in the body. (1)
1.3 The following organism ferment lactose when grown on MacConkey agar
A) Neisseria meningitidis.
B) Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
C) Klebsiella pneumoniae.
D) Acinetobacter baumanii.
(1)
1.4 Most common pathogen(s) associated with intravenous catheter infections
include:
A) 5. epidermidis.
B) 5. aureus.
C) Corynebacterium spp.
D) 5. saphrophyticus.
(1)
1.5 Identify the organism that is motile at 22°C and not motile at 37°C.
A) Clostridium perfringens.
B) Yersinia enterocolitica.
C) Salmonella paratyphi.
D) Stenotrophomonas maltophilia.
(1)
1.6 The reverse CAMP test can be used for the identification of:
A) Bacillus cereus.
B) Bacillus subtilis.
C) Clostridium tetani.
D) Clostridium perfringens.
(1)
1.7 Pus containing yellow sulphur granules is associated with:
A) Actinomycosis israeli.
B) Listeria monocytogenes infection.
C) Burkholderia cepcia infection.
D) Chlamydia trachomatis infection.
Medical Microbiology 2B (MMB621S) 1st Opportunity Examination Paper
2
(1)
November 2024
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

l.8 Rickettsia conori is the causative organism of:
A)
Brill-Zinsser disease.
B) Boutonneusefeve~
C) Epidemic typhus.
D) Rocky Mountain spotted fever.
(1)
1.9 Which of the following drugs form part of the 2nd generation cephalosporins:
A) Cefoxitin & cefaclor.
B) Cephalothin & cefazolin.
C) Amikacin, & streptomycin.
D) Ceftriaxone & cefotaxime.
(1)
1.10 You received a blood culture for a possible Brucellossis. How long should this
blood culture be incubated in an automated blood culture machine before it can
be called negative?
A) 48 hours.
B) 14 days.
C) 96 hours.
D) 21 days.
(1)
1.11 Pyrogenic exotoxins
A)
Facilitate the spread of the organisms.
B) It stimulates the release of lysosomal enzymes
C) Is responsible for the haemolysis of red blood cells.
D) Enhances delayed hypersensitivity reactions.
(1)
1.12 The PorB/Protein I of Neisseria species:
A) is the major porin protein and assists the organism to penetrate the
columnar epithelial cells of the host in order to cause an infection.
B) is the protein that is present in the outer membrane of the Neisseria and
promotes adherence of the gonococcus to the host cells.
C) blocks the antibodies that have been produced against the Neisseria
species.
D) is the protein which inhibits the phagocytes of the organism by host cells.
(1)
1.13 The causative agent of whooping cough is:
A) Bruce/la melitensis.
B) Dipthteria species.
C) Bordatel/a pertussis.
D) Klebsiella pneumoniae.
(1)
1.14 The most common organism responsible for gas gangrene is known to be:
A)
an anaerobic spore forming gram positive bacilli.
B)
an aerobic spore forming gram positive bacilli.
C) an anaerobic gram negative bacilli.
D)
an aerobic gram negative bacilli.
(1)
Medical Microbiology 2B (MMB621S) 1°1Opportunity Examination Paper
3
November 2024
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

1.15 Protein A of 5. aureus:
A) hydrolyses hyaluronic acid in the matrix of connective
tissue.
B) breaks down lipids & enables the organisms to invade the
cutaneous tissues.
C) inhibits opsonisation and phagocytosis.
D) destroys erythrocytes & causes skin destruction.
(1)
1.16
Patients infected with enterotoxigenic serotypes of E.coli usually presents with:
A) presence of mucous and blood in faeces samples.
B) watery diarrhoea with little or no fever.
C) watery, bloody diarrhoea.
D) infantile enteritis.
(1)
1.17
The Aminoglycoside mechanism of action is:
A) Inactivation of enzymes.
B) Drug efflux.
C) Inhibition of cell wall synthesis.
D) Inhibition of protein synthesis.
(1)
1.18
The cytokines released during an infection with 5. typhi results in:
A) Leucocytosis.
B) Inflammatory reaction in the Peyer's patches.
C) Spread of the organism to the mesenteric lymph nodes.
D) Bacteraemia.
(1)
1.19 Virulence factors found in 5. pneumoniae that damages host cells are:
A) the pneumolysins.
B) the polysaccharide capsules.
C) neuramidases.
D) autolysins.
(1)
1.20
Antibiotic synergy can be defined as:
A) the presence of plasmid-mediated resistance for one mechanism results in
resistance to numerous drugs.
B) the same resistance mechanism affecting several antibiotics.
C) the interaction between drugs with each drug counteracting the
other.
D) the utilisation of a combined effect of antibiotic for therapeutic success. (1)
Medical Microbiology 2B (MMB621 S) 1st Opportunity Examination Paper
4
November 2024
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 2: TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS
[8 MARKS]
Evaluate the statements and select whether the statement is true or false. Write the word
'True' or 'False' next to the corresponding number on your ANSWERBOOKand give a reason
for calling any statement FALSE.One mark allocated to calling a statement TRUE or FALSE,
and one mark allocated to the REASON for calling a statement FALSE.
2.1 Transient bacteraemia is defined as the presence of bacteria in the blood over several
hours/days.
2.2 Severe Q fever may result in chronic febrile disease, granulomatous liver disease or
chronic infection of the heart valves.
2.3 Campylobacter species are one of the organisms associated with infections caused
by contaminated food products.
2.4 Streptolysin Sis molecules that induce proliferation of host T-lymphocytes.
2.5 Streptococcus pyogenes possess Lancefield Group C antigens on their surface.
B: SECTION SHORT/LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
.
Please answer ALL of the questions in this section.
[77 MARKS],
QUESTION 3:
[14 MARKS]
3.1 Match the organism with the test used to identify the organism. ONLYwrite the
number of the question with the matching letter in your answer book.
3.1.1 C. diphtheria
A) CAMP test
3.1.2 H. influenza
B) Elek test
3.1.3 S. aga/actiae
C) Optochin sensitivity
3.1.4 5. pneumoniae
D) Satellitism test
(4)
3.2 Categorize the following antibiotics according to its bacterial targets:
3.2.1 Vancomycin
(1)
3.2.2 Cephalosporin
(1)
3.2.3 Tetracyclines
(1)
3.2.3 Quinolones
(1)
3.3 Compare the expected results of 8. anthracis, 8. cereus and 8. subtilis for motility,
catalase, lecithinase production and fermentation of mannitol, using a table.
(12x½=6)
Medical Microbiology 2B (MMB621S) 1st Opportunity Examination Paper
5
November 2024
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |
QUESTION 4
[10 MARKS]
4.1 Discuss how a scientist can distinguish E.coli 0157:H7 from the other E.coli
species in the diagnostic laboratory.
(5)
4.2 A 4-year-old boy presented with a one-week history of general malaise, mild
fever, indolence, and anorexia. He subsequently developed dysphagia,
difficulties opening the mouth and eventually dehydration. Due to parental
concerns about the boy's refusal of fluids, a paediatrician was consulted. At that
time of presentation, he showed signs of trismus and muscle rigidity. Together
with the lack of immunization and a toenail infection, the doctor suspected
generalised tetanus.
4.2.1 Identify the causative pathogen of generalised tetanus.
(2)
4.2.2 Illustrate, using a drawing the gram stain morphology and gram reaction
you expect to see for this organism.
(3)
QUESTION 5
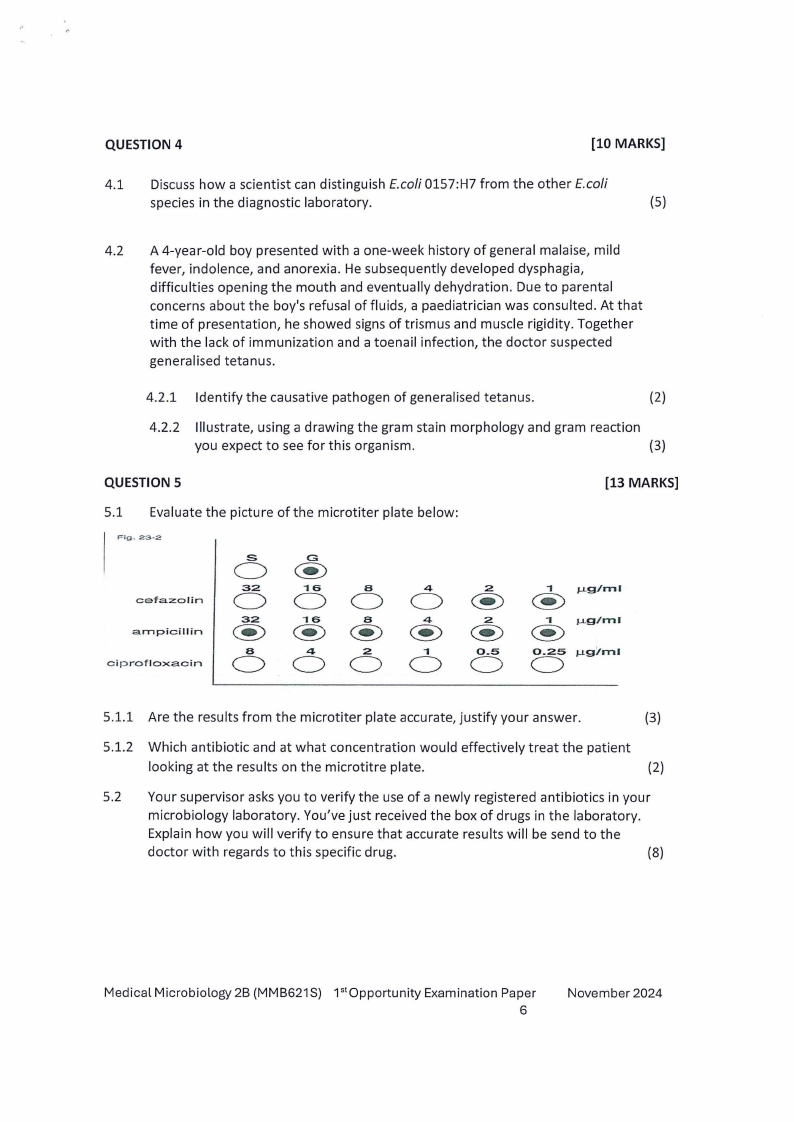
5.1 Evaluate the picture of the microtiter plate below:
Fig. 23-2
I
cefazolin
ampicillin
ciprofloxacin
s
G
C)
32
"16
a
4
2
C) C) C) C)
32
"16
a
4
2
8
4
2
...
0.5
C) C) C) C) C)
[13 MARKS]
... µg/ml
@)
... µg/ml
@)
0.25
µg/ml
C)
5.1.1 Are the results from the microtiter plate accurate, justify your answer.
(3)
5.1.2 Which antibiotic and at what concentration would effectively treat the patient
looking at the results on the microtitre plate.
(2)
5.2 Your supervisor asks you to verify the use of a newly registered antibiotics in your
microbiology laboratory. You've just received the box of drugs in the laboratory.
Explain how you will verify to ensure that accurate results will be send to the
doctor with regards to this specific drug.
(8)
Medical Microbiology 2B (MMB621S) 1st Opportunity Examination Paper
6
November 2024
 |
7 Page 7 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 6
[20]
6.1 A pregnant woman presented with a vaginal discharge but with no further symptoms of
infection. Her doctor collected a vaginal swab and submitted it to the diagnostic
medical microbiology laboratory for analysis. Study the slides below, presenting the
laboratory findings and then answer questions 6.1.1- 6.1.6, based on the case study.
A)· Gram stain result from the vaginal swab:
;
I
B) The culture from the vaginal swab
on a blood agar after incubation:
I '·
C) Catalase test result:
D) Additional test that were preformed:
6.1.1 Report your findings on the gram-stained slide, presented in slide A.
(3)
6.1.2 Report your findings of the growth seen on slide B.
(2)
6.1.3 Report the catalase results from the test presented in slide C.
(1)
6.1.4 Identify the reagent used for the catalase test.
(2)
6.1.5 Discuss the principle of the catalase test.
(4)
6.1.6 Name the tests that were done in slide D, and by using a labelled
illustration of the test, explain the principle of the test.
QUESTION 7
7.1 Design a flow chart for the identification of gram-positive cocci.
(8)
[20]
(20)
END OF QUESTION PAPERi;.::-~...,.c,-,,......,-,.,,,,,,.,...,,--=,,..,,......
. ..
,_c.;-.::,;.....:i: ..... ,.... ~l,;-..,~---.......-•.---
-i..;-~-~~~,
Medical Microbiology 2B (MMB621 S) 1st Opportunity Examination Paper
2024
7
November
..,:.





