 |
ORC711S - Operations Research - 1st Opp - June 2023 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAm I BIA unlVERSITY
OF SCIEnCE AnD TECHn OLOGY
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND THE BUILT ENVIRONMENT
DEPARTMENTOF Civil, Mining and Process Engineering
QUALIFICATION : Bachelors of Engineering in Mining Engineering
QUALIFICATION CODE: 08BMEG
LEVEL: 7
COURSECODE: ORC711S
COURSENAME: OPERATIONSRESEARCH
SESSION: JUNE 2023
DURATION: 3 HOURS
PAPER: THEORY
MARKS: 100
EXAMINER(S)
MODERATOR:
SECONDOPPORTUNITYQUESTION PAPER
Dr Lawrence Madziwa
Prof Mallikarjun Rao Pillalamarry
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer all questions.
2. Read all the questions carefully before answering.
3. Marks for each questions are indicated at the end of each question.
4. Please ensure that your writing is legible, neat and presentable.
PERMISSIBLEMATERIALS
1. Examination paper.
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF 7 PAGES (Including this front page)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |
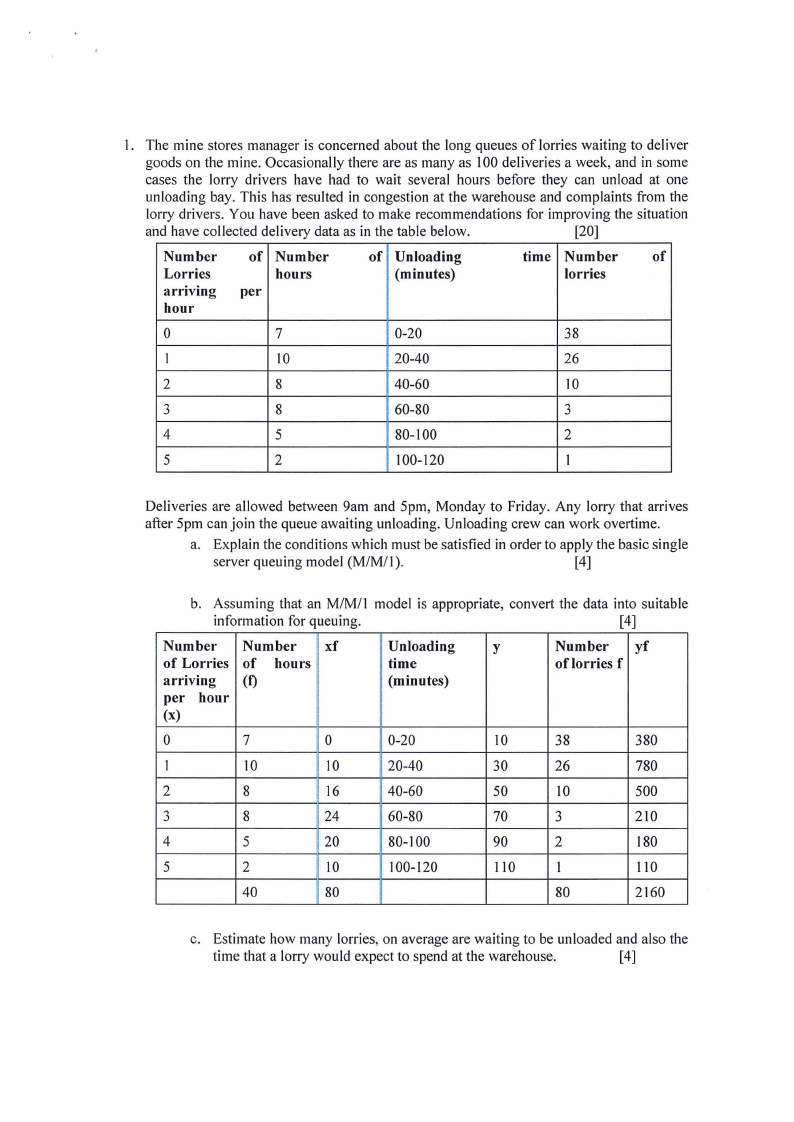
I. The mine stores manager is concerned about the long queues of lorries waiting to deliver
goods on the mine. Occasionally there are as many as I 00 deliveries a week, and in some
cases the lorry drivers have had to wait several hours before they can unload at one
unloading bay. This has resulted in congestion at the warehouse and complaints from the
lorry drivers. You have been asked to make recommendations for improving the situation
and have collected delivery data as in the table below.
[20]
Number
Lorries
arriving
hour
of Number
hours
per
of Unloading
(minutes)
time Number
of
lorries
0
7
0-20
38
I
10
20-40
26
2
8
40-60
10
3
8
60-80
3
4
5
80-100
2
5
2
100-120
I
Deliveries are allowed between 9am and 5pm, Monday to Friday. Any lorry that arrives
after 5pm can join the queue awaiting unloading. Unloading crew can work overtime.
a. Explain the conditions which must be satisfied in order to apply the basic single
server queuing model (M/M/1).
[4]
b. Assuming that an M/M/1 model is appropriate, convert the data into suitable
information for queuing.
[4]
Number Number xf
of Lorries of hours
arriving (t)
per hour
(x)
Unloading
y
time
(minutes)
Number yf
of lorries f
0
7
0
0-20
10
38
380
I
10
10
20-40
30
26
780
2
8
16
40-60
50
10
500
3
8
24
60-80
70
3
210
4
5
20
80-100
90
2
180
5
2
10
100-120
110
l
110
40
80
80
2160
c. Estimate how many lorries, on average are waiting to be unloaded and also the
time that a lorry would expect to spend at the warehouse.
[4]
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |
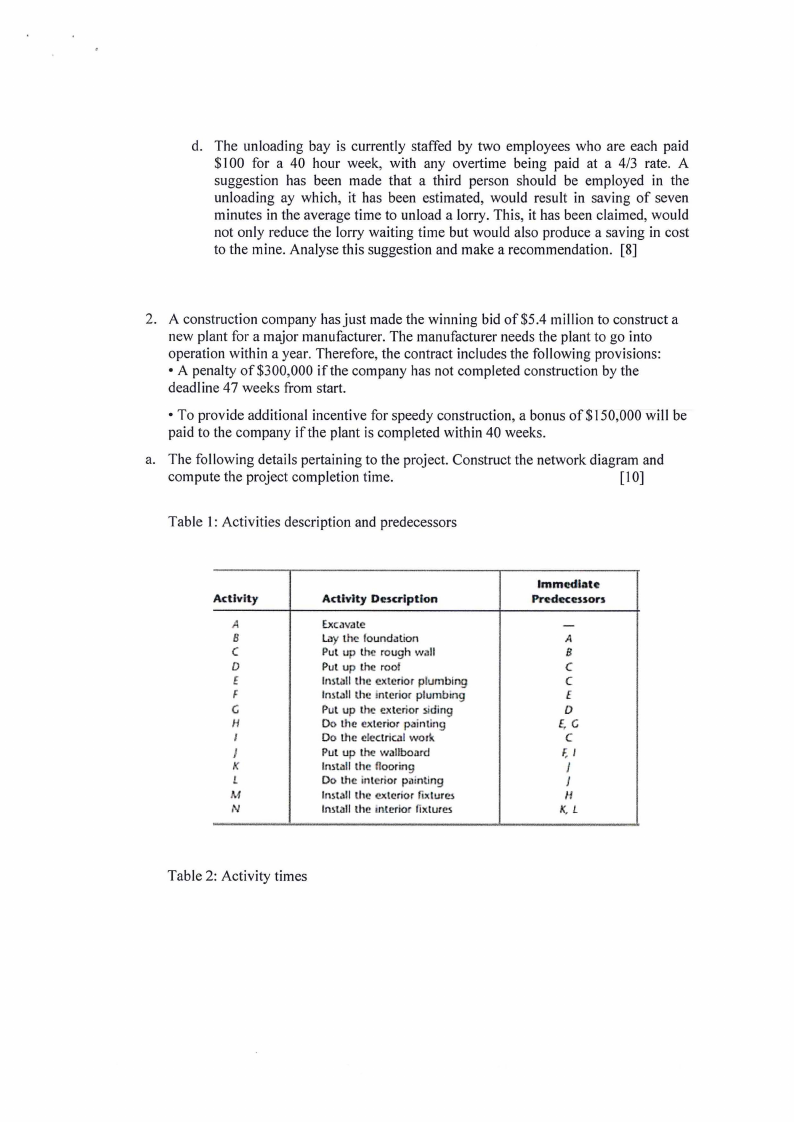
d. The unloading bay is currently staffed by two employees who are each paid
$100 for a 40 hour week, with any overtime being paid at a 4/3 rate. A
suggestion has been made that a third person should be employed in the
unloading ay which, it has been estimated, would result in saving of seven
minutes in the average time to unload a lorry. This, it has been claimed, would
not only reduce the lorry waiting time but would also produce a saving in cost
to the mine. Analyse this suggestion and make a recommendation. [8]
2. A construction company has just made the winning bid of $5.4 million to construct a
new plant for a major manufacturer. The manufacturer needs the plant to go into
operation within a year. Therefore, the contract includes the following provisions:
• A penalty of $300,000 if the company has not completed construction by the
deadline 47 weeks from start.
• To provide additional incentive for speedy construction, a bonus of $150,000 will be
paid to the company if the plant is completed within 40 weeks.
a. The following details pertaining to the project. Construct the network diagram and
compute the project completion time.
[ 10]
Table 1: Activities description and predecessors
AcUvlty
A
B
C
D
t
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
Activity Description
E.xc.:ivate
L'ly the foundntion
Pul up th rough willl
Put up the roof
IIHUlllthe cxtcr or plumbing
lrulllll thl! interior plumbing
Pul up the e,,cterior .siding
Do the exterior pciintlng
Do th<?electrical work
Put up the wallboa.rd
!mt.ill the flooring
Do the intimor pilintlng
IIHtall the cxterlor fllCtur~
!rut.all the mtcrlor fixtures
lmmC?dlate
Pr~CCC!SSOrs
-
A
8
C
C
E
D
E, C
C
F, l
J
1
H
K, L
Table 2: Activity times
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |
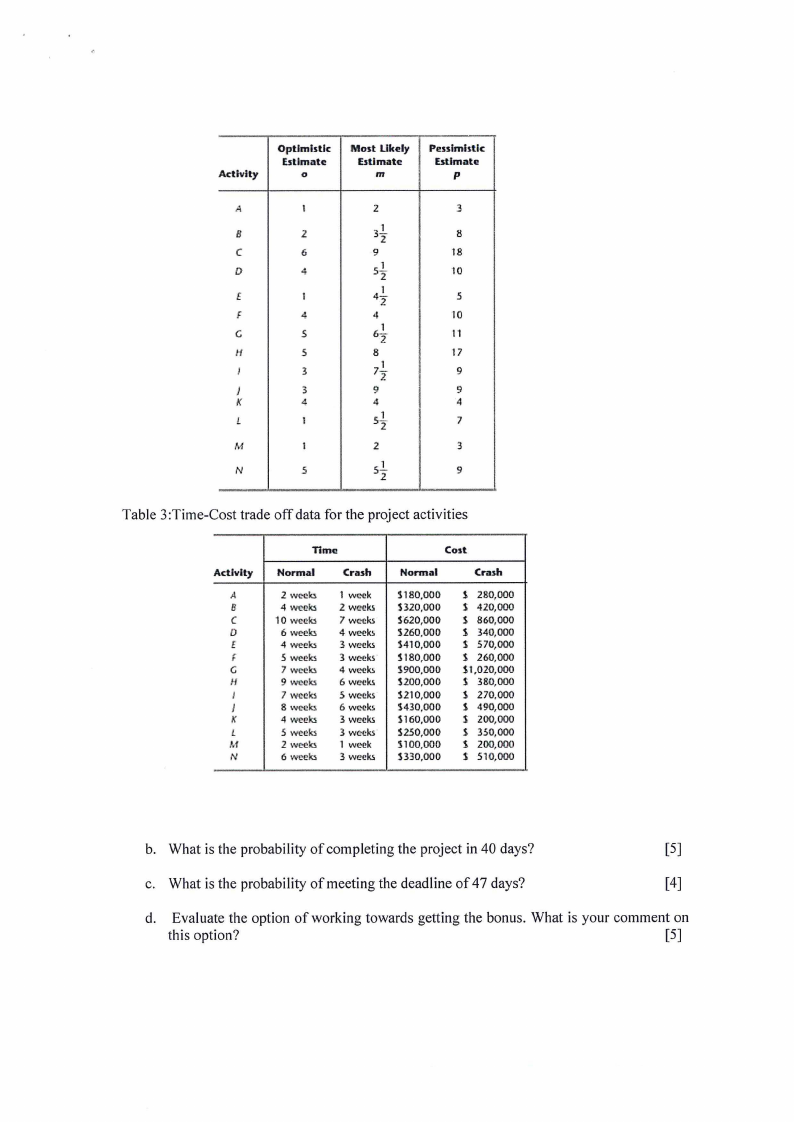
Activity
Optimistic
Estimate
0
Most Likely
Estimate
m
Pessimistic
Estimate
p
A
I
8
2
C
6
D
4
f
I
f
4
G
5
H
5
I
3
J
3
K
4
L
I
M
I
N
5
2
3
3l
2
8
9
18
sl
2
10
4..!..
2
5
4
-io
6..!..
2
11
8
17
7..!..
2
9
9
9
4
4
sl2
7
2
3
sl
2
9
Table 3 :Time-Cost trade off data for the project activities
Activity
A
8
C
D
E
f
G
H
I
J
I<
L
M
N
Time
Cost
Normal
Crash
Normal
Crash
2 weeks
4 weeks
10 Wet!k5
6 wet:?!c.
4 weeks
5 week5
7 weeks
9 weeks
7 weeks
8 weeks
4 weeks
5 weeks
2 weeks
6 weeks
1 W(c'ek
2 W!!i!ks
7 weeks
4 weC?k~
3 weeks
3 weeks·
4 W(c'C!ks
6 weeks
5 weeks
6 W<.'ek5
3 weeks
3 weeks·
1 week
3 weeks
5180,000
1320,000
S620,000
'!260,000
1410,000
S180,000
$900,000
U00,000
S210,000
'!430,000
S160,000
S250,000
Sl00,000
B30,000
$ 280,000
s 420,000
s 860,000
1 340,000
s 570,000
s 260,000
1·1,020,000
s 380,000
s 270.000
1 490,000
s 200,000
s 350,000
1 200,000
s 510,000
b. What is the probability of completing the project in 40 days?
[5]
c. What is the probability of meeting the deadline of 47 days?
[4]
d. Evaluate the option of working towards getting the bonus. What is your comment on
this option?
[5]
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |
3. You are responsible for transporting four items on a limited space of 10 tons from
Windhoek to Swakopmund. There are four different items that your company can
transport between Windhoek and Swakopmund. Each item has a weight in tons, a net
profit in thousands of dollars, and a total number of items that is available for
shipping as shown in Table below. Use dynamic programming to determine how
many of each item should be shipped to maximize profits.
[20]
Item
1
2
3
4
Weight
1
4
3
2
Profit/ Unit($)
3
9
8
5
Number Available
6
1
2
2
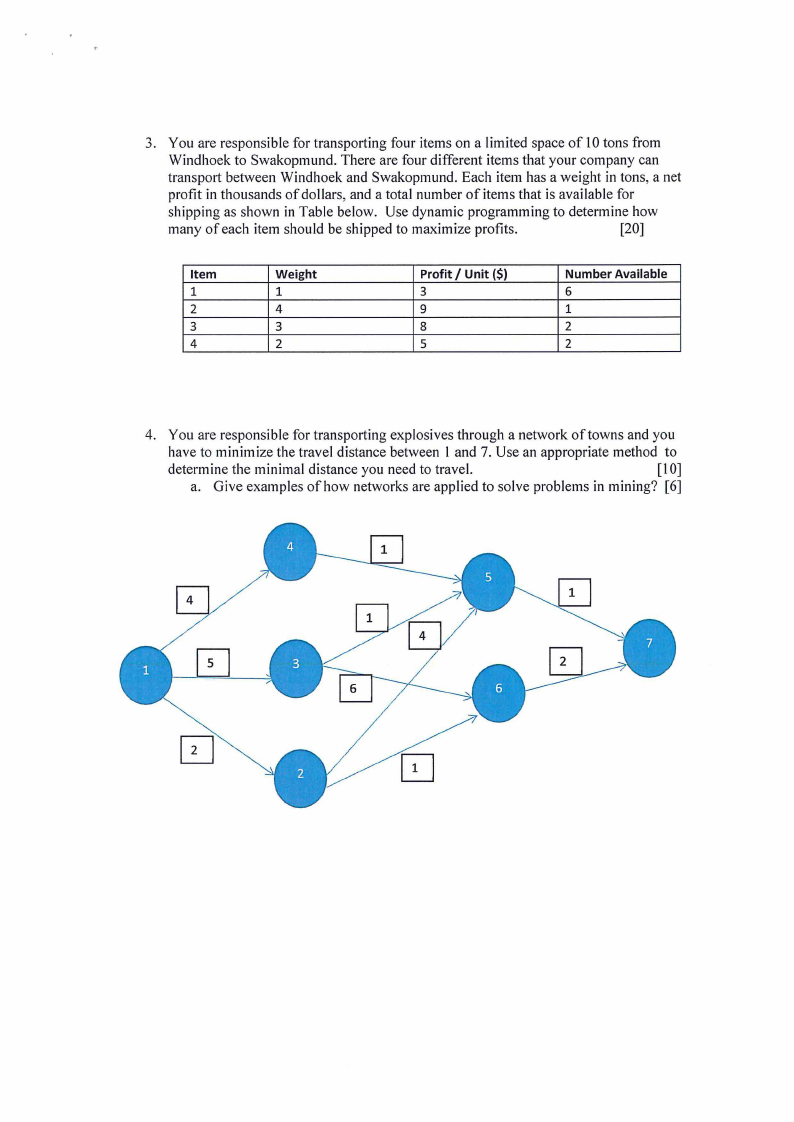
4. You are responsible for transporting explosives through a network of towns and you
have to minimize the travel distance between I and 7. Use an appropriate method to
determine the minimal distance you need to travel.
[IO]
a. Give examples of how networks are applied to solve problems in mining? [6]
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |

5. One representation of economic order quantity (EOQ) inventory model is;
Q = 2.j2CA/c
Where Q is the economic order quantity
C is the cost of placing an order
A is the annual demand in units
c is the cost of holding one unit in stock for one year
Data relevant to component K used at a mine in 22 different sections include;
• Purchase price: $15 per 100,
• Annual usage: 100,000 units ,
• Cost of buying office: fixed 15,575 per annum and variable is $12 per order,
• Rent of warehouse: $3,000 per annum,
• Heating: $700 per annum
• Interest: 25% per annum, insurance 0.05% per annum based on total purchases,
deterioration has been expressed as 1% per annum of all items purchased.
Questions:
a. Calculate the EOQ for component K.
[5]
b. Calculate the percentage change in total annual variable costs relating to component K
if the annual usage was: (i) 125,000 units, and (ii) 75,000 units.
[8]
c. Use the answers for question b above to comment on the sensitivity of the variable
costs to changes in the annual usage.
[4]
d. Describe two methods to help you modify your EOQ calculations if management
decided that the expected total investment in stocks was 30% too high. [3]
(End of Exam)
 |
7 Page 7 |
▲back to top |

.-l
p
= p S/i
().JI,) sA/l
Lq = (s - 1)! (Sfl - J.)
l
l
=
Lr1
+-}.
11
tq
Wq=T
w
W=~111t+-J1.l
~)s (A)k Po
p
=-----,-----;:-----1
[I;.f~ak1!
µ
]
+
1
s!
f\\µ
S/1
(S/l - A)
= ·(J./p. /l
Pn.
n!
P for n :5 ·
Q
(J/µ 11
Pn. - --I,---n,,--sp
0 for n > s





