 |
LAE621S- LABOUR ECONOMICS- 2ND OPP- NOV 2023 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAmlBIA UnlVERSITY
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECHnOLOGY
FACULTY OF COMMERCE, HUMAN SCIENCE AND EDUCATION
DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS, ACCOUNTING AND FINANCE
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF ECONOMICS
QUALIFICATION CODE:
07BECO
LEVEL: 7
COURSE CODE: LAE612S
COURSE NAME: LABOUR ECONOMICS
SESSION: NOVEMBER 2023
DURATION: 3 HOURS
PAPER:THEORY
MARKS: 100
SECOND OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER(S) MR. PINEHAS NANGULA
MODERATOR: MRS LAVINIA HOFNI
INSTRUCTIONS
I. Answer ALL the questions
2. Write clearly and neatly.
3. Number the answers clearly.
PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS
I. Scientific calculator
2. Pen and Pencil
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF _5_ PAGES (Including this front page)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION ONE
Multiple choice questions
[20MARKS]
1. Which of the following is NOT a unique characteristic of the labour market?
a) Employer only purchases the services of the workers by means of a contractual
relationship.
b) The worker's personality characteristics can't be fully determined by the employer
before employment starts.
c) The worker's personality characteristics change over time.
d) The worker's remuneration is affected by personal taxation and his or her standard of
living but is unaffected by inflation.
2. Which of the following group of people is NOT defined as part of the labour force?
a) Informal-sector employees
b) Self-employed
c) Unemployed
d) Full-time students
3. Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the slope of an indifference
curve?
I. An indifference curve is downward sloping.
II. For a person who places higher value on an additional hour of leisure, his or her
indifference curve is relatively flatter.
III. The slope of an indifference curve is also called the marginal rate of technical
substitution.
a) Only [I] is correct.
b) Only [II] is correct.
c) Only [III] is correct.
d) Only [I] and [III] are correct.
4. An increase in non-labour income due to a rise in interest earned from stocks and bonds
would cause
a) an income effect.
b) a substitution effect.
c) both an income effect and a substitution effect.
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

d) neither an income nor a substitution effect.
5. Ottilie's hourly wage increases from N$ l 00 to N$ l 50 per hour as a result of promotion.
Which of the following is INCORRECT?
a) Her utility increases.
b) She increases her hours of work, if the income effect is more dominant.
c) She increases her hours of work, if the substitution effect is more dominant.
d) She decreases her hours of work, if the income effect is more dominant.
6. The firm's labour demand curve in the short run
a) is upward sloping.
b) is the downward-sloping segment of the value of the marginal product curve.
c) is the downward-sloping segment of the marginal product of labour curve.
d) is vertical.
7. In the long run, the profit-maximising firm will select labour and capital so that
a) labour quantity equals capital quantity.
b) the wage per unit oflabour equals the rental cost of a unit of capital.
c) marginal product of labour equals marginal product of capital.
d) marginal product divided by wage per unit of labour equals marginal product of capital
divided by rental cost per unit of capital
8. Use the information from the following table to answer :
Firm A
Wage (W)
Rent (R)
Labour (E)
Output= 100
200
200
100
Output= 100
150
200
120
FirmB
Wage (W)
Rent (R)
Labour (E)
Output= 100
200
200
100
Output= 100
150
200
150
Capital (K)
150
120
Capital (K)
150
100
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
I. The elasticity of substitution of firm A equals 1.33.
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |
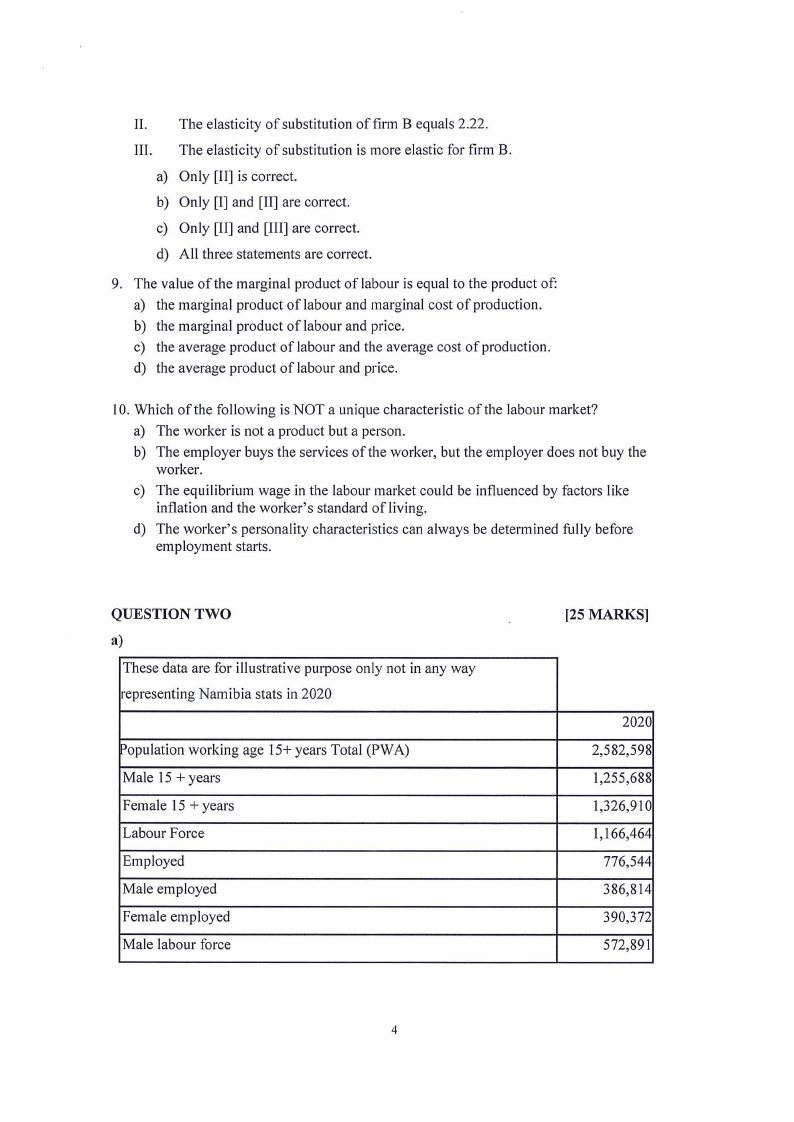
II. The elasticity of substitution of firm B equals 2.22.
III. The elasticity of substitution is more elastic for firm B.
a) Only [II] is correct.
b) Only [I] and [II] are correct.
c) Only [II] and [III] are correct.
d) All three statements are correct.
9. The value of the marginal product of labour is equal to the product of:
a) the marginal product of labour and marginal cost of production.
b) the marginal product of labour and price.
c) the average product oflabour and the average cost of production.
d) the average product of labour and price.
10. Which of the following is NOT a unique characteristic of the labour market?
a) The worker is not a product but a person.
b) The employer buys the services of the worker, but the employer does not buy the
worker.
c) The equilibrium wage in the labour market could be influenced by factors like
inflation and the worker's standard ofliving.
d) The worker's personality characteristics can always be determined fully before
employment starts.
QUESTION TWO
a)
These data are for illustrative purpose only not in any way
representing Namibia stats in 2020
Population working age 15+ years Total (PWA)
Male 15 + years
Female 15 + years
Labour Force
Employed
Male employed
Female employed
Male labour force
[25 MARKS]
2020
2,582,598
1,255,688
1,326,910
1,166,464
776,544
386,814
390,372
572,891
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

Female labour force
Youth labour force
Youth employed
594,215
616,988
332,614
Use the information provided in the table above to calculate:
i) Labour force participation rate
ii) Labour force absorption rate
iii) Namibia unemployment rate in 2020
iv) Male absorption rate
v) Female absorption rate
b) Explain the main differences between the labour market and the goods market.
[3 marks]
[3 marks]
[3 marks]
[3 marks]
[3 marks]
[10 marks]
QUESTION THREE
[25 MARKS]
a) Explain, with the aid of two separate figures, how the wage increase in the unionised sector
would have an impact on wages and on employment in the unionised sector and non-
unionised sector, assuming an upward-sloping labour supply curve in both sectors. Explain
why unemployment takes place in both sectors.
[10 marks]
b) Use a graphic illustration to describe briefly what the influence of each of the following
would be on the market supply of labour:
i)
An increase in immigrants
[2 marks]
ii) A reduction in wage rates
[2 marks]
iii) More women entering the labour market
[2 marks]
iv) More students studying full-time
[2 marks]
c) Analyse the impact of a simultaneous increase in demand and supply on market wage and
employment.
[7 marks]
QUESTION FOUR
[30 MARKET]
a)
Production
function
is
Q(K, E)
= 10{11
3
£"2where
K
is
capital
and
E
is
employment
in
work hours. The initial cost of employment per hour is N$45.00, cost capital per hour is
N$55.00 and the total cost available is N$5000. Use the information above to construct
5
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |
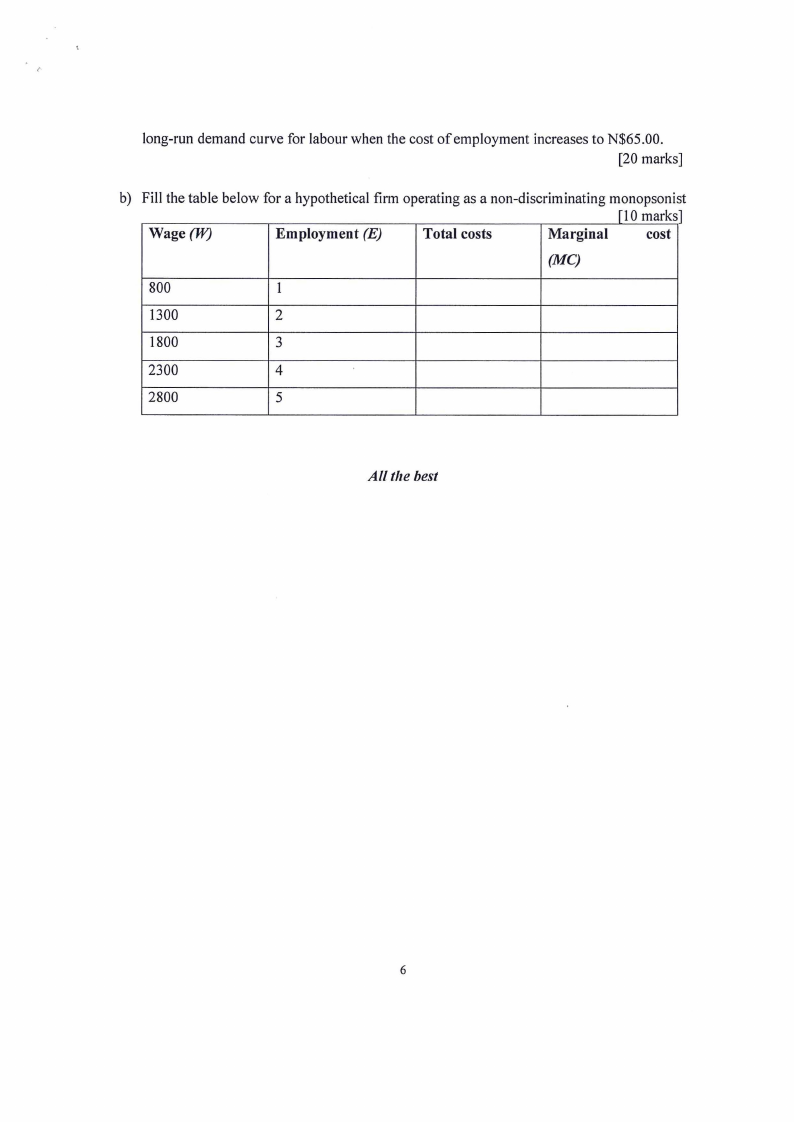
long-run demand curve for labour when the cost of employment increases to N$65 .00.
[20 marks]
b) Fill the table below for a hypothetical firm operating as a non-discriminating monopsonist
[IO marks ]
Wage(W)
Employment (E)
Total costs
Marginal
cost
(MC)
800
I
1300
2
1800
3
2300
4
2800
5
All the best
6





