BIO521S AND IBC521S - BIOCHEMSITRY OR INTRODUCTION TO BIOCHEMISTRY - 1ST OPP - NOVEMBER 2024
 |
BIO521S AND IBC521S - BIOCHEMSITRY OR INTRODUCTION TO BIOCHEMISTRY - 1ST OPP - NOVEMBER 2024 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAm I Bl A un IVERSITY
OF SCIEnCE
Faculty of Health, Natural
Resources andApplied
Sciences
School of Health Sciences
Department of Clinical
Health Sciences
13 Jackson Kaujeua Street
Private Bag 13388
Windhoek
NAMIBIA
T: +254 51 207
F: +254 512079970
E: dchs@nust.nu
W: www.nust.na
QUALIFICATION : BACHELOR OF MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCESAND BACHELOR OF
HUMAN NUTRITION
QUALIFICATION CODE: 08BMLS OR 08BOHN
LEVEL: 6
COURSE:BIOCHEMISTRY OR INTRODUCTION TO
BIOCHEMISTRY
COURSECODE: BIO521S
AND IBC521S
DATE: NOVEMBER 2024
SESSION: 1
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 100
FIRST OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION: QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER:
MODERATOR:
Mr Junias Natangwe Jackson
Ms Vanessa Tjijenda
Mr George Waliomuzibu Mukisa
INSTRUCTIONS:
1. Answer all questions on the separate answer sheet.
2. Please write neatly and legibly.
3. Do not use the left side margin of the exam paper. This must be allowed for the
examiner.
4. No books, notes and other additional aids are allowed.
5. Mark all answers clearly with their respective question numbers.
PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS:
1. Non-Programmable Calculator
ATTACHMENTS:
NONE
This paper consists of 6 pages including this front page
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

1SECTIONA: MULTIPLE CH
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
[10 MARKS]
Evaluate the statements in each numbered section and select the most appropriate answer or phrase
from the given possibilities. Fill in the appropriate letter next to the number of the correct
statement/phrase on your ANSWERSHEET.
[10]
1.1. Which one of the following is a ketose:
H
OH
H Oil
CMzOH
A
B
C
D
1.2. Which of the following statements is correct about column chromatography:
a) Resolution improves as column length increases
b) Mobile phase is a porous solid material kept in the column with appropriate chemical
characteristics
c) Stationary phase is a buffered solution that percolates through the mobile phase
d) Large proteins exit the column faster than tiny proteins:
1.3. Which of the following catalyses the reversible degradation of 2-phosphoglycerate to
phosphoenolpyruvate:
a) Trypsin
b) Enolase
c) Chymotrypsin
d) Hexokinase
1.4. If the free energy change (LiG)for a reaction is -50.45 kJ/mol, the reaction is:
a) Exothermic.
b) Exergonic.
c) Endergonic.
d) At equilibrium.
1.5. Which of the following is a choline-containing lipid:
a) Phosphatidylethanolamine
b) Phosphatidylserine
c) Sphingomyelin
d) Phosphatidylglycerol
1.6. Which of the following enzyme is responsible for the conversion of glucose 1-phosphate to
glucose 6-phosphate:
a) Epimerase
b) Phosphoglucomutase
c) Glycogen phosphorylase
d) lsomerase
1.7. Which of the following condenses acyl and malonyl groups:
a) Acetyl co-A ACPtransacetylase
b) Malonyl co-A ACPtransferase
Biochemistry/ introduction to biochemistry (BIO521S/IBC521S)
2
l51 Opportunity November 2024
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

c) ~-ketoacyl ACPsynthase
d) Acyl carrier protein
1.8. Which of the following is called "bad" Cholesterol:
a) Cholesterol
b} Triglyceride
c) HDL
d) LDL
1.9. Which of the following is a building block of proteins:
a) Fatty acid
b) Amino acid
c) Nucleotide
d) Monosaccharide
1.10. What are enzymes:
a) Proteins
b) Lipids
c) Carbohydrates
d) Nucleic acids
QUESTION 2: TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS
[10 MARKS]
Evaluate the statements and select whether the statement is true or false. Write the word 'True'
or 'False' next to the corresponding number on your ANSWERSHEET.
[10]
2.1 Glycogen, starch, and cellulose are all chains of amino acids.
2.2 A simple sugar that is a building block of carbohydrates is called a polysaccharide
2.3 In uncompetitive inhibition, kmincreases as an inhibitor is added.
2.4 Two monosaccharide are joined through a peptide bond to form a disaccharide
2.5 Amino acid is one of the major macromolecules
2.6 The chemical structure of a competitive inhibitor resembles that of the enzymes substrate
2.7 Active transport requires energy and involves the movement of solute from the lower
concentration side of a membrane to the higher concentration side
2.8 NADPH is a oxidising agent for fatty acid biosynthesis
2.9 The formation of "ketone bodies" occurs when acetyl-CoA from fatty acid metabolism is
unable to enter the citric acid cycle due to a low concentration of oxaloacetate
2.10 The enzymes for the glycolysis pathway and for fatty acid biosynthesis occur in the cytosol
Biochemistry/ introduction to biochemistry (B1O521S/IBC521S}
3
1st Opportunity November 2024
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

fSECTIONB: SHORT/LONGANSWERQUESTIONS
Please answer ALL of the questions in this section.
QUESTION 3
[35)
3.1. Write a mechanism for the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA. Assume all of the required
coenzymes are present.
[6]
3.2. What is protein denaturation? Is there any change in the primary structure when a protein is
denatured? What are some factors that can lead to protein denaturation?
[4]
3.3. Describe allosteric regulation of enzyme activity?
[4]
3.4. What is the prosthetic group that hemoglobin and myoglobin's oxygen binding ability
depends on?
[1]
3.5. Briefly explain the Cori cycle which is linked metabolic pathways
[5]
3.6. Define cooperativity to binding oxygen
[3]
3.7. What is oxidative phosphorylation?
[2]
3.8. List four (4) non covalent interaction in the biomolecules
[4]
3.9. How are proteins separated by electrophoresis?
[3]
3.10. What are Glycolipids and what are their important functions?
[3]
QUESTION 4: CALCULATIONS
[9]
4.1. What is the [H+] of a solution with a pH of 4.5?
[3]
4.2. What do you understand by pKa
[2]
4.3. Calculate the pH of a buffer that contains 0.7 M ammonia and 0.9 M ammonium chloride.
(pK0 = 9.248).
[4]
QUESTION 5: ENZYMES
[10)
5.1 At what substrate concentration would an enzyme with a kcatof 30.0 s-1 and a Kmof 0.0050 M
operate at one-quarter of its maximum rate?
[4]
5.2 Determine the fraction of Vmaxthat would be obtained at the following substrate
concentrations: [SJ=~km, 2 km,and 10 km
[3]
2
5.3 An enzyme that catalyzes the reaction X .= Y is isolated from two bacterial species. The
enzymes have the same Vmaxbut different Kmvalues for the substrate X. Enzyme A has a Kmof
2.0 µM, and enzyme B has a Km of 0.5 µM. The plot below shows the kinetics of reactions
carried out with the same concentration of each enzyme and with [X] = 1 µM. Which curve
corresponds to which enzyme?
[3]
Biochemistry/ introduction to biochemistry (B1O521S/IBC521S)
4
1stOpportunity November 2024
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |
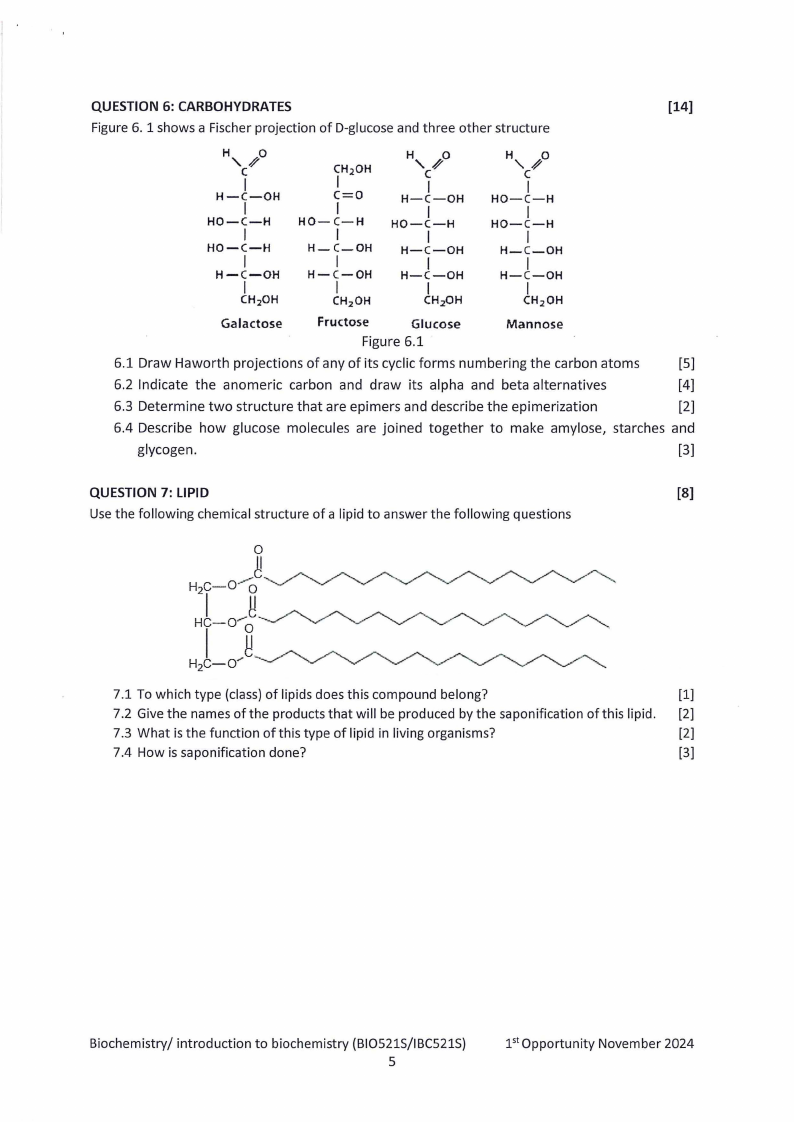
QUESTION 6: CARBOHYDRATES
[14]
Figure 6. 1 shows a Fischer projection of 0-glucose and three other structure
H '~o
C
I
H-C-OH
I
HO-C-H
I
HO-C-H
I
H-C-OH
I
CH 2 0H
Ga lactose
CH.20H
I
C=O
I
HO-C-H
I
H-C-OH
I
H-C-OH
I
CH2 0H
'~ H
0
C
I
H-C-OH
I
HO-C-H
I
H-C-OH
I
H-C-OH
I
CH20H
Fructose
Glucose
Figure 6.1
'~ H 0
C
I
HO-C-H
I
HO-C-H
I
H-C-OH
I
H-C-OH
I
CH20H
Mannose
6.1 Draw Haworth projections of any of its cyclic forms numbering the carbon atoms
[5]
6.2 Indicate the anomeric carbon and draw its alpha and beta alternatives
[4]
6.3 Determine two structure that are epimers and describe the epimerization
[2]
6.4 Describe how glucose molecules are joined together to make amylase, starches and
glycogen.
[3]
QUESTION 7: LIPID
[8]
Use the following chemical structure of a lipid to answer the following questions
0
.
H2C-0.....-o
Hbo,__,H_
H,L - 0
to'
7.1 To which type (class) of lipids does this compound belong?
[1]
7.2 Give the names of the products that will be produced by the saponification of this lipid. [2]
7.3 What is the function of this type of lipid in living organisms?
[2]
7.4 How is saponification done?
[3]
Biochemistry/ introduction to biochemistry (BIO521S/IBC521S)
5
1st opportunity November 2024
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |
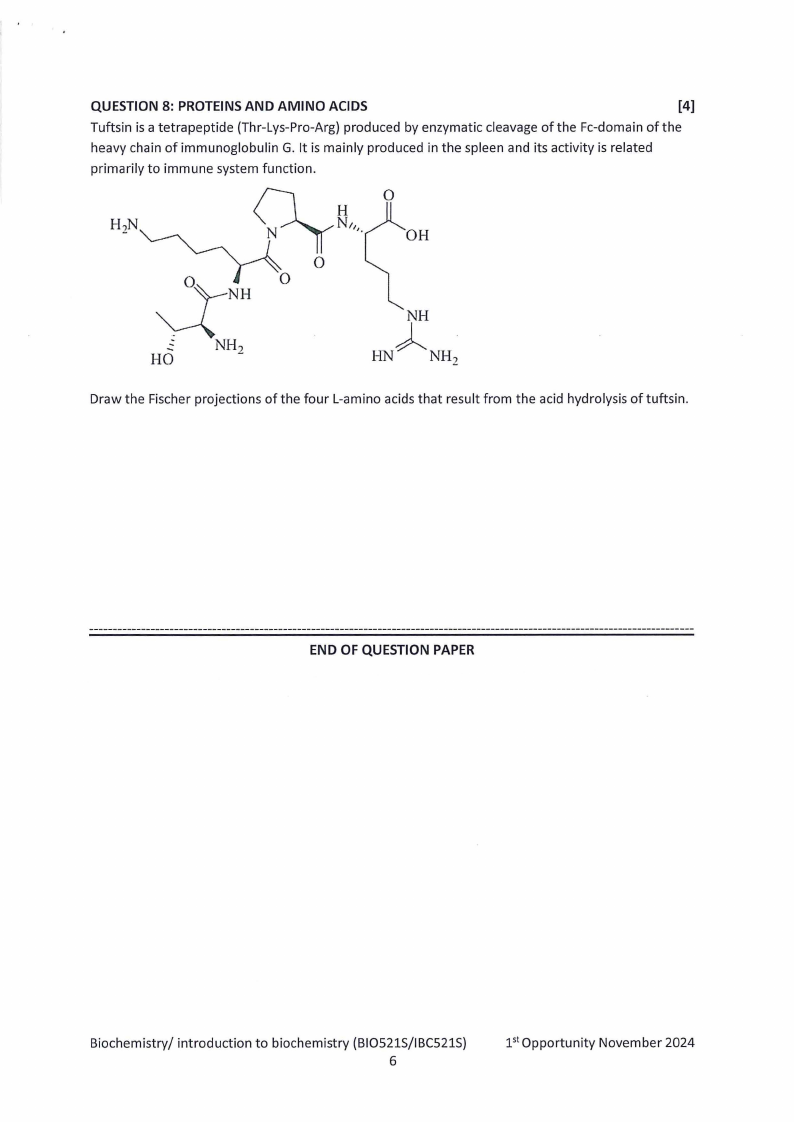
QUESTION 8: PROTEINS AND AMINO ACIDS
[4]
Tuftsin is a tetra peptide (Thr-Lys-Pro-Arg) produced by enzymatic cleavage of the Fe-domain of the
heavy chain of immunoglobulin G. It is mainly produced in the spleen and its activity is related
primarily to immune system function.
OH
Draw the Fischer projections of the four L-amino acids that result from the acid hydrolysis of tuftsin.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
END OF QUESTION PAPER
Biochemistry/ introduction to biochemistry (B1O521S/IBC521S)
6
1st Opportunity November 2024





