 |
IFN712S - INTERNATIONAL FINANCE - 2ND OPP - JAN 2020 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

-
FACULTY OF
NAMIBIA UNIVERSITY
OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
MANAGEMENT SCIENCES
DEPARTMENT OF ACCOUNTING, ECONOMICS AND FINANCE
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF ECONOMICS
QUALIFICATION CODE: 07BECO
LEVEL: 7
COURSE CODE: IFN712S
COURSE NAME: INTERNATIONAL FINANCE
SESSION: FEBRUARY 2020
DURATION: 3 HOURS
PAPER: THEORY
MARKS: 100
SECOND OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION PAPER
EXAMINER(S) | MR. MALLY LIKUKELA
MODERATOR: | MRS. BLESSING MUSARIRI
INSTRUCTIONS
This paper consist of section A,B and C
Answer ALL questions
Number your answers in accordance with the question paper.
Start each section answer on a new page
Write clearly and legibly
PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS
1. Pen
2. Ruler
3. Calculator
THIS EXAMINATION PAPER CONSISTS OF 7 PAGES (Including this front page)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

SECTION A
QUESTION ONE
[20 MARKS]
Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
1) Which of the following would be included as contributing positively to the Namibian balance
of merchandise trade?
A) Purchase by Air Namibia of an airplane made by the European firm, Airbus.
B) Sale of a Ministry of Finance Treasury bill to a Japanese bank.
C) Sale by a Air Namibia to an Italian student, of a ticket from Rome to New York.
D) Purchase by the Russian government of wheat from a Agro Namibia grain firm.
E) A capital export in the form of construction of a foreign factory by a U.S. firm.
2) Which of the following are long-term financial instruments?
A) A six-month loan
B) A negotiable certificate of deposit
C) A bankers acceptance
D) A U.S. Treasury bill
E) None of the above
3) Which of the following are short-term financial instruments?
A) A bankers acceptance
B) AUS. Treasury bill
C) A negotiable certificate of deposit
D) A six-month loan
E) All of the above
4) Which of the following statements about financial markets and securities are true?
A) A debt instrument is long term if its maturity is ten years or longer.
B) The maturity of a debt instrument is the time (term) to that instrument's expiration
date.
C) A debt instrument is intermediate term if its maturity is less than one year.
D) A bond is a long term security that promises to make periodic payments called
dividends to the firm's residual claimants.
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

5) A coupon bond pays the owner of the bond
A) the same amount every month until maturity date.
B) the face value of the bond plus an interest payment once the maturity date has been
reached.
C) the face value at the maturity date.
D) a fixed-interest payment every period and repays the face value at the maturity date.
E) none of the above.
6) If a $5,000 coupon bond has a coupon rate of 13 percent, then the coupon payment every
year is
A) $13.
B) $1,300.
C) $650.
D) $130.
E) None of the above.
7) An $8,000 coupon bond with a $400 coupon payment every year has a coupon rate of
A) 10 percent
B) 8 percent
C) 40 percent
D) 5 percent
8) With an interest rate of 5 percent, the present value of $100 next year is approximately
A) $95.
B) $105.
C) $100.
D) $90.
9) Which of the following $1,000 face-value securities has the highest yield to maturity?
A) A 5 percent coupon bond with a price of $600
B) A 5 percent coupon bond with a price of $800.
C) A5 percent coupon bond with a price of $1,200.
D) A 5 percent coupon bond with a price of $1,500.
E) A 5 percent coupon bond with a price of $1,000.
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

10) If a $10,000 face-value discount bond maturing in one year is selling for $5,000, then its
yield to maturity is
A) 50 percent.
B) 10 percent.
C) 100 percent.
D) 5 percent.
11) The current yield on a $5,000, 8 percent coupon bond selling for $4,000 is
A) 8 percent.
B) 5 percent.
C) 10 percent.
D) 20 percent.
E) none of the above.
12) What is the return on a 5 percent coupon bond that initially sells for $1,000 and sells for
$1,200 next year?
A) 5 percent
B) -5 percent
C) 10 percent
D) 25 percent
E) None of the above
13) If the interest rates on all bonds rise from 5 to 6 percent over the course of the year, which
bond would you prefer to have been holding?
A) A bond with one year to maturity
B) A bond with ten years to maturity
C) A bond with five years to maturity
D) A bond with twenty years to maturity
14) In which of the following situations would you prefer to be making a loan?
A) The interest rate is 25 percent and the expected inflation rate is 50 percent.
B) The interest rate is 4 percent and the expected inflation rate is 1 percent.
C) The interest rate is 9 percent and the expected inflation rate is 7 percent.
D) The interest rate is 13 percent and the expected inflation rate is 15 percent.
15) The nominal interest rate minus the expected rate of inflation
A) is a better measure of the incentives to borrow and lend than is the nominal interest
rate.
B) defines the real interest rate.
C) is a more accurate indicator of the tightness of credit market conditions than is the
3
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

nominal interest rate.
D) indicates all of the above.
E) indicates only (a) and (b) of the above.
16) A credit market instrument that pays the owner a fixed coupon payment every year until
the maturity date and then repays the face value is called a
A) discount bond.
B) fixed-payment loan.
C) simple loan.
D) coupon bond.
17) A
the
pays the owner a fixed coupon payment every year until the maturity date, when
value is repaid.
A) coupon bond; discount
B) discount bond; face
C) discount bond; discount
D) coupon bond; face
18) The interest rate that equates the present value of payments received from a debt
instrument with its value today is the
A) simple interest rate.
B) yield to maturity.
C) discount rate.
D) real interest rate.
19) When bond interest rates become more volatile, the demand for bonds ____ and the
interest rate
.
A) increases; rises
B) increases; falls
C) decreases; rises
D) decreases; falls
20) In the foreign exchange market, the______of one country is traded for the
of another country.
A ) currency; currency
B ) currency; financial instruments
C ) currency; goods
D ) goods; goods
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |

SECTION B
QUESTION 1
Define the following concepts
a. Current account
b. Trade balance
c. Official reserve assets
d. Eurobond
e. Foreign exchange market.
[15 MARKS]
QUESTION 2
[30 MARKS]
Discuss the advantages and the disadvantages of the Euro Bonds
QUESTION 3
Discuss about how any five [5] of the following factors affects exchange of any given country
1. balance of payments
2. inflation
3. Interest rate
4. Money Supply
5. National Income
6. Resource Discoveries
7. Capital Movements
8. Political factors
SECTION C
QUESTION 1
Discuss they key characteristics of Bonds
[15 MARKS]
 |
7 Page 7 |
▲back to top |
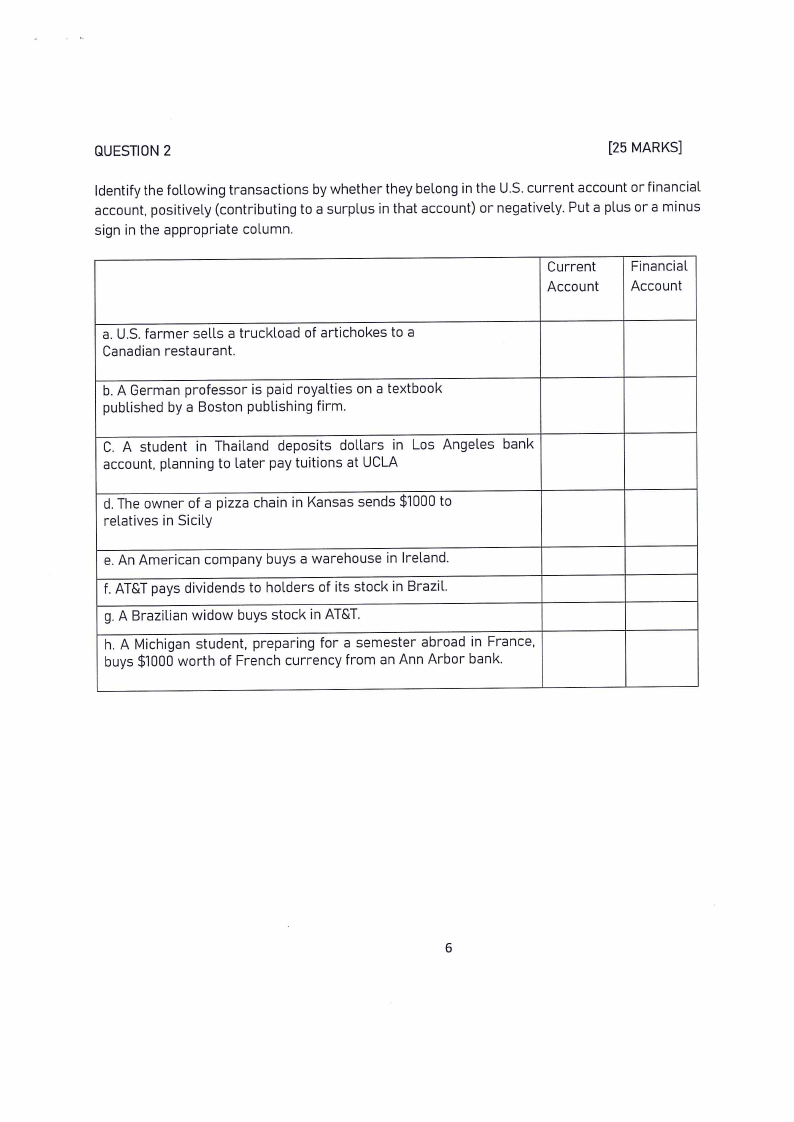
QUESTION 2
[25 MARKS]
Identify the following transactions by whether they belong in the U.S. current account or financial
account, positively (contributing to a surplus in that account) or negatively. Put a plus or a minus
sign in the appropriate column.
Current
Account
Financial
Account
a. U.S. farmer sells a truckload of artichokes to a
Canadian restaurant.
b. A German professor is paid royalties on a textbook
published by a Boston publishing firm.
C. A student in Thailand deposits dollars in Los Angeles bank
account, planning to later pay tuitions at UCLA
d. The owner of a pizza chain in Kansas sends $1000 to
relatives in Sicily
e. An American company buys a warehouse in Ireland.
f. AT&T pays dividends to holders of its stock in Brazil.
g. A Brazilian widow buys stock in AT&T.
h. A Michigan student, preparing for a semester abroad in France,
buys $1000 worth of French currency from an Ann Arbor bank.
 |
8 Page 8 |
▲back to top |

“The Pe ar
fans acoel owl has Lio
AE
atxcally ar wmacles adlacadserq
Soclkmn 6
Wosecer | Cueshe
&SSyS IU
Le rot
midako ¢
Fwvee .





