 |
NIE811S - NUTRITION IN EMERGENCY - 1ST OPP - JUNE 2022 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAmlBIA unlVERSITY
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECHnOLOGY
FACULTY OF HEALTH, APPLIED SCIENCES AND NATURAL RESOURCES
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOROF HUMAN NUTRITION
QUALIFICATION CODE: 08BOHN
LEVEL: 8
COURSE CODE: NIE811S
COURSE NAME: NUTRITION IN EMERGENCY
SESSION: JUNE 2022
PAPER:THEORY
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 108
EXAMINER(S)
FIRST OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION-QUESTION PAPER
MR WALIOMUZIBU MUKISA GEORGEWILLIAM
MODERATOR: PROFSYVESTERRODGERSMOYO
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALL the questions.
2. Write clearly and neatly.
3. Number the answers clearly.
PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS
NONE
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF 8 PAGES (Including this front page)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

SECTION A:
{25 MARKS)
QUESTION 1. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
{20 MARKS)
Select the most appropriate answer from the options provided. (Each correct answer earns
1 mark)
1.1 During rapid nutrition assessment the indicator often used is:
a. Height for age
b. Weight for age
c. Weight for height
d. None of the above
1.2 During rapid nutrition assessment, children identified with oedema are classified as:
a. Moderately malnourished
b. Moderate to severely malnourished
c. Wasted and stunted
d. None of the above
1.3 What is the approximate length of children 6 months of age:
a. 80-85cm
b. 70-75cm
c. 100-110cm
d. 60-65cm
1.4 In emergency situations, the maximum height of children to be measured is often
limited at 100cm, not 110cm. This is that:
a. In developing countries most children are stunted and thus, using 110cm will
result in the inclusion of many stunted children in the sample
b. Instruments used in an emergency are not often accurate and thus, to minimise
errors in measurements 110cm is the most appropriate
c. In emergency situations it is often easier to obtain children measuring 100cm
compared to 110cm
d. In emergency situations, it is waste of time and resources to focus on children
110cm more than those of 100cm.
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

1.5 Disaster can be defined as a product of impact and vulnerability:
a. True
b. False
1.6 The radioactive leak in the Chernobyl nuclear station in Ukraine caused a massive
man-made disaster that killed thousands of people. Which year did this disaster
occur:
a. 1990
b. 1985
C. 1996
d. 1986
1.7 The preparedness phase involves an analysis of the risk of exposure to disaster:
a. True
b. False
1.8 Which of the following phase of disaster involves drawing lessons learned to prevent
reoccurrence of the disaster:
a. Pre-disaster phase
b. Post-disaster phase
c. Intermediate phase
d. None of the above
1.9 Crude mortality rate in an emergency can be defined as the number of deaths per
1000 inhabitants per day:
a. True
b. False
1.10 In a refugee crisis in Northern Iraq in 1991, children under five years accounted for
only 18% of the total refugee population, but they accounted for 64% of the overall
refugee mortality rate. This is because:
a. Health care services were very poor in the camps
b. There was massive food insecurity in the camps
c. Children are more vulnerable in disaster situations compared to other age groups
d. There was limited care and inappropriate feeding practices in the camps
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

1.11 Of the following which is the immediate goal for any intervention in humanitarian
emergencies:
a. Stop people from moving from one place to another
b. Provide food aid
c. Provide proper sanitation and hygiene services
d. Provide necessary health care services
e. None of the above
1.12 In emergency situations the immediate cause of death in children under five years
can be attributed to:
a. Measles
b. Micronutrient deficiencies
c. Malnutrition
d. Food insecurity
1.13 Before any intervention is given during an emergency, a rapid assessment is
required. Of the following which is the most probable reason for conducting a rapid
assessment first:
a. To save the lives of the affected people
b. To determine the number of malnourished children
c. To determine the exact needs of the affected communities
d. To determine the level of food stocks in the camp
1.14 In an emergency, there is the involvement of different organisations to support the
affected communities. Of the following which is the major reason for the
involvement of these organisations:
a. Many people have been displaced and thus need support
b. There is always no functioning government to support the affected communities
c. The harmed groups and bandits are many and therefore local authorities can't
manage them
d. The local resources are insufficient to support the needs of the affected
communities
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

1.15 The following are United Nations agencies are involved in humanitarian assistance
during disasters:
a. WHO
b. USAID
c. WFP
d. IOM
1.16 The major mandate of OXFAM during an emergency is:
a. Offer nutrition services
b. Provide food aid to the effected communities
c. Support education and food security
d. Provide water and sanitary services
1.17 Of the following, which is the organisation mandated to support early recovery from
emergencies:
a. WFP
b. FAO
c. UNDP
d. UNHCR
1.18 During emergency the Humanitarian Coordinator reports to Humanitarian Country
Team:
a. True
b. False
1.19 Of the following which is the main difference between employment generation
schemes and gratuitous relief:
a. Employment generation schemes provides food for free to the affected
communities and gratuitous people pay for the food
b. Gratuitous relief involves maximum participation of the affected communities
and employment generation schemes there is limited participation
c. Employment generation schemes involves condition transfer and gratuitous
relief is free
d. None of the above
1.20 The main objective of Targeted Supplementary Feeding Program is to prevent
severely malnourished children from dying:
a. True
b. False
5
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 2. TRUE-FALSE QUESTIONS
(5 MARKS)
Evaluate the statements in each numbered section and determine whether the statement
is true or false. Next to the question number, fill in the appropriate answer, using Tfor a
True, and Ffor a false statement/phrase. (Each correct answer earns 1 mark)
2.1 Giving iron too early in treatment can have toxic effects.
2.2 All severely malnourished children should be given antibiotics.
2.3 Giving IV fluids too quickly can cause heart failure in a severely malnourished child.
2.4 Diuretics should be given to reduce oedema
2.5 Unless CMV is used to prepare feeds, the child needs multivitamins drops.
SECTION B:
QUESTION 3
(51 MARKS)
(51 MARKS)
Read each question completely, and on your ANSWERSHEETn, ext to the question number,
please write the full answer to the questions.
3.1 Explain the four (4) phases of disasters
(8 marks)
3.2 Outline five (5) immediate measures that are undertaken to reduce the
vulnerability of the population during a disaster
(5 marks)
3.3 Explain the advantages of coordination of activities in emergency situations (6 marks)
3.4 Explain the role and responsibilities of the following agencies during
emergency response and preparedness
(8 marks)
3.5 Outline three (3) advantages of Non-Government Organisations (NGOs)
in emergency situations
(3 marks)
6
 |
7 Page 7 |
▲back to top |
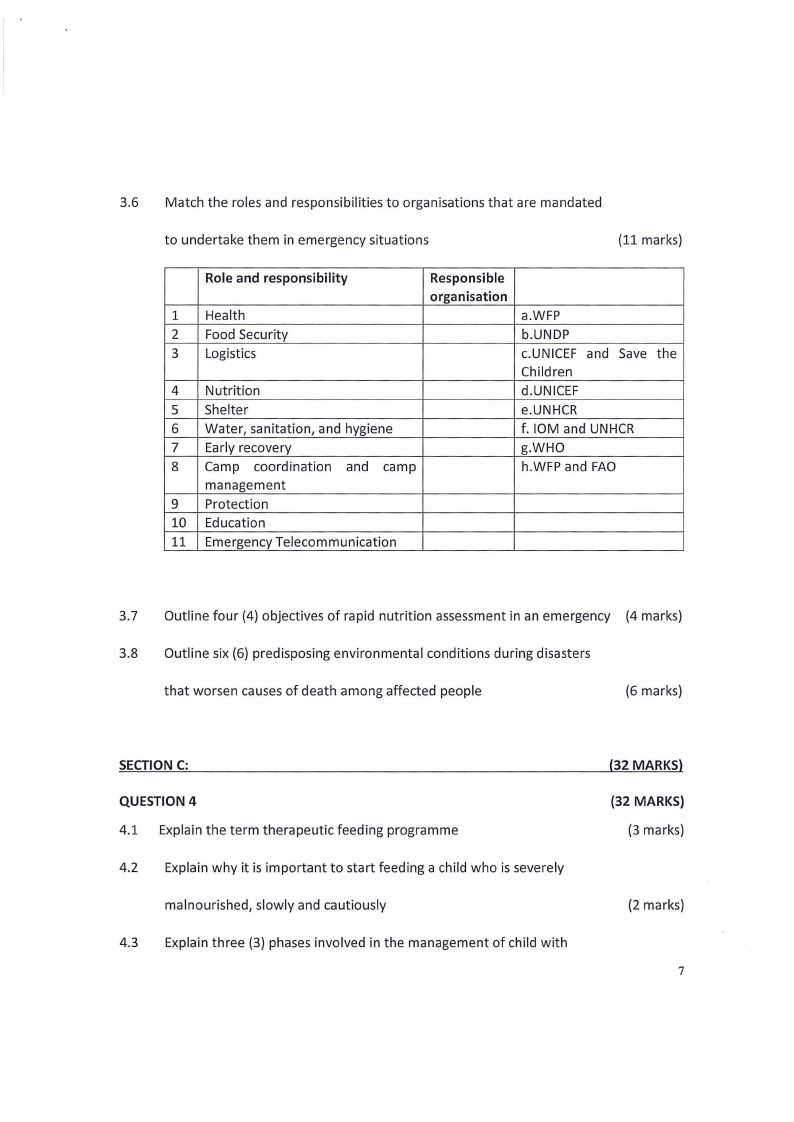
3.6 Match the roles and responsibilities to organisations that are mandated
to undertake them in emergency situations
(11 marks)
Role and responsibility
Responsible
organisation
1 Health
a.WFP
2 Food Security
b.UNDP
3 Logistics
c.UNICEF and Save the
Children
4 Nutrition
d.UNICEF
5 Shelter
e.UNHCR
6 Water, sanitation, and hygiene
f. IOM and UNHCR
7 Early recovery
g.WHO
8 Camp coordination and camp
h.WFP and FAO
management
9 Protection
10 Education
11 Emergency Telecommunication
3.7 Outline four (4) objectives of rapid nutrition assessment in an emergency (4 marks)
3.8 Outline six (6) predisposing environmental conditions during disasters
that worsen causes of death among affected people
(6 marks)
SECTION C:
QUESTION 4
4.1 Explain the term therapeutic feeding programme
4.2 Explain why it is important to start feeding a child who is severely
malnourished, slowly and cautiously
4.3 Explain three (3) phases involved in the management of child with
(32 MARKS)
(32 MARKS}
(3 marks)
(2 marks)
7
 |
8 Page 8 |
▲back to top |

severe acute malnutrition
(6 marks)
4.4 CMV is included in F-75 and F-100 to correct electrolyte imbalance.
What are two important minerals in this mix and why?
(2 marks)
4.5 Explain why it is dangerous to give iron early during the treatment
of severely malnourished child
(3 marks)
4.6 What is blanket supplementary feeding program
(1 marks)
4.7 Outline three (3) objectives of blanket supplementary feeding programme (3 marks)
4.8 Complete the following abbreviations in full.
(4 marks)
4.8.1 CMV
4.8.2 RUTF
4.8.3 RUSF
4.8.4 ReSoMal
4.8.5 Explain four (4) essential emergency relief measures undertaken
during emergency to reduce incidences of death
(8 marks)
!!!!!!!!!!!GOODLUCK!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
8





