CAH610S - COST AND MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING FOR HOSPITALITY AND TOURISM - 2ND OPP - JANUARY 2023
 |
CAH610S - COST AND MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING FOR HOSPITALITY AND TOURISM - 2ND OPP - JANUARY 2023 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |
nAm I BIA un IVERSITY
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECHnOLOGY
FACULTYOFCOMMERCEH, UMANSCIENCEAS ND EDUCATION
ECONOMIC,ACCOUNTINGAND FINANCE
QUALIFICATIONCODE:07BHOM & 07BOTM
COURSECODE:CAH610S
DATE:JANUARY 2023
LEVEL:6
COURSENAME: COST& MANAGEMENT
ACCOUNTING FOR HOSPITALITY& TOURISM
MODE: FT
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 100
SECONDOPPORTUNITYEXAMINATION PAPER
EXAMINER(S) Sheehama, K.G.H.
MODERATOR: Odada, L.
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALL the questions.
2. Write clearly and neatly.
3. Number the answers clearly.
NON - PROGRAMMABLECALCUTOR
1. Examination paper
2. Examination script
THIS QUESTIONPAPERCONSISTSOF 6 PAGES(INCLUDING THIS FRONT PAGE)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |
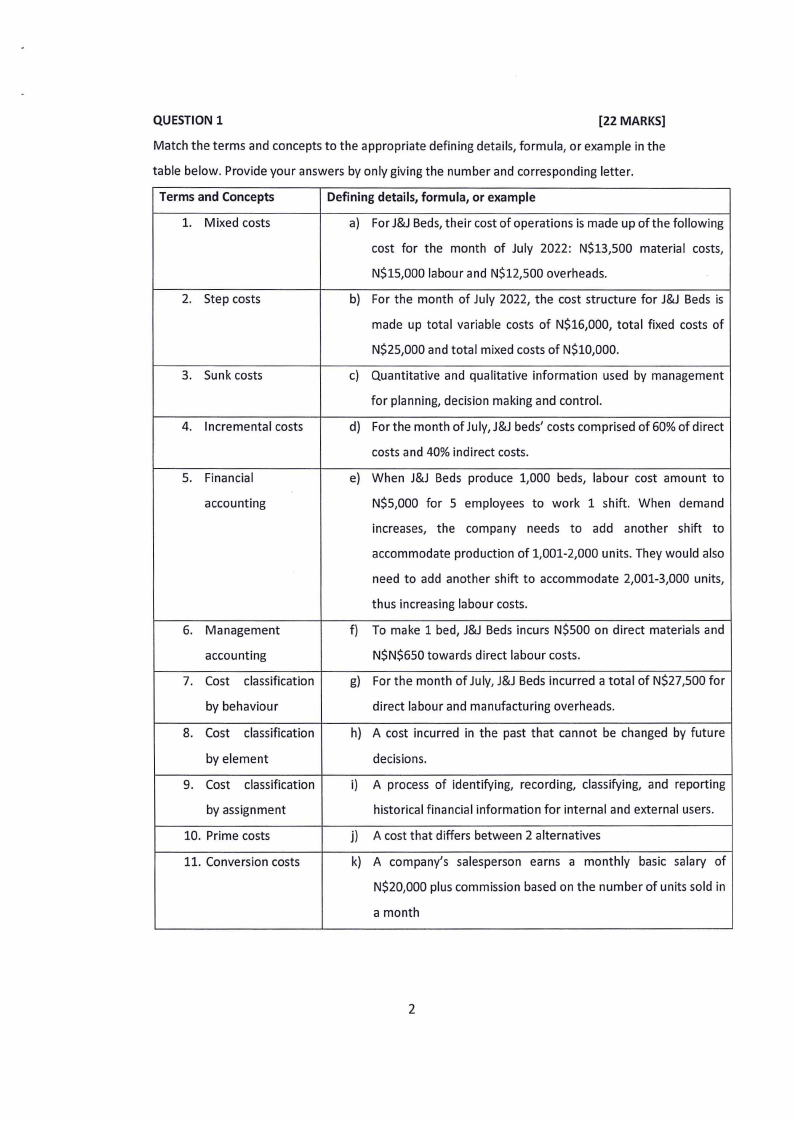
QUESTION 1
[22 MARKS]
Match the terms and concepts to the appropriate defining details, formula, or example in the
table below. Provide your answers by only giving the number and corresponding letter.
Terms and Concepts
Definingdetails,formula, or example
1. Mixed costs
a) For J&JBeds,their cost of operations is made up of the following
cost for the month of July 2022: N$13,500 material costs,
N$15,000 labour and N$12,500 overheads.
2. Step costs
b) For the month of July 2022, the cost structure for J&J Beds is
made up total variable costs of N$16,000, total fixed costs of
N$25,000 and total mixed costs of N$10,000.
3. Sunk costs
c) Quantitative and qualitative information used by management
for planning, decision making and control.
4. Incremental costs
d) For the month of July, J&J beds' costs comprised of 60% of direct
costs and 40% indirect costs.
5. Financial
e) When J&J Beds produce 1,000 beds, labour cost amount to
accounting
N$5,000 for 5 employees to work 1 shift. When demand
increases, the company needs to add another shift to
accommodate production of 1,001-2,000 units. They would also
need to add another shift to accommodate 2,001-3,000 units,
thus increasing labour costs.
6. Management
f) To make 1 bed, J&J Beds incurs N$500 on direct materials and
accounting
N$N$650 towards direct labour costs.
7. Cost classification
g) For the month of July, J&J Beds incurred a total of N$27,500 for
by behaviour
direct labour and manufacturing overheads.
8. Cost classification
h) A cost incurred in the past that cannot be changed by future
by element
decisions.
9. Cost classification
i) A process of identifying, recording, classifying, and reporting
by assignment
historical financial information for internal and external users.
10. Prime costs
j) A cost that differs between 2 alternatives
11. Conversion costs
k) A company's salesperson earns a monthly basic salary of
N$20,000 plus commission based on the number of units sold in
a month
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION2
[10 MARKS]
For questions 2.1- 2.2, just write the answer only (the correct letter chosen) in your answer
sheet/answer book and not on the question paper. Do not copy the question and the
answers again. Example: 2.1.i. (a)
2.1 You are hired as an assistant management accountant at Katutura Wood Joinery Ltd,
a manufacturing firm. You are provided with the following information:
Variable costs
Prime
Semi- Variable costs
Conversion
N$
275 000
N$
190 000
The prime costs of Katutura Wood Joinery Ltd vary in proportion to production
changes and consist of direct materials and direct labour only. Forty per cent(40%) of
the prime cost is direct labour while manufacturing overheads are fixed.
You are required to determine:
i. The total direct material costs for the period
a) N$110 000
b) N$165 000
c) N$111000
d) N$85 000
ii. The total manufacturing overheads for the period
a) N$100 000
b) N$110 000
c) N$80 000
d) N$90 000
iii. The total manufacturing costs for the period
a) N$274 000
b) N$354 000
c) N$275 000
d) N$355 000
2.2 John, a friend of yours, has recently set up a small business making curtains. She has
supplied you with the following figures, and has asked for your advice on a few issues:
Costs per month
Direct materials
Direct labour
Production overheads
N$
88000
100 000
40000
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

The above total production costs are based on producing 2 400 curtains per month.
You are required to calculate:
i. The unit cost per curtain
a) N$53.33
b) N$95.00
c) N$78.33
d) N$58.33
ii. The selling price per curtain if Tura-babe wanted a markup of 20%
a) N$120
b) N$105
c) N$114
d) N$115
QUESTION3
(22 MARKS)
Lolo Fruits Store management uses the First in First Out (FIFO) inventory valuation method
and is in dispute on which method of inventory valuation should be used. The records
currently show that on 28 February 2022 the store had a closing balance of 600 fruits worth
N$6 000 in total. The following information regarding the movement of fruits was provided
to you by the store manager during the month of March 2022.
Receipts{purchases)from supplierswere asfollows:
• 1 March: Received 2 500 fruits at N$15 per fruit.
• 2 March: Received 1 050 fruits at a total cost of N$16 380.
• 4 March: Received 1300 fruits at N$16.80 per fruit.
• 5 March: Received 1100 fruits at N$17.40 per fruit.
The issuemade to customerswere asfollow:
• 3 March: Dispatched 1900 fruits.
• 6 March: Dispatched 1 780 fruits.
REQUIRED:
Record the above movement of the inventory in the store ledger card of Lolo Fruits Store and
determine the number of units and the total value in N$ as of 10 March 2022
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |
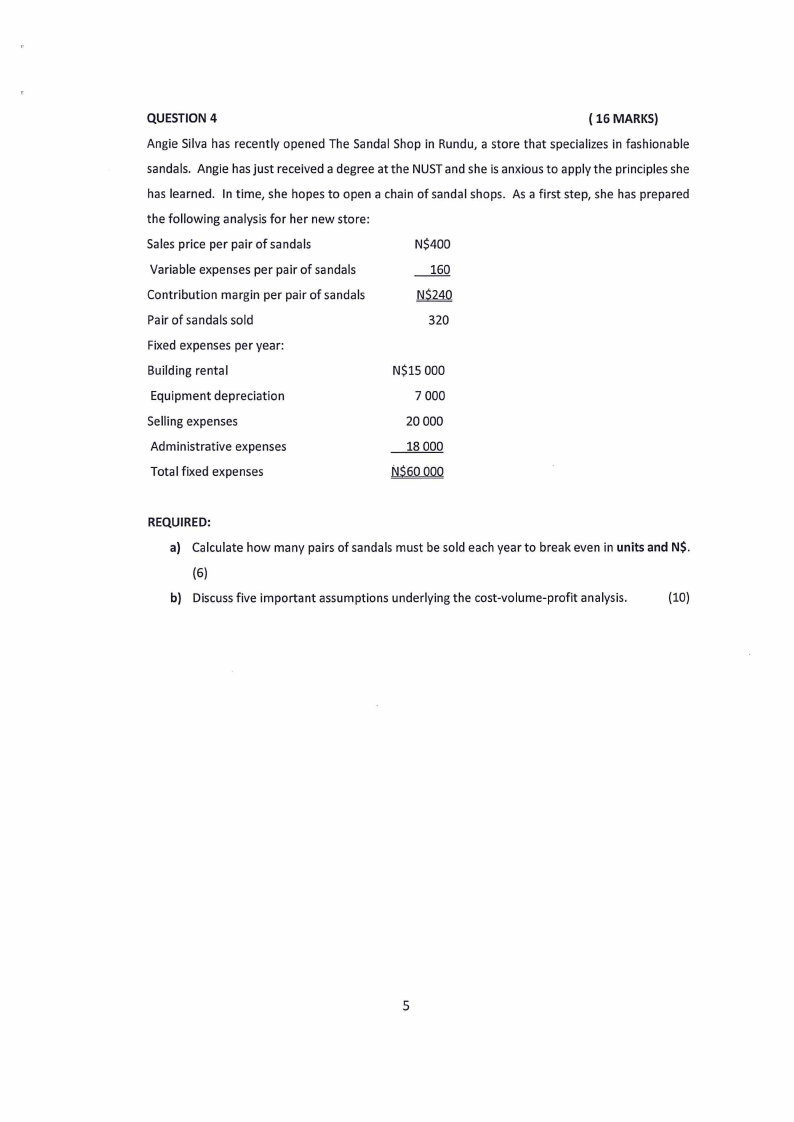
QUESTION4
( 16 MARKS)
Angie Silva has recently opened The Sandal Shop in Rundu, a store that specializes in fashionable
sandals. Angie has just received a degree at the NUSTand she is anxious to apply the principles she
has learned. In time, she hopes to open a chain of sandal shops. As a first step, she has prepared
the following analysis for her new store:
Sales price per pair of sandals
N$400
Variable expenses per pair of sandals
___l§_Q
Contribution margin per pair of sandals
N$240
Pair of sandals sold
320
Fixed expenses per year:
Building rental
N$15 000
Equipment depreciation
7 000
Selling expenses
20 000
Administrative expenses
Total fixed expenses
18 000
NS6oooo
REQUIRED:
a) Calculate how many pairs of sandals must be sold each year to break even in unitsand N$.
(6)
b) Discuss five important assumptions underlying the cost-volume-profit analysis.
(10)
5
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |

QUESTIONS
(30 MARKS)
Natu Ltd manufactures a product called "E-Roll". Information for the past year was asfollows:
Fixed costs
N$150 000
Sales (18 000 units)
N$450 000
Variable cost ratio
40%
You are required to calculate the following:
a) Variable cost per unit
(2)
b) Contribution margin per unit (2)
c) Contribution margin ratio
(2)
d) Total contribution margin
(2)
e) Break-even-point in units.
(3)
f) Break-even-point in value (N$) (3)
g) Margin of safety in units
(3)
h) Margin of safety ratio
(3)
i) The company is presently planning to reduce the current selling price of its product
by 10%. A market survey indicates that volume will increase by 20% at this new price,
but that the higher volume of production will cause fixed costs to increase by N$5 000
per year. Should the company proceed with the change? Give reasons for your
answer. Show all necessary calculations.
(10)
END OF EXAMINATIONQUETION PAPER
6





