 |
MMB621S - MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY 2B - 1ST OPP - NOV 2022 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAmlBIA unlVERSITY
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECHnOLOGY
FACULTYOF HEALTHAPPLIEDSCIENCESAND NATURALRESOURCES
DEPARTMENTOF HEALTHSCIENCES
QUALIFICATION:BACHELOROF MEDICAL LABORATORYSCIENCES
QUALIFICATIONCODE: 0SBMLS
LEVEL: 6
COURSECODE: MMB621S
COURSENAME: MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY2B
SESSION:
November 2022
PAPER:
THEORY
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS:
100
FIRSTOPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER(S) Mrs Fredrika Engelbrecht
MODERATOR: Ms Vanessa Tjijenda
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALL the questions.
2. Write clearly and neatly.
3. Number the answers clearly.
THIS QUESTION PAPERCONSISTSOF 5 PAGES(Excluding this front page)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

MMB621S MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY 2B: 1st OPPORTUNITY QUESTION PAPER
NOVEMBER 2022
QUESTION 1
Assess the following statements and decide whether they are true or false.
Write only the number of the question and next to it TRUE for a true statement
and FALSE for a false statement and give a reason for calling a statement
FALSE. (2 marks allocated to false with a reason, 1 mark allocated to true)
1.1 The K antigens of enterobacteriaciae is associated with:
A) The flagellar proteins.
B) Components of the polysaccharide capsule.
C) The lipopolysaccharides in the outer membrane.
D) The types of linkages between sugar components.
1.2 Quinolone antibiotics act on organisms through:
A) Inhibiting DNA synthesis.
B) Inhibiting folic acid synthesis.
C) Inhibiting cell wall synthesis.
D) Inactivating enzymes.
1.3 Virulence factors found in S. pneumoniae that damages host cells are:
A) the pneumolysins.
B) the polysaccharide capsules.
C) neuramidases.
D) autolysins.
1.4 Abacterial pyuria can be defined as:
A) urine containing excess pus cells and a sterile culture.
B) urine containing excess pus cells and numerous bacteria.
C) urine containing numerous bacteria with no pus cells.
D) urine containing no bacterial and no pus cells in the.
1.5 A short course (48hrs) of Glycopeptide antibiotic would be used to treat a:
A) S. aureus infection acquired from an intravenous catheter.
B) Coagulase-negative staphylococcal infection acquired from
an intravenous catheter.
C) Corynebacterial infection acquired from an intravenous
catheter.
D) Both A and C.
1.6 Leptospira can be classified as:
A) A strict anaerobe.
B) A commensal of the human intestine.
C) A strict aerobe.
D) As a fastidious organism.
(25)
[10]
Page 1 of 5
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

MMB621S MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY 28: 1st OPPORTUNITY QUESTION PAPER
NOVEMBER 2022
1.7 The lag between the onset of infection and production of antibodies can be
define as:
A) the time when a person is already infected but antibodies are not
yet produced.
B) the time when a person is not yet infected with and organism.
C) the time when a person's immune system is not able to cope with
an infection.
D) the time when a person's body do not recognise the infection as
foreign.
1.8 Identify the organism that is motile at 22°C and not motile at 37°C.
A) Clostridium perfringens.
B) Salmonella paratyphi.
C) Yersinia enterocolitica.
D) Stenotrophomonas maltophilia.
1.9 Bacitracin sensitivity assists in the positive identification of:
A) S. pyogenes.
B) S. pneumoniae.
C) S. agalactiae.
D) S. bovis.
1.10 Brucella is an organism known to be:
A) often transferred from person to person.
B) a zoonotic infection.
C) only causing infections amongst animals.
D) not a pathogenic organism.
QUESTION 2
Choose the correct answer and report only the suitable letter next to the
relevant question number.
[15]
2.1 Staphylococcus aureus belongs to the coagulase positive group of
organisms.
2.2 Boric acid is a bacteriostatic agent that inhibits the growth of organisms
when it is added to urine to give a final concentration of 1.8%.
2.3 Gram negative cocci usually in pairs (diplococci) with flattened
adjacent sides "Kidney bean"/"Coffee bean" shape are associated with
Acinetobacter species.
2.4 Fermentation is an anaerobic metabolic process.
2.5 lndole differentiates between Proteus vulgaris and Proteus mirabilis.
2.6 Beta-lactamases is antibiotic that inactivates the f3-lactam ring.
2.7 lgM antibodies will indicate that the patient is in the convalescent stage
of the disease and that he has previously been exposed to the
micro-organism.
Page 2 of 5
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |
MMB621S MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY 28: 1st OPPORTUNITY QUESTION PAPER
NOVEMBER 2022
2.8 R. prowazekii directly causes human infection.
2.9 Pseudomembrane colitis is associated with the organism Corynebacterium
perfringens.
2.10 Coxiella burnetii is associated with Q fever
SECTION 8
(35-)
QUESTION 3
[9]
3.1 Categorize the following antibiotics according to its bacterial targets:
A) Vancomycin
[1]
B) Aminoglycosides
[1]
C) Tetracyclines
[1]
D) Quinolones
[1]
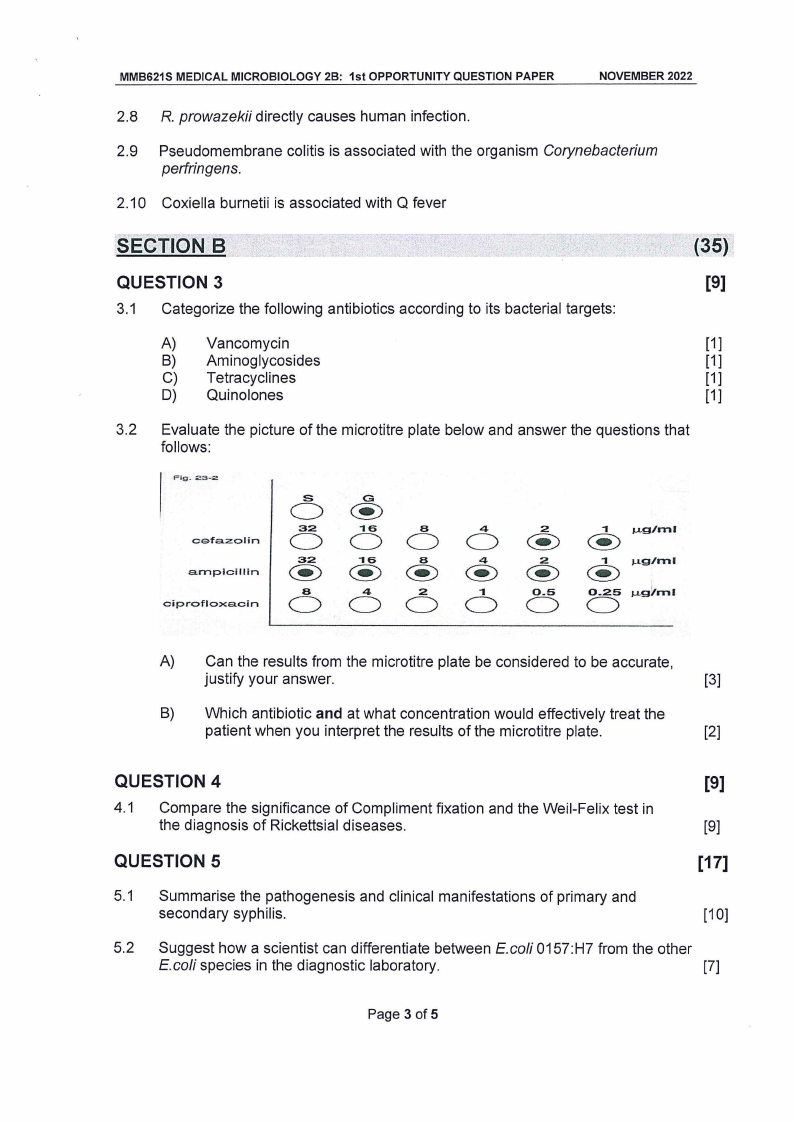
3.2 Evaluate the picture of the microtitre plate below and answer the questions that
follows:
Fig. 23-2
cefazolin
a.mpicillin
ciprofloxacin
s
G
C) @)
32
16
a
4
2
1
µg/ml
C) C) C) C)
32
16
a
4
2
@) @) @)
1
µg/ml
a
4
2
1
o.s
0.25
µg/ml
C) C) C) C) C) C)
A) Can the results from the microtitre plate be considered to be accurate,
justify your answer.
[3]
B) Which antibiotic and at what concentration would effectively treat the
patient when you interpret the results of the microtitre plate.
[2]
QUESTION 4
[9]
4.1 Compare the significance of Compliment fixation and the Weil-Felix test in
the diagnosis of Rickettsial diseases.
[9]
QUESTION 5
[17]
5.1 Summarise the pathogenesis and clinical manifestations of primary and
secondary syphilis.
[1 OJ
5.2 Suggest how a scientist can differentiate between E.coli 0157:H? from the other
E.coli species in the diagnostic laboratory.
[7]
Page 3 of 5
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

MMB621S MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY 2B: 1st OPPORTUNITY QUESTION PAPER
NOVEMBER 2022
SECTION C.
(40)'
QUESTION 6
6.1 A 4-year-old Caucasian boy presented with a one-week history of general
malaise, mild fever, indolence, and anorexia. He subsequently developed
dysphagia, sialorrhoea, difficulties opening the mouth and eventually
dehydration. Due to parental concerns about the boy's refusal of fluids, a
paediatrician was consulted. At that time of presentation, he showed signs of
trismus and muscle rigidity. Together with the lack of immunization and a
toenail infection, the doctor suspected generalised tetanus.
[20]
A)
Identify the causative pathogen of generalised tetanus.
[2]
B) Illustrate by means of a drawing the gram stain morphology and gram
reaction you expect for this organism.
[2 x ½ = 1]
6.2 A pregnant woman presented with a vaginal discharge but with no further
symptoms of infection. Her doctor collected a vaginal swab and submitted
it to the diagnostic medical microbiology laboratory for analysis.
Study the slides below presenting the laboratory findings from the pregnant
patient and then answer the questions.
1) Gram stain result from the
vaginal swab:
i
I
....
2) The culture from the vaginal swab
on a blood agar after incubation.
2) Catalase test result:
4) Additional test that were
preformed:
A) Report your findings on the gram-stained slide, presented in slide 1.
[3]
B) Report your findings of the growth seen on slide 2.
[2]
C) Report the catalase results from the test presented in slide 3.
[1]
D) Identify the reagent used for the catalase test.
[2]
Page 4 of 5
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |

MMB621S MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY 2B: 1st OPPORTUNITY QUESTION PAPER
NOVEMBER 2022
E) Discuss the principle of the catalase test.
[3]
F) Name the test that were done in slide 4, and by using a labelled
illustration of the test, explain the principle of the test.
[6]
QUESTION 7
7.1 Design a flow chart for the identification of gram-positive cocci.
[20]
[20]
TOTAL: 100 MARKS
Page 5 of 5





