 |
LET621S - LAND ECONOMICS AND TAXATION - 2ND OPP - JAN 2025 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAmlBIA unlVERSITY
OF SCIEn CE Ano TECHn OLOGY
FACULTYOF ENGINEERINGAND THE BUILTENVIRONMENT
DEPARTMENT OF LANDAND SPATIALSCIENCES
QUALIFICATION{S): DIPLOMA IN PROPERTYSTUDIES
BACHELOR OF LAND ADMINISTRATION
BACHELOR OF PROPERTYSTUDIES
QUALIFICATION{S)CODE: 06DIPS
07BLAM
08BOPS
NQF LEVEL:6
COURSECODE: LET621S
COURSENAME: LAND ECONOMICS AND TAXATION
EXAMSSESSION:JANUARY 2025
PAPER:
THEORY
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS:
100
SECONDOPPORTUNITY/SUPPLEMENTARYEXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER(S) MR SAMUEL ATO K. HAYFORD
MODERATOR: MR VERINJAERAKO KANGOTUE
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Read the entire question paper before answering the Questions.
2. Please write clearly and legibly!
3. The question paper contains a total of 5 questions.
4. You must answer ALLQUESTIONS.
5. Make sure your Student Number is on the EXAMINATION BOOK{S).
PERMISSIBLEMATERIALS
1. Non-programmable Scientific Calculator
THIS QUESTION PAPERCONSISTSOF 6 PAGES{Including this front page)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

Land Economics and Taxation
LET621S
Question 1
For each of the following statements indicate whether it is 'TRUE' or 'FALSE'. Each correct answer
carries 1 mark.
{20)
a) At any location the use that returns a highest gross land rent than any other use can be
treated as the highest and best use of that site.
b) Given any urban use of land (i.e. Residential, industrial or commercial), operations carried on
within their areas of highest and best use are profitable, but not as profitable as those
carried on within their zones of transference
c) Landlords usually make rental concessions during periods when the supply of tenants is low.
This occurs during and when an economy experiences rapid growth.
d) When high supply of tenants prevails when an economy experiences a boom, landlords
frequently demand more rent.
e) Land resources managers and policymakers for land resource use must respect the
constraints posed by the three frameworks for analysing the use of land resources.
f) Biological framework concerned with the natural environment in which the operators find
themselves. This includes differences in weather, climate etc, such as hours of sunlight,
temperatures, rainfall, humidity.
g) Land use capacity measures the productive potential of a given parcel of land utilised for a
given use at a given time with a specified technological and production conditions.
h) According to Ricardo's theory on land rent when crops are produced for central city market,
land located near the city enjoys rent advantage over those located at greater distance and
therefore will be used first
Second Opportunity/Supplementary Question Page 2 of 6
January 2025
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

Land Economics and Taxation
LET621S
i) For any two parcels of different locations, the magnitude of rent advantage associated with
the use of land closer to the market correspond with the differences in transportation cost
between the two areas to the market.
j) Beyond the no-rent point any production carried on will call for reduction of payment that
normally goes to labour and management (cost of production).
k) The principle of equity is that taxes should be fair and based on people's 'ability to pay'.
I) In situations where the law fixes the rate of property tax in primary legislation, the tax
revenues will vary according to changes in market values and regular revaluations.
m) Amount of tax payable on a taxable property satisfies the principle of equity and bears a
semblance of regressive tax system, because the amount of tax increases with decreasing
rateable values.
n) Property tax satisfies the principle of equity because it is a progressive tax system, the rate of
tax rises with increasing rateable values of property.
o) In situations with declining property values in a taxing district due to declining economic
activities, revenues generated from property tax will decline.
p) The tax collected helps in the country's development in areas like mobilising revenue for
national development in a transparent fair effective and efficient manner.
q) The of a land resource base to provide product for human use over time is affected by its
self-renewal and regenerative qualities
r) Resourcessuch as mineral and coal are being continually replenished.
s) Land resources are classified for conservation purposes according to the relative fixity and
exhaustibility of their supply.
Second Opportunity/Supplementary Question Page 3 of 6
January 2025
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |
Land Economics and Taxation
LET621S
t) Usually, operators are inclined to make first use of those land areas that have the lowest use
capacities for their particular enterprise.
[20]
Question 2
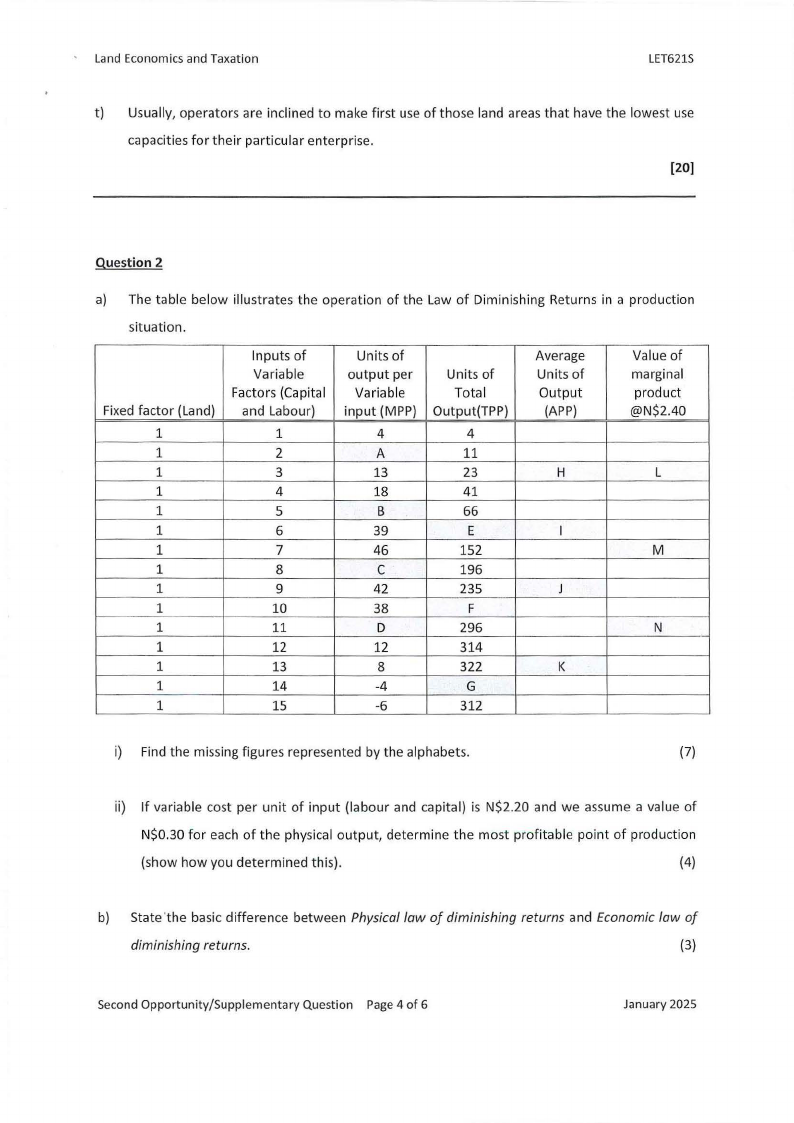
a) The table below illustrates the operation of the Law of Diminishing Returns in a production
situation.
Fixed factor (Land)
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Inputs of
Variable
Factors (Capital
and Labour)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Units of
output per
Variable
input (MPP)
4
A
13
18
B
39
46
C
42
38
D
12
8
-4
-6
Units of
Total
Output(TPP)
4
11
23
41
66
E
152
196
235
F
296
314
322
G
312
Average
Units of
Output
(APP)
H
I
J
K
Value of
marginal
product
@N$2.40
L
M
N
i) Find the missing figures represented by the alphabets.
(7)
ii) If variable cost per unit of input (labour and capital) is N$2.20 and we assume a value of
N$0.30 for each of the physical output, determine the most profitable point of production
(show how you determined this).
(4)
b) State 'the basic difference between Physicallaw of diminishingreturns and Economiclaw of
diminishingreturns.
(3)
Second Opportunity/Supplementary Question Page 4 of 6
January 2025
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

Land Economics and Taxation
LET621S
[14]
Question 3
a) The yield capacities of four grades of land are respectively given in the table below.
I Land
I Unit of Output (in tonnes)
A
B
C
D
130
X
107
85
Cost of Capital and labour amounting to N$355 was incurred on each of these tracts of land.
Additional Information
• Cost of capital experienced a uniform upward adjustment by N$60
• A combined total of 440 tonnes of output was harvested from the four (4) parcels of
land.
i) Determine the amount of land rent that accrues to each of these tracts of land as they are
employed successively in a production. [correct your answers to the two decimal place]
(13)
ii) By whose theory does land rents emerge and calculated in this way?
(1)
iii) Mention any three (3) underlying assumptions of Ricardo's theory of land rent?
(3)
b) Calculate the expected land value if an expected return of N$3000 is discounted at 5%
interest rate for 10 years.
(3)
[20]
Question 4
a) What do understand by 'land use capacity'?
(4)
b) List the two (2) major components of land use capacity.
(1)
Second Opportunity/Supplementary Question Page 5 of 6
January 2025
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |

Land Economics and Taxation
LET621S
c) Mention and briefly explain, with simple examples, any two (2) requirements/series of tests
which a land assessedfor its potential highest and best use must pass.
(6)
[11)
Question 5
a) Differentiate between the 'tax base of a rateable property (house)' and the 'tax base of a
taxing (local) authority'
(3)
b) Examine in detail any four (4) effects of land taxation on land use and ownership.
(20)
c) Explain in detail the principles that provide a good basis for evaluating taxation forms. (12)
[35)
Second Opportunity/Supplementary Question Page 6 of 6
January 2025





