 |
RES511S - REMOTE SENSING 1 -1ST OPP - JUNE 2023 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAmlBIA unlVERSITY
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECHnOLOGY
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND THE BUILT ENVIRONMENT
DEPARTMENT OF LAND & SPATIALSCIENCES
QUALIFICATION(S):Bachelor of Geoinformation Technology; Diploma in Geomatics;
Bachelor of Geomatics
QUALIFICATIONCODE(S): 07BGEI; 06DGEM;
06DGEO; 07BGEO
LEVEL: 5
COURSECODE: RESSllS
COURSENAME: REMOTESENSING1
SESSION:JUNE 2023
PAPER:THEORY
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 100
FIRSTOPPORTUNITYEXAMINATION QUESTIONPAPER
EXAMINER(S)
Dr Oluibukun Ajayi
MODERATOR:
Ms Celeste Espach
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALL the questions.
2. Write clearly and neatly.
3. Number the answers clearly.
4. All calculations, unless otherwise specified, must be rounded off to the
3rd decimal.
5. Include the formulas used for each worked calculation
PERMISSIBLEMATERIALS
Calculator and required stationery
THIS QUESTION PAPERCONSISTSOF_5_ PAGES(Including this front page)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

Remote Sensing 1
SECTION ONE - Short answer questions (39.5 marks in all)
RES511S
1.1 What are the five (5) keywords that define Remote Sensing?
(2.5)
1.2 What is the most important source of EM energy at the earth's surface?
(1)
1.3 What is the most important cause of Mie scattering?
(1)
1.4 At what speed does EM energy travel (in a vacuum)?
(1)
1.5 What kind of energy and frequency level does light with a long wavelength have?
(2)
1.6 In the field of EM radiation, differentiate between a blackbody and a white body?
(4)
1.7 Differentiate between geometric correction and atmospheric correction.
(4)
1.8 Highlight 4 advantages and 4 disadvantages of remote sensing.
(4)
1.9 What are atmospheric transmission windows?
(2)
1.10 What type of atmospheric scattering causes the sky to be blue in the day?
(1)
1.11 In which atmospheric levels do the different satellite orbit paths fall?
(2)
1.12 What are the four (4) levels in image processing?
(2)
1.13 Which Radar sensors would you use to capture: (explain your reasoning).
a. Leaves on a tree (~2 cm in size).
(2)
b. The woody component of that same tree where branches and the trunk typically range
from 5-15 cm.
(2)
c. The woody component of the same tree where branches and trunk typically ranges from
15-30 cm.
(2)
First Opportunity Question Paper
Page /2
June 2023
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |
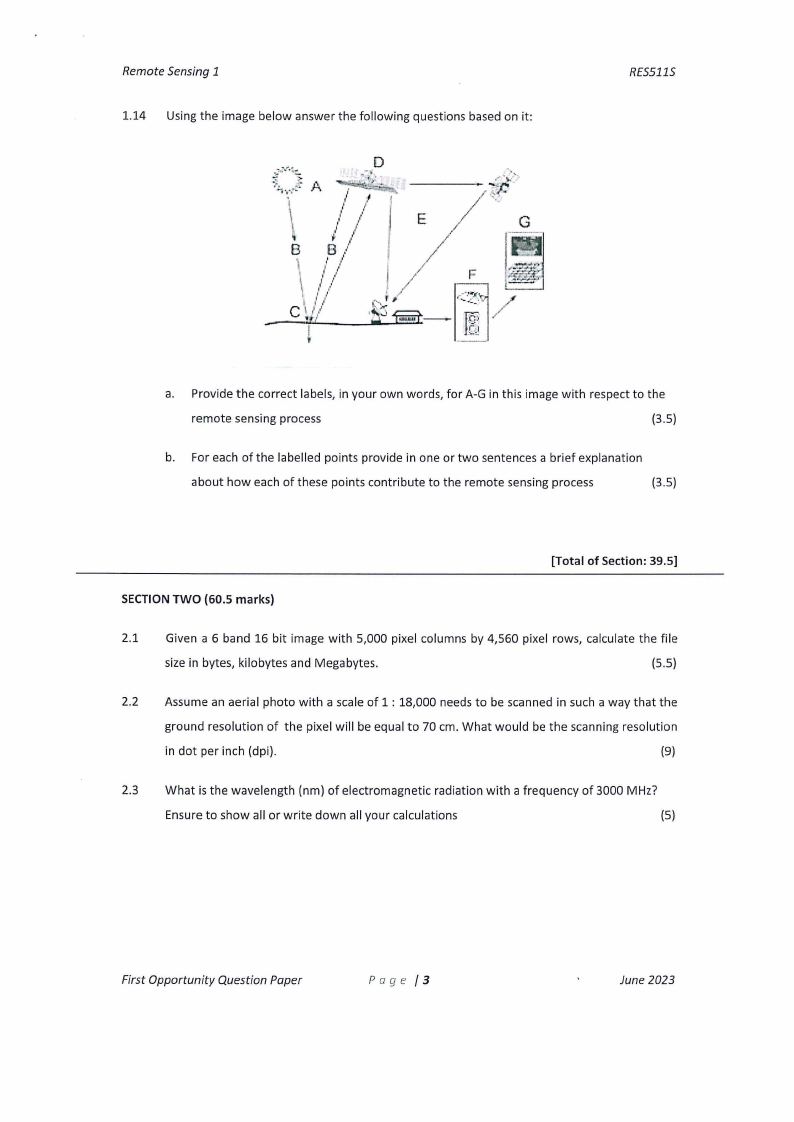
Remote Sensing 1
1.14 Using the image below answer the following questions based on it:
RES5115
a. Provide the correct labels, in your own words, for A-Gin this image with respect to the
remote sensing process
(3.5)
b. For each of the labelled points provide in one or two sentences a brief explanation
about how each of these points contribute to the remote sensing process
(3.5)
[Total of Section: 39.5]
SECTION TWO {60.5 marks)
2.1 Given a 6 band 16 bit image with 5,000 pixel columns by 4,560 pixel rows, calculate the file
size in bytes, kilobytes and Megabytes.
(5.5)
2.2 Assume an aerial photo with a scale of 1 : 18,000 needs to be scanned in such a way that the
ground resolution of the pixel will be equal to 70 cm. What would be the scanning resolution
in dot per inch (dpi).
(9)
2.3 What is the wavelength (nm) of electromagnetic radiation with a frequency of 3000 MHz?
Ensure to show all or write down all your calculations
(5)
First Opportunity Question Paper
Page /3
June 2023
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

Remote Sensing 1
RES5115
2.4 As a Remote Sensing student, you have been saddled with the responsibility of converting
the analogue aerial photos of Windhoek acquired in 1961 to digital format. Your first step
would be to approach the Directorate of Survey and Mapping to order for the photographs
and you will need to specify the address of the photograph covering Windhoek. If the
coordinates of Windhoek is 22.5609° S, 17.0658° E, what is the aerial photo address you will
need to obtain these photos?
(10)
Tip: Provide a degree square diagram and full explanation of how you arrived at your final
address.
2.5 Sentinel 2 (S2) is a 12 bit optical sensor which has 13 bands. Four bands have a spatial
resolution of 10 m, six bands have a spatial resolution of 20 m and three bands have a spatial
resolution of 60 m. A single tile for a S2 image is delivered as a tile covering an area of
100*100 km. Use this information to calculate the following items:
a. What is the ON value range you would get on an uncorrected S2 image?
(3)
b. What would be the total file size you would need for a single S2 tile? Show all your
calculations. Ensure to account for the different spatial resolutions of each band. (8)
2.6 An area 30 km long in the north-south direction and 24 km in the east-west direction is to be
photographed using a drone equipped with a camera lens having 30 cm focal length for the
purpose of constructing a mosaic. The photograph size is 20 cm x 20 cm. The average scale is
to be 1: 12,000 effective at an elevation of 400 m above datum. Overlap is to be at least 60%
and the side lap is to be at least 30%. An intervalometer will be used to control the interval
between exposures. The ground speed of the aircraft will be maintained at 200 km per hour.
The flight lines are to be laid out in a north-south direction on an existing map having a scale
of 1:60,000. The two outer flight lines are to coincide with the east and west boundaries of
the area. Determine the following data for the flight plan.
a. Flying height
(2)
b. Theoretical ground spacing of flight lines
(3)
c. Number offlight lines required
(2)
d. Actual spacing of flight lines
(2)
e. Spacing flight lines on flight map
(2)
f. Ground distance between exposures
(2)
First Opportunity Question Paper
Page /4
June 2023
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

Remote Sensing 1
g. Adjusted ground distance between exposures
h. Exposure interval
i. Number of photographs per fight line
j. Total number of photographs
RES511S
(3)
(1)
(2)
{l)
[Total of Section: 60.5]
First Opportunity Question Paper
Page /5
June 2023





