 |
CMA611S- COST AND MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING 201- 1ST OPP- JUNE 2023 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAmlBIA UnlVERSITY
OF SCIEn CE Ano TECHn OLOGY
FACULTY OF COMMERCE, HUMAN SCIENCESAND EDUCATION
DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS, ACCOUNTING AND FINANCE
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF ACCOUNTING
QUALIFICATION CODE: 07BOAC LEVEL: 6
COURSE CODE: CMA611S
COURSE NAME: COST& MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING201
SESSION: JUNE 2023
DURATION: 3 HOURS
PAPER: THEORYAND CALCULATIONS
MARKS: 100
FIRST OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINERS
Ms Kangala, H. and Sheehama, K.G.H.
MODERATOR Tjondu, K.
INSTRUCTIONS
• Answer ALL the questions in blue or black ink only. NO PENCIL.
• Start each question on a new page, number the answers correctly and clearly.
• Write clearly, and neatly showing all your workings/assumptions.
• Work with at least four (4) decimal places in all your calculations and only round off only
final answers to two (2) decimal places.
• Questions relating to this examination may be raised in the initial 30 minutes after the start
of the examination. Thereafter, candidates must use their initiative to deal with any
perceived errors or ambiguities and any assumptions made by the candidate should be
clearly stated.
PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS
• Silent, non-programmable calculators
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF_ 4_ PAGES (excluding this front page)
0
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |
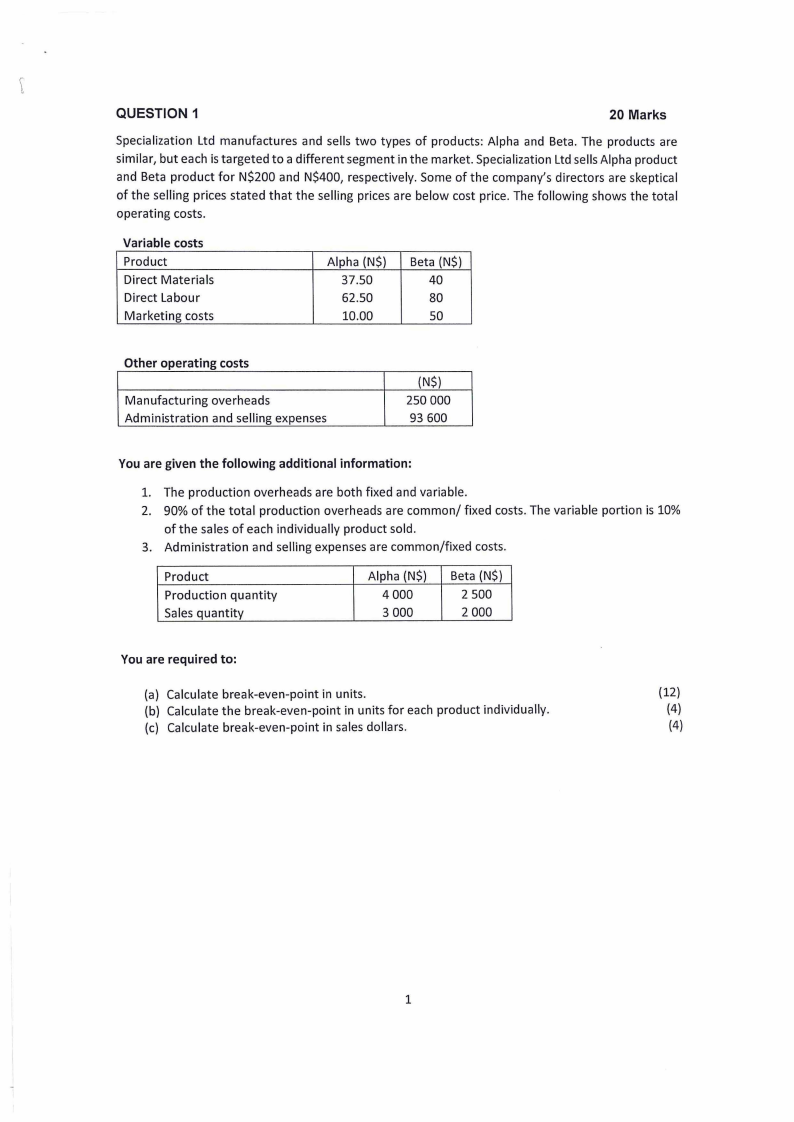
QUESTION 1
20 Marks
Specialization Ltd manufactures and sells two types of products: Alpha and Beta. The products are
similar, but each is targeted to a different segment in the market. Specialization Ltd sells Alpha product
and Beta product for N$200 and N$400, respectively. Some of the company's directors are skeptical
of the selling prices stated that the selling prices are below cost price. The following shows the total
operating costs.
Variable costs
Product
Direct Materials
Direct Labour
Marketing costs
Alpha (N$)
37.50
62.50
10.00
Beta (N$)
40
80
so
Other operating costs
Manufacturing overheads
Administration and selling expenses
(N$)
250 000
93 600
You are given the following additional information:
1. The production overheads are both fixed and variable.
2. 90% of the total production overheads are common/ fixed costs. The variable portion is 10%
ofthe sales of each individually product sold.
3. Administration and selling expenses are common/fixed costs.
Product
Production quantity
Sales quantity
Alpha (N$)
4000
3 000
Beta (N$)
2 500
2 000
You are required to:
(a) Calculate break-even-point in units.
(b) Calculate the break-even-point in units for each product individually.
(c) Calculate break-even-point in sales dollars.
(12)
(4)
(4)
1
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |
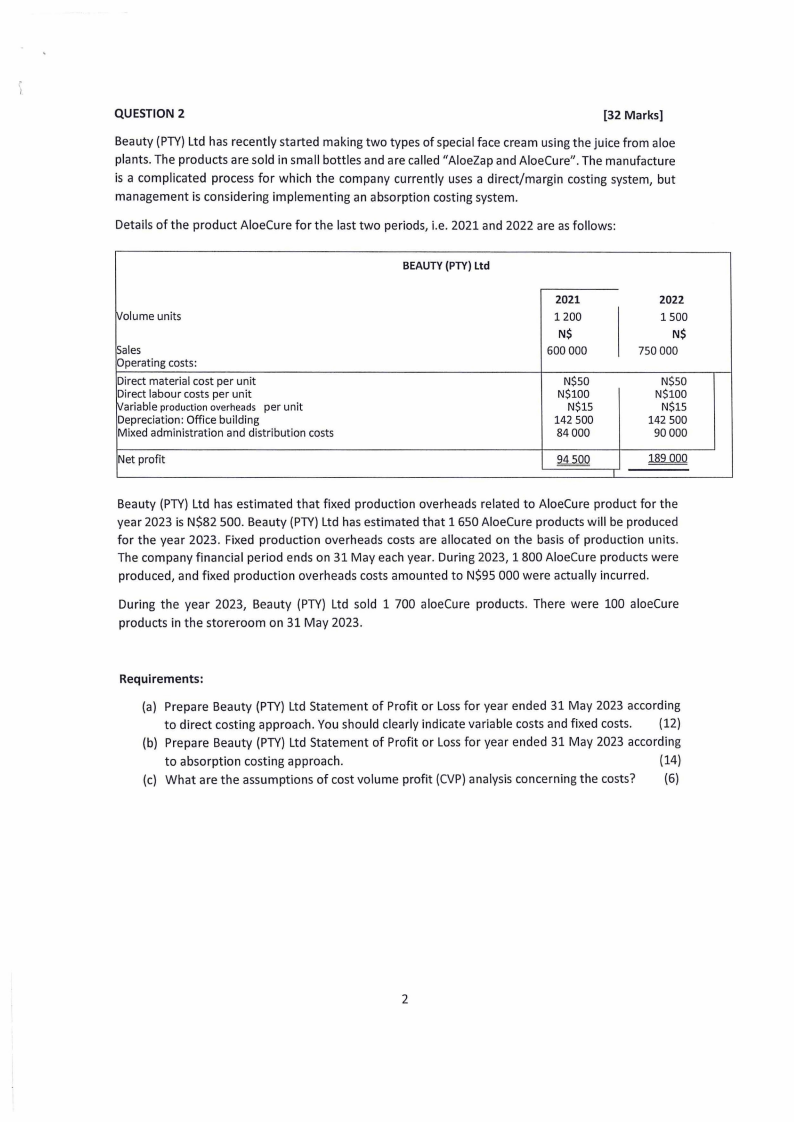
QUESTION 2
[32 Marks]
Beauty (PTY)Ltd has recently started making two types of special face cream using the juice from aloe
plants. The products are sold in small bottles and are called "AloeZap and AloeCure". The manufacture
is a complicated process for which the company currently uses a direct/margin costing system, but
management is considering implementing an absorption costing system.
Details of the product AloeCure for the last two periods, i.e. 2021 and 2022 are as follows:
BEAUTY(PTY) Ltd
il/olume units
~ales
Operating costs:
Direct material cost per unit
Direct labour costs per unit
Variable production overheads per unit
Depreciation: Office building
Mixed administration and distribution costs
Net profit
2021
1200
N$
600 000
2022
1500
N$
750 000
N$50
N$100
N$15
142 500
84000
94 500
I
N$50
N$100
N$15
142 500
90000
189 000
Beauty (PTY)Ltd has estimated that fixed production overheads related to AloeCure product for the
year 2023 is N$82 500. Beauty (PTY)Ltd has estimated that 1 650 AloeCure products will be produced
for the year 2023. Fixed production overheads costs are allocated on the basis of production units.
The company financial period ends on 31 May each year. During 2023, 1800 AloeCure products were
produced, and fixed production overheads costs amounted to N$95 000 were actually incurred.
During the year 2023, Beauty (PTY) Ltd sold 1 700 aloeCure products. There were 100 aloeCure
products in the storeroom on 31 May 2023.
Requirements:
(a) Prepare Beauty (PTY) Ltd Statement of Profit or Loss for year ended 31 May 2023 according
to direct costing approach. You should clearly indicate variable costs and fixed costs. (12)
(b) Prepare Beauty (PTY)Ltd Statement of Profit or Lossfor year ended 31 May 2023 according
to absorption costing approach.
(14)
(c) What are the assumptions of cost volume profit (CVP)analysis concerning the costs? (6)
2
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |
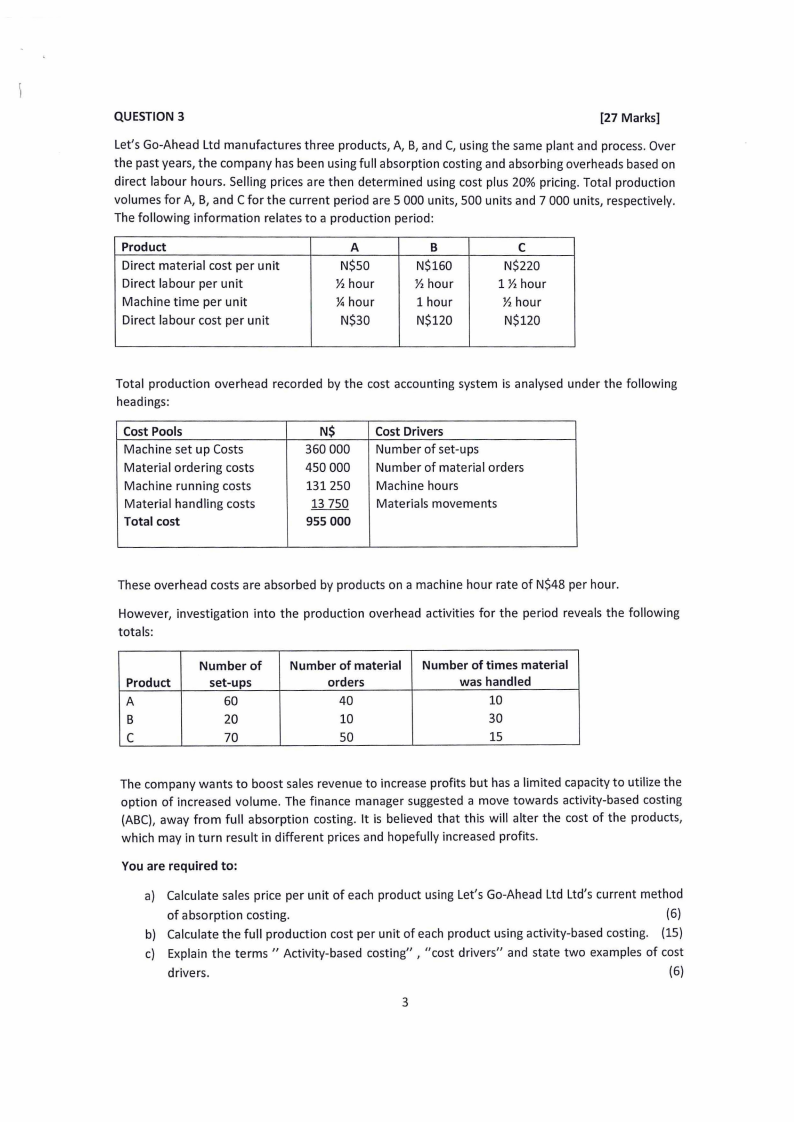
QUESTION 3
[27 Marks]
Let's Go-Ahead Ltd manufactures three products, A, B, and C, using the same plant and process. Over
the past years, the company has been using full absorption costing and absorbing overheads based on
direct labour hours. Selling prices are then determined using cost plus 20% pricing. Total production
volumes for A, B, and C for the current period are 5 000 units, 500 units and 7 000 units, respectively.
The following information relates to a production period:
Product
Direct material cost per unit
Direct labour per unit
Machine time per unit
Direct labour cost per unit
A
N$50
½ hour
¼ hour
N$30
B
N$160
½ hour
1 hour
N$120
C
N$220
1 ½ hour
½ hour
N$120
Total production overhead recorded by the cost accounting system is analysed under the following
headings:
Cost Pools
Machine set up Costs
Material ordering costs
Machine running costs
Material handling costs
Total cost
N$
360 000
450 000
131250
13 750
955 000
Cost Drivers
Number of set-ups
Number of material orders
Machine hours
Materials movements
These overhead costs are absorbed by products on a machine hour rate of N$48 per hour.
However, investigation into the production overhead activities for the period reveals the following
totals:
Product
A
B
C
Number of
set-ups
60
20
70
Number of material
orders
40
10
50
Number of times material
was handled
10
30
15
The company wants to boost sales revenue to increase profits but has a limited capacity to utilize the
option of increased volume. The finance manager suggested a move towards activity-based costing
(ABC), away from full absorption costing. It is believed that this will alter the cost of the products,
which may in turn result in different prices and hopefully increased profits.
You are required to:
a) Calculate sales price per unit of each product using Let's Go-Ahead Ltd Ltd's current method
of absorption costing.
(6)
b) Calculate the full production cost per unit of each product using activity-based costing. (15)
c) Explain the terms " Activity-based costing" , "cost drivers" and state two examples of cost
drivers.
(6)
3
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |
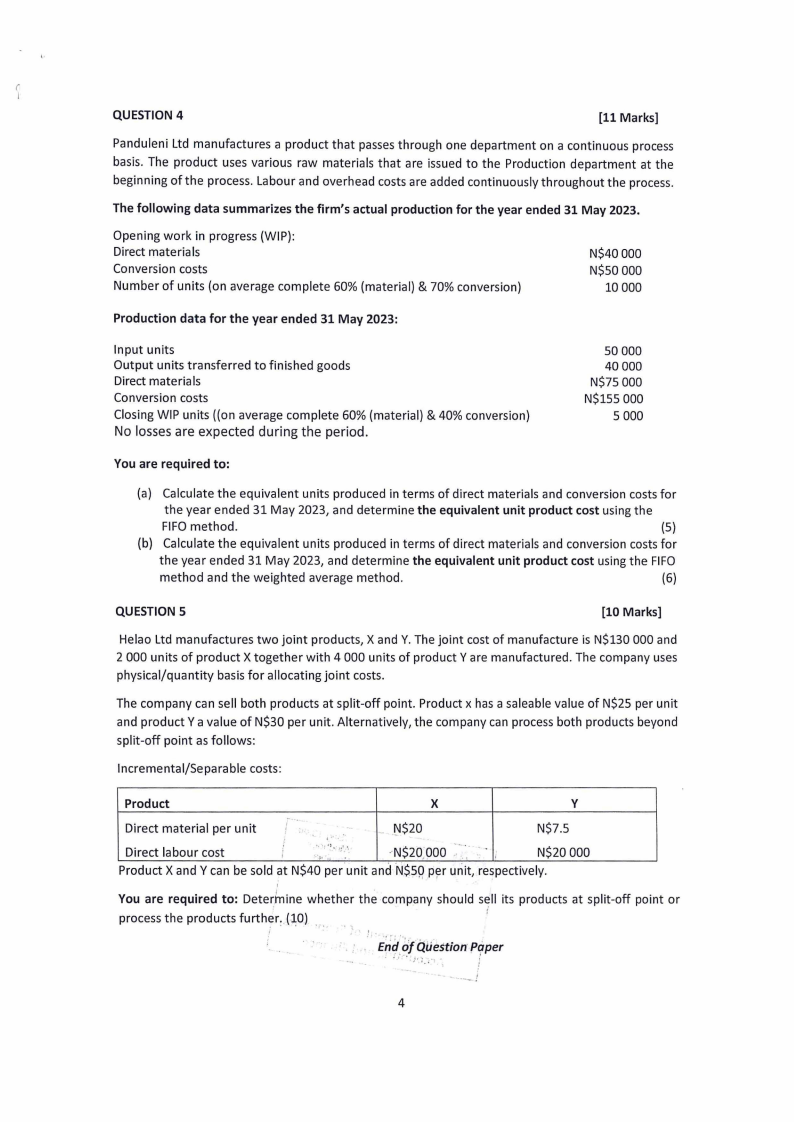
(
I
QUESTION 4
[11 Marks]
Panduleni Ltd manufactures a product that passes through one department on a continuous process
basis. The product uses various raw materials that are issued to the Production department at the
beginning of the process. Labour and overhead costs are added continuously throughout the process.
The following data summarizes the firm's actual production for the year ended 31 May 2023.
Opening work in progress (WIP):
Direct materials
Conversion costs
Number of units (on average complete 60% (material) & 70% conversion)
N$40 000
N$50 000
10000
Production data for the year ended 31 May 2023:
Input units
Output units transferred to finished goods
Direct materials
Conversion costs
Closing WIP units ((on average complete 60% (material) & 40% conversion)
No losses are expected during the period.
50 000
40000
N$75 000
N$155 000
5 000
You are required to:
(a) Calculate the equivalent units produced in terms of direct materials and conversion costs for
the year ended 31 May 2023, and determine the equivalent unit product cost using the
FIFO method.
(5)
(b) Calculate the equivalent units produced in terms of direct materials and conversion costs for
the year ended 31 May 2023, and determine the equivalent unit product cost using the FIFO
method and the weighted average method.
(6)
QUESTION 5
[10 Marks]
Helao Ltd manufactures two joint products, X and Y. The joint cost of manufacture is N$130 000 and
2 000 units of product X together with 4 000 units of product Y are manufactured. The company uses
physical/quantity basis for allocating joint costs.
The company can sell both products at split-off point. Product x has a saleable value of N$25 per unit
and product Ya value of N$30 per unit. Alternatively, the company can process both products beyond
split-off point as follows:
Incremental/Separable costs:
Product
X
y
- ..
Direct material per unit
I
I
.. _['1$20
N$7.5
Direct labour cost
;
,.·,.,i ·1;'_·,
I
.•,."
--.
.·.N$20;000
-
N$20 000
Product X and Y can be sold at N$40 per unit and N$5R p~r unit, respectively.
'
You are required to: Determ. ine whether the company should sei ll its products at split-off
process the products furth?L (-10) ... . ,
point or
EnddfQuestion paper
. ... .
i
4





